 | |
 Keio Corporation headquarters building | |
| Type | Public (K.K) |
|---|---|
| TYO: 9008 | |
| Industry | Public transport Real estate Retail |
| Predecessor | Keio Electric Railway (京王電気軌道) |
| Founded | Shinjuku, Tokyo, Japan (June 1, 1948) |
| Founder | Tokutarō Inoue |
| Headquarters | , Japan |
Key people | Yasushi Komura (Chairman)[1] Satoshi Tsumura (President) |
| Revenue | ¥429.19 billion (FY2008) |
| Total assets | ¥660.161 billion (FY2008) |
| Owner | The Master Trust Bank of Japan (9.44%) Nippon Life (5.03%) Taiyo Life (4.80%) T&D Holdings (4.55%) Trust & Custody Services Bank (4.50%) Sumitomo Mitsui Trust Bank (2.99%) Dai-ichi Life (1.82%) STATE STREET BANK WEST CLENT - TREATY 505234 (1.77%) Trust & Custody Services Bank (1.64%) Mitsubishi Bank (1.60%) Fukoku Life (1.57%) Keikyu (0.64%) JR East (0.52%) Yamanashi Chuo Bank (0.50%) Tokyu Corporation (0.37%) Tokyu Construction (0.33%) Odakyu Electric Railway (0.17%) Keisei Electric Railway (0.15%) Sagami Railway (0.10%) Seibu Holdings (0.07%) Sanrio (0.07%) Kinki Nippon Railway (0.02%) |
Number of employees | 2276 (2007) |
| Subsidiaries | Keio Dentetsu Bus Keio Department Store Keio Plaza Hotel |
| Website | www |
Keio Corporation (京王電鉄株式会社, Keiō Dentetsu Kabushiki-gaisha) (TYO: 9008) is a private railway operator in Tokyo, Japan, and the central firm of the Keio Group (京王グループ, Keiō Gurūpu) that is involved in transport, retail, real estate and other industries.
The name "Keio" (京王) is derived from taking one character each from the places through which the railway runs: "Tōkyō" (東京) and "Hachiōji" (八王子).[2] The Keio railway network connects the western suburbs of Tokyo (Chōfu, Fuchū, Hachiōji, Hino, Inagi, Tama) and Sagamihara in Kanagawa with central Tokyo at Shinjuku Station.
Network overview
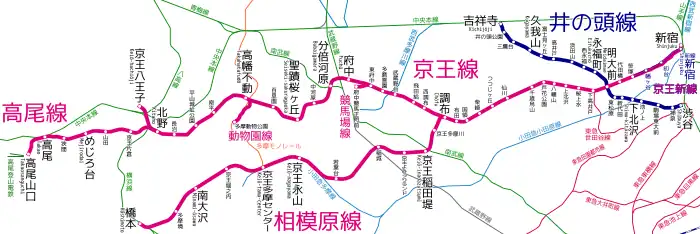
Lines
The Keio network is based around the central Keiō Line, 37.9 km (23.5 mi), 32 stations.
| Line | Section | Station No. | Length (km) | Stations | Date opened | Maximum speed (km/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keiō Line | Shinjuku - Keiō Hachiōji | 37.9 | 32 | April 15, 1913 | 110 | |
| Keiō Sagamihara Line | Chōfu - Hashimoto | 22.6 | 12 | 1916 | 110 | |
| Keiō Takao Line | Kitano - Takaosanguchi | 8.6 | 7 | March 20, 1931 | 105 | |
| Keiō Inokashira Line | Shibuya - Kichijōji | 12.7 | 17 | 1934 | 90 | |
| Keiō New Line | Shinjuku - Sasazuka | 3.6 | 4 | 1980 | ||
| Keiō Dōbutsuen Line | Takahatafudō - Tama-Dōbutsukōen | 2.0 | 2 | April 29, 1964 | ||
| Keiō Keibajō Line | Higashi-Fuchū - Fuchū-Keiba-Seimon-mae | 0.9 | 2 | April 29, 1955 | ||
| Total | 7 lines | 88.3 |
The Keio Inokashira Line does not share track with the Main Line. It intersects with the Keio Line at Meidaimae Station.
