_IWM_Q_038895.jpg.webp) | |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name | Astraea |
| Operators | |
| Preceded by | Apollo class |
| Succeeded by | Eclipse class |
| Built | 1893–1896 |
| In commission | 1894–1923 |
| Completed | 8 |
| Retired | 8 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type | protected cruiser |
| Displacement | 4,360 tons |
| Length | |
| Beam | 49 ft 6 in (15.09 m) |
| Draught | 19 ft (5.8 m) |
| Propulsion |
|
| Speed |
|
| Range |
|
| Complement | 318 |
| Armament | |
| Armour |
|
The Astraea class was an eight ship class of protected cruisers built for the Royal Navy during the 1890s. The ships served on a number of foreign stations during their careers, particularly in the waters of the Indian and Pacific Oceans, and around the Cape of Good Hope. Already obsolete by the outbreak of the First World War, most continued to see service in a variety of roles, though rarely in a front line capacity. By the end of the war the majority were being used as training or depot ships, and they were soon sold out of the service and scrapped. However, one ship, HMS Hermione, was bought by the Marine Society and used as a training ship until 1940.
Design and construction
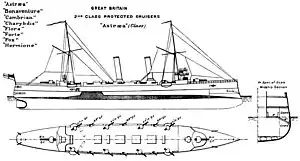
The eight ships were ordered under the provisions of the 1889 Naval Defence Act as an improved design of the precedingApollo-class cruisers.[1] They were to displace 1000 tons more than the Apollos, and were to have improved sea-keeping abilities, and heavier and better placed armament.[1] The result was a design with a full length deck that gave a higher freeboard amidships, and placed the main armament higher on the superstructure. Though this made them drier ships, the design was criticised for being a larger and more expensive development of the Apollos, but without offering any substantial increase in armament, speed or endurance.[1] The increased weight did however make them more seaworthy, and the design provided the basis for the development of future protected cruisers.[1] The ships were built at several of the principal navy dockyards: three at Devonport, two at Pembroke, and one each at Sheerness, Chatham and Portsmouth.[1]
Service
All eight ships spent at least some time on foreign stations, particularly in the Indian and Pacific Oceans, and despite their obsolescence, all but Forte went on to see service in a variety of roles during the First World War. Bonaventure was the first ship to be launched, in late 1892.[1][2] She served on the Pacific Station during the early part of her career, but was converted into a submarine depot ship in 1907.[3][4] She spent the First World War serving in this role, and was sold for scrapping in 1920.[2] The nameship of the class, Astraea, was the third of the class to be launched, on 17 March 1893, behind Bonaventure and Cambrian.[1][5] Astraea served on the China Station and in the Indian Ocean, before joining the Grand Fleet at the Nore in 1912.[3] She moved to the Cape of Good Hope and West African Station in 1913, and spent the war there, bombarding Dar es Salaam and taking part in the blockade of Königsberg.[3] She was paid off after the war and was sold in 1920.[5] Cambrian served on the Australia Station and in the Indian Ocean, before returning to Britain in 1913 to be paid off and put up for sale.[3] The outbreak of the First World War led to the navy retaining her and commissioning her as a stoker's training ship named Harlech in 1916.[3][6] She was renamed Vivid in 1921 and was sold in 1923.[6]

Charybdis spent most of her career in British waters, with occasional voyages to the Indian Ocean and Far East commands.[3] She became part of the 12th Cruiser Squadron on the outbreak of war, but was damaged in a collision in 1915 and was laid up at Bermuda.[3] Used for harbour service from 1917 she was converted to a mercantile vessel and loaned to a shipping firm in 1918. She was returned to the navy in 1920, sold in 1922 and broken up the following year.[3][7] Flora also served in China and India, and was on the sale list on the outbreak of war.[3] Retained for use as a depot ship, she was renamed Indus II in 1915 and was sold in 1922.[8] Forte served on the Cape and West African station, until being laid up and finally sold in 1914, the first of the class to leave service.[3][9] Fox served in British and East Indian waters in the pre-war period.[3] She was particularly active off the East African and Egyptian coasts during the war, and was paid off and sold in 1920.[3][10] HMS Hermione was the longest-lived of the class.[11] Serving alternately in British waters and at the Cape, she was in reserve by the outbreak of war.[3] She briefly became a guard ship at Southampton, but by 1916 she was serving as the headquarters for coastal motor launches and motor torpedo boats.[3] Paid off in 1919 she was sold to the Marine Society in 1922 and was renamed Warspite.[11] She was finally broken up in 1940.[3][11]
Ships

| Name | Builder | Laid down | Launched | Completed | Fate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astraea | Devonport Dockyard | 17 March 1893 | 5 November 1895 | Sold in 1920 | ||||
| Bonaventure | Devonport Dockyard | 2 December 1892 | 5 July 1894 | Sold in 1920 | ||||
| Cambrian | Pembroke Dockyard | 30 January 1893 | Sold in 1923 | |||||
| Charybdis | Sheerness Dockyard | 1891 | 15 June 1893 | 14 January 1896 | Sold in 1922 | |||
| Flora | Pembroke Dockyard | 21 November 1893 | Sold in 1923 | |||||
| Forte | Chatham Dockyard | 9 December 1893 | Sold in 1914 | |||||
| Fox | Portsmouth Dockyard | 15 June 1893 | 14 April 1896 | Sold in 1920 | ||||
| Hermione | Devonport Dockyard | 7 November 1893 | 14 January 1896 | Sold in 1940 | ||||
| Sources: Conway's 1860–1905, p. 77; Jane's, p. 62 | ||||||||
Notes
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Gardiner (ed.). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1860–1905. p. 77.
- 1 2 Colledge. Ships of the Royal Navy. p. 44.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Gardiner (ed.). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1906–1921. p. 15.
- ↑ Fighting Ships of World War I. p. 90.
- 1 2 Colledge. Ships of the Royal Navy. p. 24.
- 1 2 Colledge. Ships of the Royal Navy. p. 58.
- ↑ Colledge. Ships of the Royal Navy. p. 67.
- ↑ Colledge. Ships of the Royal Navy. p. 128.
- ↑ Colledge. Ships of the Royal Navy. p. 131.
- ↑ Colledge. Ships of the Royal Navy. p. 133.
- 1 2 3 Colledge. Ships of the Royal Navy. p. 162.
References
- Colledge, J. J.; Warlow, Ben (2006) [1969]. Ships of the Royal Navy: The Complete Record of all Fighting Ships of the Royal Navy (Rev. ed.). London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-281-8.
- Gardiner, Robert; Chesneau, Roger; Kolésnik, Eugène M.; Campbell, N. J. M. (1979). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1860–1905. Conway. ISBN 0-85177-133-5.
- Gardiner, Robert; Gray, Randal; Budzbon, Przemysław (1985). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1906–1921. Conway. ISBN 0-85177-245-5.
- Jane's Fighting Ships of World War One. New York: Military Press. 1990 [1919]. ISBN 0-517-03375-5.