 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ferrocenium hexafluorophosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.410 |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10F6FeP | |
| Molar mass | 330.999 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | dark blue powder |
| Density | 1.808 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | (decomposes) |
| Solubility in acetonitrile | Soluble |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic | |
| P21/c | |
Lattice volume (V) |
1215.8(5) Å3 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P305+P351+P338 | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Ferrocenium tetrafluoroborate |
Related compounds |
Ferrocene |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
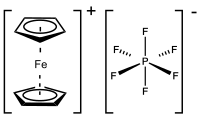
Ferrocenium hexafluorophosphate is an organometallic compound with the formula [Fe(C5H5)2]PF6. This salt is composed of the cation [Fe(C5H5)2]+ and the hexafluorophosphate anion (PF−
6). The related tetrafluoroborate is also a popular reagent with similar properties. The ferrocenium cation is often abbreviated Fc+ or Cp2Fe+. The salt is deep blue in color and paramagnetic.
Ferrocenium salts are one-electron oxidizing agents, and the reduced product, ferrocene, is relatively inert and readily separated from ionic products. The ferrocene–ferrocenium couple is often used as a reference in electrochemistry. In acetonitrile solution that is 0.1 M in NBu4PF6, the Fc+/Fc couple is +0.641 V with respect to the normal hydrogen electrode.[3]
Preparation and structure
Commercially available, this compound may be prepared by oxidizing ferrocene with ferric salts followed by addition of hexafluorophosphoric acid.[3]
The compound is monoclinic with well-separated cation and anion; the PF−
6 may rotate freely. The average Fe-C bond length is 2.047 Å, which is virtually indistinguishable from the Fe-C distance in ferrocene.[2]
References
- ↑ "Ferrocenium hexafluorophosphate 388297". Sigma-Aldrich.
- 1 2 R. Martinez; A. Tiripicchio (1990). "Structure of ferrocenium hexafluorophosphate". Acta Crystallogr. C46 (2): 202–205. doi:10.1107/S0108270189005883.
- 1 2 Connelly, N. G.; Geiger, W. E. (1996). "Chemical Redox Agents for Organometallic Chemistry". Chem. Rev. 96 (2): 877–910. doi:10.1021/cr940053x. PMID 11848774.