Shu 蜀 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 934–965 | |||||||||
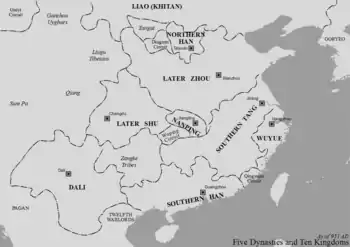 Later Shu shown in light red | |||||||||
| Capital | Chengdu | ||||||||
| Common languages | Ba–Shu Chinese | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Emperor | |||||||||
• 934 | Emperor Gaozu | ||||||||
• 934–965 | Emperor Houzhu | ||||||||
| Historical era | Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period | ||||||||
• Established in Chengdu | 934 934 | ||||||||
• Surrendered to Song | 965 965 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | China | ||||||||
Shu, referred to as Later Shu (traditional Chinese: 後蜀; simplified Chinese: 后蜀; pinyin: Hòu Shǔ) and Meng Shu (Chinese: 孟蜀) in historiography, was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was located in present-day Sichuan with its capital in Chengdu and lasted from 934 to 965.
Rulers
| Temple name | Posthumous name | Family name and given name | Reign | Era names and their corresponding years | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高祖 | Emperor Wénwǔ Shèngdé Yīngliè Míngxiào (文武聖德英烈明孝皇帝) | Mèng Zhīxíang (孟知祥) | 934 | Míngdé (明德) 934 | |||||
| 後主 | Prince Gongxiao of Chu (楚恭孝王) | Mèng Chǎng (孟昶) | 934–965 | Míngdé (明德) 934–938 Guǎngzhèng (廣政) 938–965 | |||||
Rulers family tree
| Later Shu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
References
- Mote, F.W. (1999). Imperial China (900–1800). Harvard University Press. pp. 11–15. ISBN 0-674-01212-7.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.