History
The company's earliest predecessor was the Nippon Electric Railway (日本電気鉄道) founded in 1905.[2] In 1906 the company was reorganized as the Musashi Electric Railway (武蔵電気鉄道), and in 1910 was renamed yet again to Keio Electric Tramway (京王電気軌道).[2] It began operating its first stretch of interurban between Sasazuka and Chōfu in 1913.[2] By 1923, Keiō had completed its main railway line (now the Keiō Line) between Shinjuku and Hachiōji.[2] Track along the Fuchū – Hachiōji section was originally laid in 1,067 mm gauge by the Gyokunan Electric Railway (玉南電気鉄道); it was later changed to match the rest of the line's 1,372 mm gauge.[2]
The Inokashira Line began operating in 1933 as a completely separate company, Teito Electric Railway (帝都電鉄).[2] This company had also planned to link Ōimachi with Suzaki (now Kōtō ward), though this never materialized.[2] In 1940, Teito merged with the Odakyu Electric Railway, and in 1942 the combined companies were merged by government order into Tōkyō Kyūkō Dentetsu (東京急行電鉄) (now Tokyu Corporation).[2]
In 1947, the shareholders of Tokyu voted to spin off the Keio and Inokashira lines into a new company, Keiō Teito Electric Railway (京王帝都電鉄).[2] The Teito name was dropped in 1998 in favor of Keio Electric Railway (京王電鉄, Keiō Dentetsu), though "KTR" placards and insignia can still be seen occasionally.[2] The company's English name was changed to Keio Corporation on June 29, 2005.[2]
Priority seats
.jpg.webp)
Keiō was among the first railway companies to introduce priority seats on its trains. Priority seats are those reserved for the physically handicapped, elderly, pregnant women, and people with infants. These special seats, which were initially called "Silver seats" but renamed in 1993, were inaugurated on Respect for the Aged Day on September 15, 1973.
Rolling stock
All Keio trains have longitudinal (commuter-style) seating.
1,372 mm (4 ft 6 in) gauge lines
- 7000 series (since 1984)
- 8000 series (since 1992)
- 9000 series (since 2001)
- 5000 series (2nd generation) (since 2017)
The first of a fleet of five new ten-car 5000 series EMUs was introduced on 29 September 2017, ahead of the start of new evening reserved-seat commuter services from Shinjuku in spring 2018.[3]
 7000 series (8-car set)
7000 series (8-car set) 8000 series (6-car set+4-car set)
8000 series (6-car set+4-car set).jpg.webp) 9000 series (10-car set)
9000 series (10-car set) 5000 series (II)
5000 series (II)
1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) gauge lines
- 1000 series (2nd generation) (since 1996)
 1000 series (II)
1000 series (II)
Former rolling stock
1,372 mm (4 ft 6 in) gauge lines
- 5000 series (from 1963 until 1996)
- 6000 series (from 1972 until 2011)
 5000 series (I)
5000 series (I) 6000 series (4-car set)
6000 series (4-car set)
1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) gauge lines
- 1000 series (from 1957 until 1984)
- 3000 series (from 1962 until 2011)
 1000 series (I)
1000 series (I) 3000 series (refurbished)
3000 series (refurbished)
Related companies
Transport
Taxi
- Keio Jidousha
Retail
- Keio Department Store
- Keio Store
Other
- Keio Realty and Development
- Keio Travel Agency
- Keio Plaza Hotel
- Keio Construction
References
- ↑ "Company Profile". Retrieved 9 January 2024.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "京王ハ ン ド ブック 2 0 2 1" [Keio Handbook 2021] (PDF). keio.co.jp (in Japanese). 2021. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 December 2021. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ↑ 京王5000系営業運転開始 [Keio 5000 series enters revenue service]. Tetsudo Hobidas (in Japanese). Japan: Neko Publishing Co., Ltd. 29 September 2017. Archived from the original on 29 September 2017. Retrieved 29 September 2017.