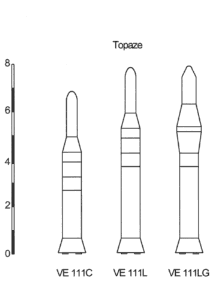
 Topaze versions | |
| Function | Sounding rocket |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | SEREB |
| Country of origin | France |
| Size | |
| Height | VE111C: 7.07 metres (23.2 ft) VE111L: 7.90 metres (25.9 ft) |
| Mass | VE111C: 2,900 kilograms (6,400 lb) VE111L: 3,434 kilograms (7,571 lb) |
| Stages | 1 |
| Associated rockets | |
| Derivative work | Saphir, Diamant |
| Launch history | |
| Status | Retired |
| Launch sites | CIEES |
| Total launches | 14 |
| First flight | 19 December 1962 |
| Last flight | 1965 |
| VE111C stage | |
| Powered by | NA802 |
| Maximum thrust | 120 kilonewtons (27,000 lbf) |
| Propellant | Solid |
| VE111L / VE111LG stage | |
| Powered by | NA803 |
| Maximum thrust | 147 kilonewtons (33,000 lbf) |
| Propellant | Solid |
Topaze (Véhicule Expérimental 111 Topaze) is the designation of a French sounding rocket.[1] The Topaze was developed by several French companies, notably Nord Aviation and Sud Aviation,[2] and built by SEREB (a joint venture of Nord and Sud, now known as Aérospatiale) and was the first guidable French sounding rocket.
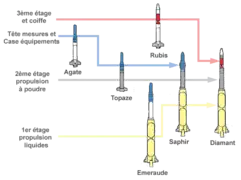
It was part of the Pierres précieuses (fr.: gemstones) program, that included five prototypes Agathe, Topaze, Emeraude, Rubis and Saphir,[3] leading up to the Diamant orbital rocket.
The name indicates that it is a "Véhicule Expérimental" (Experimental Vehicle) with 1 stage, using solid propulsion (code 1), and guided (code 1).
The Topaze was launched 14 times from the CIEES launch site in Hammaguir (Hammaguira Bacchus pad), Algeria, by ONERA.[4]
Versions
There were three versions of the Topaze:[4][1]
- Topaze versions
 VE111C
VE111C VE111L
VE111L VE111LG
VE111LG
Topaze VE111 / Topaze VE111C
Details[5] [6]
Launches
There were launches between 1962 and 1964, reaching an apogee of 80 km (49 mi).[1][5]
| Date | Mission Description | Apogee (km) |
|---|---|---|
| 1962 December 19 | Test mission | 80 |
| 1963 March 22 | Test mission | 80 |
| 1963 March 28 | Test mission | 80 |
| 1963 June 21 | Test mission | 80 |
| 1963 June 27 | Test mission | 80 |
| 1963 October 24 | Test mission | 80 |
| 1964 June 4 | MSBS test, failure | |
| 1964 October 21 | MSBS test | 80 |
| 1964 December 11 | MSBS test | 80 |
| 1964 December 15 | MSBS test | 80 |
Topaze VE111L
Details[5] [8]
- payload mass: 360 kg (840 lb)
- total mass: 3434 kg (7570 lb)
- length: 7.90 m (25.9 ft)
- range: 110 km (68 mi)
- liftoff thrust 147.0 kN
- Soleil NA803 solid rocket engine[9]
Launches
- This version was launched eight times between 21 December 1963 and 21 May 1965, with apogees up to 110 km (68 mi).[1][5]
| Date | Mission Description | Apogee (km) |
|---|---|---|
| 1963 December 21 | Test mission | 110 km |
| 1964 March 11 | Test mission | 110 km |
Topaze VE111LG
Details[5]
- Soleil NA803 solid rocket engine
Launches
This version was launched two times in 1965.[1][5]
| Date | Mission Description | Apogee (km) |
|---|---|---|
| 1965 May 18 | Test mission | 100 km |
| 1965 May 21 | Test mission | 100 km |
Other uses
The Topaze was also used as the second stage of the Diamant rocket, the launch vehicle for France's first satellite, the Asterix-1, and the Saphir rocket.[5][3][10]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Topaze (VE-111)". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 2023-07-30.
- ↑ News Digest. // Aviation Week & Space Technology, January 7, 1963, v. 78, no. 1, p. 37.
- 1 2 Capdevila, Didier. "Les Constellations et les Pierres Précieuses". Capcom Espace. Retrieved 2023-08-29.
- 1 2 "News Digest". Aviation Week & Space Technology. Vol. 78, no. 1. January 7, 1963. p. 37.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Wade, Mark (2019). "Topaze". Encyclopedia Astronautica.
- ↑ Wade, Mark (2019). "Topaze VE111-1". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2023-11-11.
- ↑ Wade, Mark (2019). "Soleil Mammouth". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2023-11-11.
- ↑ Wade, Mark (2019). "Topaze VE111L-1". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2023-11-11.
- ↑ Wade, Mark (2019). "Soleil NA803". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2023-11-11.
- ↑ Wade, Mark (2019). "Diamant-2". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 2023-11-11.