Goshogawara
五所川原市 | |
|---|---|
 Goshogawara City Hall | |
 Flag  Seal | |
Location of Goshogawara in Aomori Prefecture | |
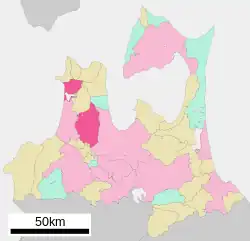 | |
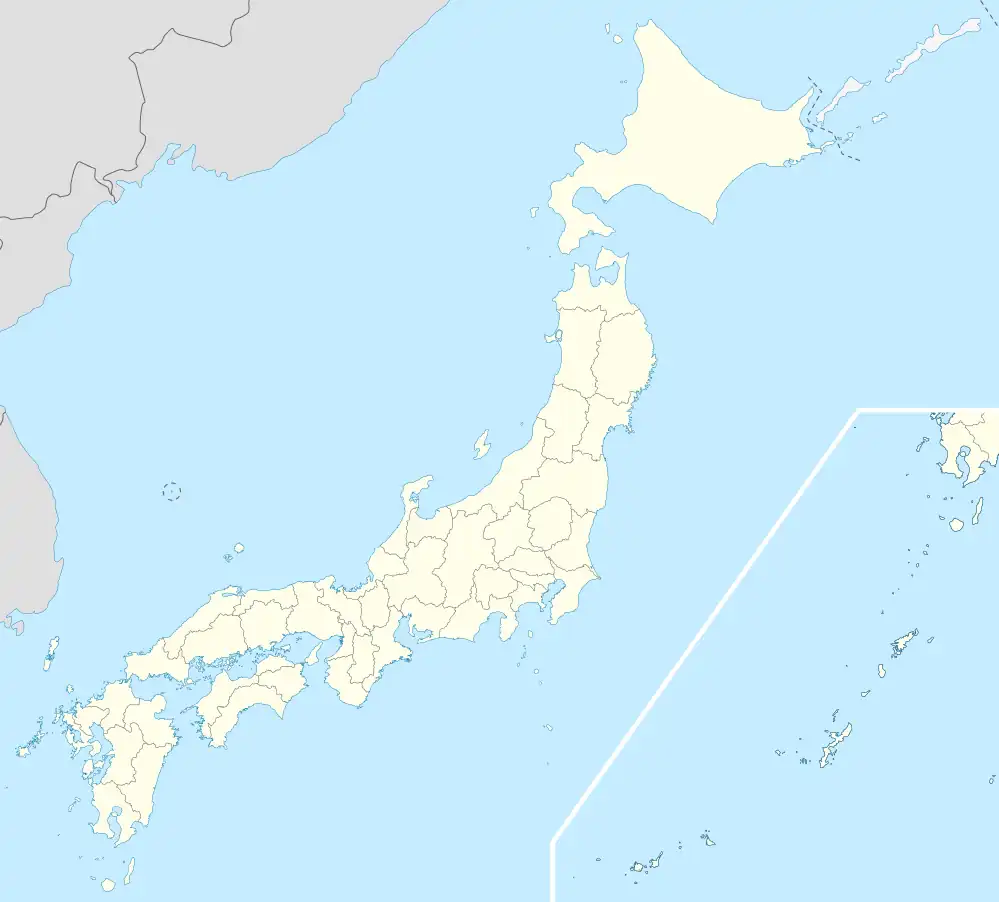 Goshogawara | |
| Coordinates: 40°48′28.9″N 140°26′24.3″E / 40.808028°N 140.440083°E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Tōhoku |
| Prefecture | Aomori |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Masatoshi Hirayama |
| Area | |
| • Total | 404.20 km2 (156.06 sq mi) |
| Population (January 31, 2023) | |
| • Total | 51,578 |
| • Density | 130/km2 (330/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| Phone number | 0173-35-2111 |
| Address | 12 Iwakichō, Goshogawara-shi, Aomori-ken 037-8686 |
| Climate | Cfa/Dfa |
| Website | Official website |
| Symbols | |
| Bird | Oriental greenfinch |
| Flower | Nohanashōbu (iris ensata var. spontanea) |
| Tree | Japanese elm |

Goshogawara (五所川原市, Goshogawara-shi) is a city located in Aomori Prefecture, Japan. As of 31 January 2023, the city had an estimated population of 51,578 in 25,615 households,[1] and a population density of 130 persons per km2. The total area of the city is 404.18 square kilometres (156.05 sq mi).
