| Lisbon Agreement for the Protection of Appellations of Origin and their International Registration of October 31, 1958, as revised at Stockholm on July 14, 1967, and as amended on September 28, 1979 | |
|---|---|
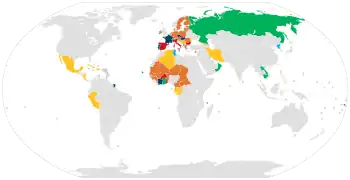 Lisbon Agreement and Geneva act
Geneva act, but not Lisbon agreement
Lisbon agreement, but not Geneva act
covered by OAPI/EU's accession (Geneva act) and to Lisbon agreement
covered by OAPI/EU's accession (Geneva act) and party to Lisbon and/or Geneva act
covered by OAPI/EU's accession (Geneva act) | |
| Signed | 31 October 1958 (Lisbon) 14 July 1967 (Stockholm) 21 May 2015 (Geneva) |
| Location | Lisbon, Stockholm, Geneva |
| Effective | 25 September 1966 (Lisbon) 31 October 1973 (Stockholm) 26 February 2020 (Geneva) |
| Signatories | 11 (Lisbon) 5 (Stockholm) 11 (Geneva) |
| Parties | 10 (Lisbon) 30 (Stockholm) 21 (Geneva)[1] |
| Depositary | Switzerland (Lisbon), Sweden (Stockholm), WIPO (Geneva) |
| Language | French (Lisbon, Stockholm) |
| Languages | Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, Spanish (Geneva) |
The Lisbon Agreement for the Protection of Appellations of Origin and their International Registration, signed on 31 October 1958, ensures that in member countries, appellations of origin receive protection when are protected in their country of origin. It lays down provisions for what qualifies as an appellation of origin, protection measures and establishes an International Register of Appellations of Origin, run by the World Intellectual Property Organization. The agreement came into force in 1966, and was revised at Stockholm (1967) and amended in 1979 and 2015. As of July 2022, 39 states are party to the convention and 1000 appellations of origin has been registered.[2]
The agreements establish a Special Union under Article 19 of the Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property (1883).[3] Some aspects of the agreement have been superseded by the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights.
Geneva Act
In May 2015, the Geneva Act to the Agreement was adopted, formally extending protection to Geographical Indication and changing the name: Geneva Act of the Lisbon Agreement on Appellations of Origin and Geographical Indications. The act furthermore allows intergovernmental organisations to become parties. On 21 May 2015, the Act was signed by 13 states: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Burkina Faso, Congo, France, Gabon, Hungary, Mali, Nicaragua, Peru, Romania and Togo. It entered into force in 2020 following ratifications/accessions by 5 parties: Albania, Cambodia, European Union, North Korea and Samoa. As of 18 January 2024, the number of parties is 21.
Parties
The treaty applies mutually between the parties of the 1958 Lisbon Agreement and the 1967 Stockholm Act, but not between a party solely to the 1958 Agreement and another party solely to the 1967 Stockholm act. The Geneva Act entered into force in 2020, and only applies between the Geneva act parties. If a state is a party to multiple Lisbon instruments, then a registered appellation of origin registered under any of the instruments applies also to parties of the other instruments the state is a party to.
| State | Lisbon Agreement[1] | Stockholm Act[1] | Geneva Act[1] | Registered AO[4] | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 May 2019 | 8 May 2019 | 26 February 2020 | 0 | ||
| 5 July 1972 | 31 October 1973 | 19 | |||
| 4 July 2013 | 4 July 2013 | Signed | 4 | ||
| 12 August 1975 | 12 August 1975 | 33 | Also covered by Geneva act through EU accession | ||
| 2 September 1975 | 2 September 1975 | Signed | 0 | Also covered by Geneva act through OAPI accession | |
| 6 July 2022 | |||||
| 26 February 2020 | 1 | ||||
| 16 November 1977 | 16 November 1977 | Signed | 0 | ||
| 30 July 1997 | 30 July 1997 | Signed | 2 | ||
| 25 September 1966 | 8 April 1975 | 20 | |||
| 1 January 1993 | 1 January 1993 | 2 September 2022 | 75 | Also covered by Geneva act through EU accession | |
| 17 January 2020 | 17 January 2020 | ||||
| 25 September 1966- 1 January 1993 | 31 October 1973- 1 January 1993 | Continued application by Czech Republic and Slovakia | |||
| 26 February 2020 | 117 | Only application to Geneva Act possible | |||
| 25 September 1966 | 12 August 1975 | 21 April 2021 | 509 | Also covered by Geneva act through EU accession | |
| 10 June 1975 | 10 June 1975 | Signed | 0 | ||
| 23 September 2004 | 23 September 2004 | 28 | |||
| 3 February 2022 | |||||
| Signed | Covered by Geneva act through EU accession | ||||
| 25 September 1966 | 0 | ||||
| 23 March 1967 | 31 October 1973 | 10 September 2021 | 28 | Also covered by Geneva act through EU accession | |
| 9 March 2006 | 9 March 2006 | 64 | |||
| 25 September 1966 | 31 October 1973 | 1 | |||
| 29 December 1968 | 24 April 1977 | Signed | 175 | Also covered by Geneva act through EU accession | |
| 15 March 2023 | Also covered by Geneva act through OAPI accession | ||||
| 20 February 2021 | |||||
| Signed | |||||
| 25 September 1966 | 26 January 2001 | 18 | |||
| 5 April 2001 | Signed | 1 | |||
| 3 June 2006 | 3 June 2006 | 2 | |||
| Signed | |||||
| 15 June 2006 | 15 June 2006 | Signed | |||
| 4 January 2005 | 4 January 2005 | 26 February 2020 | 6 | ||
| 6 October 2010 | 6 October 2010 | 5 | |||
| OAPI | 15 March 2023 | 0 | Only application to Geneva Act possible | ||
| 30 June 2021 | |||||
| 16 May 2005 | 16 May 2005 | 18 October 2022 | 10 | ||
| 25 September 1966 | 17 April 1991 | 18 January 2024 | 7 | Also covered by Geneva act through EU accession | |
| 11 August 2023 | |||||
| Signed | Signed | Covered by Geneva act through EU accession | |||
| 26 February 2020 | |||||
| 2 November 2023 | |||||
| 5 December 2023 | Also covered by Geneva act through OAPI accession | ||||
| 1 June 1999 | 1 June 1999 | 3 | |||
| 1 January 1993 | 1 January 1993 | 8 | Also covered by Geneva act through EU accession | ||
| Signed | Covered by Geneva act through EU accession | ||||
| 31 August 2021 | |||||
| 30 April 1975 | 30 April 1975 | Signed | Also covered by Geneva act through OAPI accession | ||
| 31 October 1973 | 31 October 1973 | 6 July 2023 | 8 | ||
| Signed |
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 "9. Lisbon Agreement for the Protection of Appellations of Origin and their International Registration" (PDF). WIPO. 18 October 2023. Retrieved 6 December 2023.
- ↑ "About Lisbon Agreement". WIPO. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
- ↑ "Lisbon Agreement for the Protection of Appellations of Origin and their International Registration]". WIPO. Retrieved 24 February 2012.
- ↑ "Search Appellations of Origin and Geographical Indication. Structured search". WIPO. Retrieved 6 February 2021.
External links
- Treaty text of