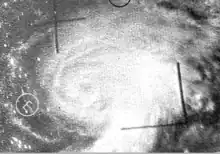
 Arlene as a minimal hurricane on August 10 | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | July 31, 1963 |
| Dissipated | August 11, 1963 |
| Category 3 hurricane | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/NWS) | |
| Highest winds | 115 mph (185 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 969 mbar (hPa); 28.61 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | None |
| Damage | $300,000 (1963 USD) |
| Areas affected | Lesser Antilles, Bermuda |
| IBTrACS | |
Part of the 1963 Atlantic hurricane season | |
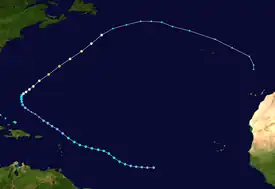
Hurricane Arlene was the first tropical cyclone of the 1963 Atlantic hurricane season and one of the wettest storms ever recorded in Bermuda. Originating from a tropical depression on July 31, Arlene quickly intensified into a Category 2 hurricane on August 2. After attaining this intensity, the storm quickly weakened and turned west. By August 4, Arlene had degenerated into a tropical depression. The storm failed to re-organize until August 7, by which time it restrengthened into a tropical storm. The following day, Arlene re-attained hurricane-status before passing directly over Bermuda. Several hours after passing the island, it reached its peak intensity with winds of 115 mph (160 km/) and a barometric pressure of 969 mbar (hPa; 28.61 inHg). By August 11, Arlene transitioned into an extratropical cyclone before being absorbed by another cyclone later that day.
Along its track, several hurricane warnings and watches were issued for the Leeward Islands; however, no damage was reported on any of the islands. The storm has its greatest impact in Bermuda where high winds and near-record rainfall downed trees, power lines and caused flooding. Damages across the island amounted to $300,000 (1963 USD; $2.1 million 2009 USD).
Meteorological history
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
Hurricane Arlene was first identified as a tropical depression on July 31 between the Lesser Antilles and the Cape Verde Islands by the TIROS VI satellite. The large cyclone, estimated at five degrees in diameter,[1] steadily tracked westward and eventually northwestward and intensified into a tropical storm on August 2.[2] Later that day, a Navy reconnaissance aircraft reached the storm and found a clear eye and a barometric pressure of 987 mbar (hPa; 29.15 inHg), resulting in Arlene being classified a hurricane.[3] This meant that the storm had rapidly intensified from a tropical depression to a hurricane within the span of 18 hours. The intensification continued for another 6 hours, at which time the storm attained its initial peak strength with winds of 100 mph (160 km/h), classifying Arlene as a Category 2 hurricane.[2]
Early on August 3, Arlene began to weaken as it turned towards the west once more.[1] The storm continued to slowly weaken before rapidly degenerating into a tropical depression on August 4.[2] The quick decrease in intensity was the result of a sudden increase in vertical wind shear near the core of the cyclone.[3] Later that day, the system passed near the northern Leeward Islands;[2] however, the depression was poorly organized.[1] The former hurricane steadily tracked northwestward and began to regenerate on August 7.[3]
As the storm began to reorganize, the forward motion had become virtually stationary but later began to increase as Arlene turned northeastward, beginning recurvature into the main belt of the Westerlies.[3] Ships in the vicinity of the depression reported that it had regained gale-force winds on August 8,[1][2] resulting in advisories on Arlene being re-initiated around that time.[3] Later that day, a Navy reconnaissance plane found hurricane-force winds around the center of the storm, resulting in Arlene being upgraded to a minimal hurricane a second time.[1]