Geography
Goshogawara occupies two discontinuous areas on Tsugaru Peninsula in western Aomori Prefecture. The Iwaki River flows through the city. The larger section is landlocked, and is in the middle of the peninsula. It contains the original town of Goshogawara, and is the population centre of the city. The smaller exclave to the north is on the Sea of Japan coast. Parts of the city are within the borders of the Tsugaru Quasi-National Park.
Neighbouring municipalities
Aomori Prefecture
Climate
The city has a humid continental climate (Köppen Dfa) characterized by warm short summers and long cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Goshogawara is 10.6 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1281 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 23.4 °C, and lowest in January, at around -1.5 °C.[2]
| Climate data for Goshogawara (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1976−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 10.1 (50.2) |
15.0 (59.0) |
21.2 (70.2) |
29.0 (84.2) |
33.5 (92.3) |
33.8 (92.8) |
36.4 (97.5) |
39.0 (102.2) |
36.2 (97.2) |
28.0 (82.4) |
23.6 (74.5) |
17.5 (63.5) |
39.0 (102.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 1.7 (35.1) |
2.6 (36.7) |
6.6 (43.9) |
13.8 (56.8) |
19.4 (66.9) |
22.8 (73.0) |
26.5 (79.7) |
28.2 (82.8) |
24.6 (76.3) |
18.2 (64.8) |
11.0 (51.8) |
4.4 (39.9) |
15.0 (59.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.1 (30.0) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
2.5 (36.5) |
8.5 (47.3) |
14.1 (57.4) |
18.0 (64.4) |
22.0 (71.6) |
23.4 (74.1) |
19.5 (67.1) |
13.1 (55.6) |
6.9 (44.4) |
1.3 (34.3) |
10.6 (51.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −4.2 (24.4) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
3.5 (38.3) |
9.4 (48.9) |
14.1 (57.4) |
18.4 (65.1) |
19.6 (67.3) |
15.0 (59.0) |
8.5 (47.3) |
3.0 (37.4) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
6.7 (44.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −14.3 (6.3) |
−15.8 (3.6) |
−12.4 (9.7) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
0.4 (32.7) |
4.8 (40.6) |
9.9 (49.8) |
10.7 (51.3) |
4.9 (40.8) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−8.8 (16.2) |
−13.7 (7.3) |
−15.8 (3.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 120.7 (4.75) |
81.9 (3.22) |
64.1 (2.52) |
62.6 (2.46) |
69.2 (2.72) |
74.9 (2.95) |
113.3 (4.46) |
139.2 (5.48) |
133.9 (5.27) |
131.3 (5.17) |
147.8 (5.82) |
141.5 (5.57) |
1,280.4 (50.41) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 186 (73) |
143 (56) |
80 (31) |
3 (1.2) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
19 (7.5) |
122 (48) |
543 (214) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 22.8 | 18.5 | 14.9 | 11.0 | 9.7 | 8.6 | 9.7 | 10.1 | 11.7 | 14.7 | 18.4 | 22.7 | 172.8 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 3 cm) | 20.6 | 16.5 | 11.0 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.0 | 13.8 | 64.5 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 22.7 | 49.4 | 115.7 | 179.6 | 202.4 | 181.2 | 160.5 | 184.7 | 160.2 | 134.2 | 74.7 | 32.0 | 1,497.4 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[3][4] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[5] the population of Goshogawara has declined over the past 40 years.
