 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Major junctions | |
| North end | Inverness, United Kingdom |
| South end | Algeciras, Spain |
| Location | |
| Countries | |
| Highway system | |
Wikimedia Commons has media related to E15.
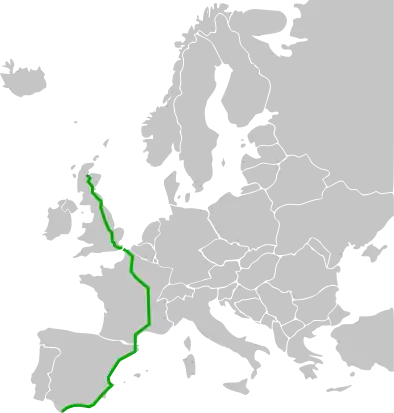
The European route E15 is part of the United Nations international E-road network. It is a north–south "reference road", running from Inverness, Scotland south through England and France to Algeciras, Spain.[1] Along most of its route between Paris and London, the road parallels the LGV Nord (as the French A1 autoroute) and High Speed 1 (as the English M20 motorway). Its length is 2,300 miles (3,700 km).
Features
The E15 has a gap at the English Channel between Dover and Calais, France. There is a ferry link between Dover and Calais. The Eurotunnel Shuttle (using the Channel Tunnel) provides an alternative link via Folkestone.
The roads in the UK are signed solely by the local number (e.g. M20).
The Autovía A-7 part of the E15 in Spain
Route
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom
 A9: Inverness - Perth
A9: Inverness - Perth M90: Perth - M90
M90: Perth - M90 M9: M90 - M8 (Interchange with E16)
M9: M90 - M8 (Interchange with E16) M8: Edinburgh
M8: Edinburgh A720: Edinburgh City Bypass
A720: Edinburgh City Bypass A1: Edinburgh - Gateshead (Interchange with E18 at A69 Newcastle upon Tyne)
A1: Edinburgh - Gateshead (Interchange with E18 at A69 Newcastle upon Tyne).svg.png.webp) A1(M): Gateshead - Pontefract (Interchange with E20 and E22 at M62)
A1(M): Gateshead - Pontefract (Interchange with E20 and E22 at M62) A1: Pontefract - Doncaster
A1: Pontefract - Doncaster.svg.png.webp) A1(M): Doncaster Bypass (Interchange with E13 at M18)
A1(M): Doncaster Bypass (Interchange with E13 at M18) A1: Doncaster - Peterborough
A1: Doncaster - Peterborough.svg.png.webp) A1(M): Peterborough - Huntingdon (Interchange with E24 at A14)
A1(M): Peterborough - Huntingdon (Interchange with E24 at A14) A1: Huntingdon - Stevenage
A1: Huntingdon - Stevenage.svg.png.webp) A1(M): Stevenage - M25
A1(M): Stevenage - M25 M25: London Orbital (Multiplex with E30 between A1(M) and A12)
M25: London Orbital (Multiplex with E30 between A1(M) and A12) A282: Dartford Crossing (Charge)
A282: Dartford Crossing (Charge) M25: London Orbital
M25: London Orbital M20: Channel Tunnel
M20: Channel Tunnel
- Gap (English Channel)
 :
:  Folkestone -
Folkestone -  Calais
Calais
 France
France
 A 16: Calais (E 40 E 402)
A 16: Calais (E 40 E 402) A 26: Calais (E 40) - Arras (E 17)
A 26: Calais (E 40) - Arras (E 17) A 1: Arras (E 17) - Combles (Start of concurrency with E 19) - Chaulnes (E 44) - Compiègne (E 46) - Roissy-en-France (End of concurrency with E 19)
A 1: Arras (E 17) - Combles (Start of concurrency with E 19) - Chaulnes (E 44) - Compiègne (E 46) - Roissy-en-France (End of concurrency with E 19) A 3: Roissy-en-France (E 19) - Paris
A 3: Roissy-en-France (E 19) - Paris- Boulevard Périphérique: Paris (E 50 E 54)
 A 6b: Paris (E 50) - Massy (E 5 E 50)
A 6b: Paris (E 50) - Massy (E 5 E 50) A 6: Massy (E 5 E 50) - Courtenay (E 511, Start of concurrency with E 60) - Auxerre - Beaune (End of concurrency with E 60, Start of concurrency with E 21) - Chalon-sur-Saône (E 607) - Mâcon (E 62, End of concurrency with E 21) - Anse
A 6: Massy (E 5 E 50) - Courtenay (E 511, Start of concurrency with E 60) - Auxerre - Beaune (End of concurrency with E 60, Start of concurrency with E 21) - Chalon-sur-Saône (E 607) - Mâcon (E 62, End of concurrency with E 21) - Anse A 46: Anse - Vaulx-en-Velin (E 611)
A 46: Anse - Vaulx-en-Velin (E 611) N 346: Vaulx-en-Velin (E 611) - Saint-Priest (E 70 E 711)
N 346: Vaulx-en-Velin (E 611) - Saint-Priest (E 70 E 711) A 46: Saint-Priest (E 70 E 711) - Givors (E 70)
A 46: Saint-Priest (E 70 E 711) - Givors (E 70) A 7: Givors (E 70) - Valence (E 713) - Orange (E 714)
A 7: Givors (E 70) - Valence (E 713) - Orange (E 714) A 9: Orange (E 714) - Nîmes (Start of concurrency with E 80) - Montpellier - Béziers (E 11) - Narbonne (End of concurrency with E 80) - Perpignan - Le Boulou
A 9: Orange (E 714) - Nîmes (Start of concurrency with E 80) - Montpellier - Béziers (E 11) - Narbonne (End of concurrency with E 80) - Perpignan - Le Boulou
 Spain
Spain
 AP-7: La Jonquera - Girona - Rubí (E-9) - Rubí (Start of concurrency with E-90) - El Vendrell (End of concurrency with E-90) - Tarragona - Castelló de la Plana - València (E-901) - Alacant(E-903) - Crevillent
AP-7: La Jonquera - Girona - Rubí (E-9) - Rubí (Start of concurrency with E-90) - El Vendrell (End of concurrency with E-90) - Tarragona - Castelló de la Plana - València (E-901) - Alacant(E-903) - Crevillent A-7: Crevillent - Murcia - Motril (E-902) - Málaga
A-7: Crevillent - Murcia - Motril (E-902) - Málaga AP-7: Málaga - Guadiaro
AP-7: Málaga - Guadiaro A-7: Guadiaro - Algeciras (E-5)
A-7: Guadiaro - Algeciras (E-5)
References
- ↑ European Agreement on Main International Traffic Arteries, 5 April 2002
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
