 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
4,4,14α-Trimethylcholestane | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H54 | |
| Molar mass | 414.762 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 98 to 99 °C (208 to 210 °F; 371 to 372 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
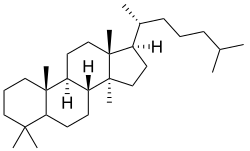
Lanostane or 4,4,14α-trimethylcholestane is a tetracyclic chemical compound with formula C
30H
54. It is a polycyclic hydrocarbon, specifically a triterpene. It is an isomer of cucurbitane.
The name is applied to two stereoisomers, distinguished by the prefixes 5α- and 5β-, which differ by the handedness of the bonds at a particular carbon atom (number 5 in the standard steroid numbering scheme).[2]
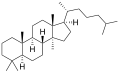 5α-Lanostane
5α-Lanostane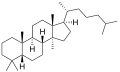 5β-Lanostane
5β-Lanostane
Replacement of a hydrogen atom attached to carbon number 3 in the 5α isomer with a hydroxyl group results in lanosterol, the biogenetic precursor of the steroids in animals.[2]
References
- ↑ Voser, W.; Montavon, M.; Günthard, Hs. H.; Jeger, O.; Ruzicka, L. (1950). "Zur Kenntnis der Triterpene. 156. Mitteilung. Zur Konstitution des Lanostadienols". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 33 (6): 1893–1910. doi:10.1002/hlca.19500330658.
- 1 2 IUPAC Commission on the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry and IUPAC-IUB Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature (1969). "The Nomenclature of Steroids — Revised Tentative Rules". European Journal of Biochemistry. 10 (1): 1–19. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00650.x.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.