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 70,222 | — |
| 1970 | 67,047 | −0.46% |
| 1980 | 68,738 | +0.25% |
| 1990 | 63,843 | −0.74% |
| 2000 | 63,208 | −0.10% |
| 2010 | 58,421 | −0.78% |
| 2020 | 51,415 | −1.27% |
History
The area of Goshogawara was part of the holdings of the Tsugaru clan of Hirosaki Domain in the Edo period. With the post-Meiji restoration establishment of the modern municipalities system on April 1, 1889, the area became part of Kitatsugaru District, Aomori, and was divided into the villages of Goshogawara, Sakae, Miyoshi, Nakagawa, Nagahashi, Nanawa, Matsushima and Itayanagi on April 1, 1889. On July 1, 1898, Goshogawara was elevated to town status. On October 1, 1954. Goshogawara absorbed the villages of Sakae, Nakagawa, Nagahashi, Matsushima and Iizume to create the city of Goshogawara. On April 1, 1958, Goshogawara absorbed a portion of the town of Kizukuri.
On March 28, 2005, the town of Kanagi, and the village of Shiura were merged into Goshogawara.
Government
Goshogawara has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city legislature of 26 members. Goshogawara, together with the town of Nakadomari contribute three members to the Aomori Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is part of Aomori 3rd district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy
The economy of Goshogawara is mixed. The city serves as a regional commercial center. Agricultural produce includes rice and apples, and commercial fishing includes clams. The Aomori Technopolis High-Tech Industrial Park is located in the city.[6]
Education
Goshogawara has 11 public elementary schools and six public junior high schools operated by the city government. The city has five public high schools operated by the Aomori prefectural Board of Education. The city also has two private high schools.
High schools
Prefectural
- Goshogawara High School
- Goshogawara Technical High School
- Goshogawara Agriculture and Forestry High School
- Kanagi High School
Private
- Goshogawara Daiichi High School
- Goshogawara Commercial High School
Transportation
Railway
![]() East Japan Railway Company (JR East) - Gonō Line
East Japan Railway Company (JR East) - Gonō Line
- Goshogawara - Togawa - Gonōkōmae - Tsugaru-Iizume - Bishamon - Kase - Kanagi - Ashino-Kōen - Kawakura
Highway
Local attractions

- Tachineputa Museum - Goshogawara is famous for its Tachineputa Festival, held annually from August 4 to August 8. The tachineputa floats are much taller than their counterparts in Aomori and Hirosaki, reaching heights of up to 23 meters.[7]
- Osamu Dazai Memorial Museum
- Lake Jūsan
- Ashino Chishōgun Prefectural Natural Park
- Goshogawara Sue Pottery Kiln Site, a National Historic Site[8]
- Sannobō Site, a National Historic Site[9]
- Tosaminato ruins, a National Historic Site[10]
Noted people from Goshogawara
- Osamu Dazai, novelist
- Bunji Tsushima, politician
- Ikuzo Yoshi, Enka singer-songwriter
- Shimizugawa Motokichi, sumo wrestler
- Kashiwado Risuke, sumo wrestler
- Kōji Hirayama, politician
- Daichi Shimoyama, basketball player
References
- ↑ Goshogawara Official statistics (in Japanese)
- ↑ Goshogawara climate data
- ↑ 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). JMA. Retrieved March 5, 2022.
- ↑ 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). JMA. Retrieved March 5, 2022.
- ↑ Goshogawara population statistics
- ↑ Goshogawara city home page(in Japanese)
- ↑ "Goshogawara Tachineputa Festival aptinet Aomori Sightseeing Guide". 16 March 2015.
- ↑ "五所川原須恵器窯跡". Cultural Heritage Online (in Japanese). Agency for Cultural Affairs. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- ↑ "山王坊遺跡". Cultural Heritage Online (in Japanese). Agency for Cultural Affairs. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- ↑ "十三湊遺跡". Cultural Heritage Online (in Japanese). Agency for Cultural Affairs. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
External links
- Official website (in Japanese)