During the day on August 9, Arlene passed directly over Bermuda with winds of 85 mph (135 km/h).[2][3] The storm continued to intensify after passing the island, with reconnaissance recorded a minimum pressure of 969 mbar (hPa; 28.61 inHg)[3] and maximum winds reached 105 mph (170 km/h).[2] The hurricane began to weaken hours later,[1] with winds decreasing below 100 mph (160 km/h) by the afternoon of August 10. Shortly after, Arlene transitioned into an extratropical cyclone, while maintaining hurricane-force winds, over the north Atlantic.[2] The remnants were absorbed by a larger cyclone near Newfoundland on August 11.[1]
Preparations and impact
| Precipitation | Storm | Location | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | mm | in | |||
| 1 | 186.7 | 7.35 | October 1939 Hurricane | [4] | |
| 2 | 172.0 | 6.77 | Nicole 2016 | [5] | |
| 3 | 153.7 | 6.05 | Arlene 1963 | [6] | |
| 4 | 151.4 | 5.96 | Cristobal 2002 | ||
| 5 | 148.0 | 5.83 | Nicole 2004 | ||
| 6 | 134.1 | 5.28 | T.D. #23A 1967 | [6] | |
| 7 | 126.2 | 4.97 | Franklin 2005 | ||
| 8 | 125.0 | 4.92 | Emily 1981 | [6] | |
| 9 | 124.0 | 4.88 | Harvey 2005 | ||
| 10 | 123.2 | 4.85 | September 1948 hurricane | [4] | |
On August 3, the National Weather Service in San Juan, Puerto Rico issued hurricane warnings for the northern Leeward Islands and a hurricane watch for the Virgin Islands. Later that day, the watch was expanded to include Puerto Rico.[7] By August 4, the hurricane warnings were lowered to gale warnings and the watch was discontinued as Arlene weakened to a tropical storm. Later that day, all warnings were canceled since the storm had further weakened to a tropical depression.[8] On August 8, after Arlene regenerated, residents in Bermuda were advised to not venture offshore on any vessel and rush all hurricane preparations to completion.[9]
In Bermuda, Arlene produced winds up to 85 mph (135 km/h) and a pressure of 974.5 mbar (hPa; 28.78 inHg) was recorded during its passage.[3] A maximum gust of 98 mph (158 km/h) was recorded at Kindley Air Force Base.[10] Tree limbs and power lines were downed across the island, a few small boats sank in rough seas and flooding was reported in some areas.[11] The hurricane produced one of the highest tropical cyclone-related rainfall totals on the island, peaking at 6.05 in (154 mm),[6] in addition to an estimated 4 ft (1.2 m) storm surge.[12] In all, damage in Bermuda amounted to $300,000 (1963 USD; $2.1 million 2009 USD).[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Gordon E. Dunn (1964). "The Hurricane Season of 1963" (PDF). United States Weather Bureau Office in Miami, Florida. Retrieved September 6, 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Hurricane Specialists Division (2009). "Easy to Read HURDAT 2008". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved September 6, 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Staff Writer (1964). "Hurricane Arlene Preliminary Report Page Three". United States Weather Bureau Office. Retrieved September 6, 2009.
- 1 2 Terry Tucker (1966). Beware the Hurricane! The Story of the Cyclonic Tropical Storms That Have Struck Bermuda and the Islanders' Folk-lore Regarding Them (1 ed.). The Hamilton Press. p. 206.
- ↑ "BWS Daily Climatology Written Summary". Bermuda Weather Service. October 26, 2016. Retrieved October 26, 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Roth, David M (January 3, 2023). "Tropical Cyclone Point Maxima". Tropical Cyclone Rainfall Data. United States Weather Prediction Center. Retrieved January 6, 2023.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ Davis and Zimmer (1964). "Hurricane Arlene Preliminary Report Page Four". United States Weather Bureau Office. Retrieved September 6, 2009.
- ↑ Hoose, Higgs and Davis (1964). "Hurricane Arlene Preliminary Report Page Five". United States Weather Bureau Office. Retrieved September 6, 2009.
- ↑ Dunn, Sugg and Moore (1964). "Hurricane Arlene Preliminary Report Page Twelve". United States Weather Bureau Office. Retrieved September 6, 2009.
- ↑ Moore and Clark (1964). "Hurricane Arlene Preliminary Report Page Thirteen". United States Weather Bureau Office. Retrieved September 6, 2009.
- ↑ United Press International (August 10, 1963). "Arlene moves out to sea after hitting Bermuda". The Bend Bulletin. Retrieved September 6, 2009.
- ↑ Dunn, Gordon E.; Miller, Banner I. (1964). Atlantic Hurricanes. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press. p. 352.