-2016.svg.png.webp)
The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide of France:
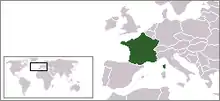
France – country in Western Europe with several overseas regions and territories. Metropolitan France extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. From its shape, it is often referred to in French as l’Hexagone ("The Hexagon").
General reference
- Pronunciation: English: /ˈfræns/ ⓘ or /ˈfrɑːns/, French: [fʁɑ̃s] ⓘ; (the French Republic: French: République française, pronounced [ʁepyblik fʁɑ̃sɛːz] ⓘ)
- Common English country name: France
- Official English country name: The French Republic
- Common endonym(s): La France
- Official endonym(s): République française
- Adjectival(s): French (can refer to people, language or anything related to the country)
- Demonym(s): French (or Frenchman/Frenchwoman)
- Etymology: Name of France
- International rankings of France
- ISO country codes: FR, FRA, 250
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:FR
- Internet country code top-level domain: .fr
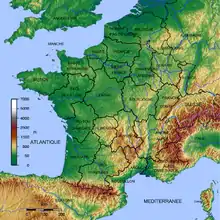
Geography of France
- France is a:
- Location:
- Northern Hemisphere, on the Prime Meridian
- Eurasia
- Europe
- mostly in Western Europe [lower-alpha 1]
- Europe
- Eurasia
- Time in France
- Extreme points of France (major towns)[2]
- North: Dunkirk at the North Sea
- South: Perpignan, at the Spanish border
- East: Haguenau, at the German border
- West: Brest, south of Land's End (England)
- High: Mont Blanc 4,810 m (15,781 ft) – highest point of Western Europe
- Low: Les Moëres −2.5 m (−8 ft)
- Land boundaries: 4,072 km (2,530 mi)
- Metropolitan France: 2,889 km (1,795 mi)
- Northern Hemisphere, on the Prime Meridian
 Spain 623 km (387 mi)
Spain 623 km (387 mi).svg.png.webp) Belgium 620 km (385 mi)
Belgium 620 km (385 mi).svg.png.webp) Switzerland 573 km (356 mi)
Switzerland 573 km (356 mi) Italy 488 km (303 mi)
Italy 488 km (303 mi) Germany 451 km (280 mi)
Germany 451 km (280 mi) Luxembourg 73 km (45 mi)
Luxembourg 73 km (45 mi) Andorra 57 km (35 mi)
Andorra 57 km (35 mi) Monaco 4 km (2 mi)
Monaco 4 km (2 mi)
- French Guiana: 1,183 km (735 mi)
- Coastline: 4,668 km (2,901 mi)
- Metropolitan France: 3,427 km (2,129 mi)
- Incorporated overseas territories: 1,241 km (771 mi)
- Population of France: 68,035,000 people (2021 estimate) – 20th most populous country
- Area of France: 674,843 km2 (260,558 sq mi) – 40th largest country
- Atlas of France
- Communes (municipalities) of France
Environment of France

- Climate of France
- Ecology of France
- Geology of France
- National parks of France
- Wildlife of France
Geographic features of France

Regions of France
- "Region" is also the name of France's main type of political division
Administrative divisions of France
Regions of France (Administrative)
Regions of France Since January 1, 2016, continental France is divided into 13 administrative Regions instead of the former 22 regions. The 5 overseas regions are untouched:

| Before 2016 | From January, 1st 2016 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1. Alsace |
12. Île-de-France |
1. Bourgogne-Franche-Comté |
12. Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur | |
Departments of France
Departments of France French departments are roughly analogous to British counties.


Municipalities of France
- Cities of France
- Capital of France: Paris – also the largest city in France, with over 2,000,000 inhabitants
- Strasbourg – official seat of the European Parliament
- Lyon – silk capital of the world and the location of the headquarters of Interpol and Euronews
- Marseille – France's largest commercial port
Demography of France
Neighbors of France
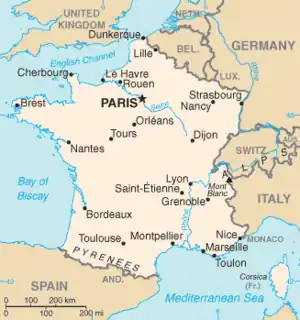
Metropolitan France is bordered by:
France is also linked to:
- United Kingdom (by the Channel Tunnel, which passes underneath the English Channel)
France's overseas departments share borders with:
- Brazil (borders French Guiana)
- Suriname (borders French Guiana)
- Sint Maarten (borders Saint-Martin)
Government and politics of France
- Form of government: unitary semi-presidential republic
- Capital of France: Paris
- Constitutional Council of France
- Elections in France
- French presidential elections: 1848 – 1958 – 1965 – 1969 – 1974 – 1981 – 1988 – 1995 – 2002 – 2007 – 2012 – 2017
- French parliamentary elections: 1795 – 1798 – 1815 – 1816 – 1820 – 1824 – 1827 – 1830 – 1831 – 1834 – 1837 – 1839 – 1842 – 1846 – 1848 – 1849 – 1852 – 1857 – 1863 – 1869 – 1871 (Feb) – 1871 (Jul) – 1876 – 1877 – 1881 – 1885 – 1889 – 1893 – 1898 – 1902 – 1906 – 1910 – 1914 – 1919 – 1924 – 1928 – 1932 – 1936 – 1945 – 1946 (Jun) – 1946 (Nov) – 1951 – 1956 – 1958 – 1962 – 1967 – 1968 – 1973 – 1978 – 1981 – 1986 – 1988 – 1993 – 1997 – 2002 – 2007 – 2012 – 2017
- French referendums: 1793 – 1795 – 1800 – 1802 – 1804 – 1815 – 1851 – 1852 – 1870 – 1945 – 1946 (May) – 1946 (Oct) – 1958 – 1961 – 1962 (Jun) – 1962 (Oct) – 1969 – 1972 – 1988 – 1992 – 2000 – 2005
- Feminism in France
- Foreign relations of France
- Liberalism and radicalism in France
- Political parties in France
- Political scandals of France
- Taxation in France
Branches of the government of France
Executive branch
Emmanuel Macron, current President of France
- Head of state: President of the French Republic
- Le Gouvernement (Cabinet of ministers)
- Head of government: Prime Minister of France
- Minister of Foreign Affairs
- Minister of the Interior
- Minister of Overseas France
- Minister of the Environment
- Minister of Transportation
- Minister of Public Works
- Minister of the Economy, Finance and Industry
- Minister of Defence
- Minister of Justice
- Minister of National Education
- Minister of Higher Education and Research
- Minister of Culture
- Minister of Agriculture
- Minister of Tourism
- Minister of the Sea
- Minister of Health
- Minister of Youth Affairs and Sports
- Minister of Budget, Public Accounting and Civil Servants
- Minister of Immigration, Integration, National identity and Co-development
- Minister of Social Affairs
- Minister of Housing
Legislative branch
- Parliament of France (Parlement) (see also: Congress of France)
- French National Assembly (Assemblée Nationale)
- French Senate (Sénat)
- French Economic and Social Council (consultative assembly)
Judicial branch
International relations of France
Foreign relations
- Foreign relations of France
- Foreign policy of François Mitterrand
- France is a nuclear power
- France–Africa relations
- France–Americas relations
- France–Asia relations
- Evolution of the French Empire
- French colonial empire
- French colonisation of the Americas
- International relations, 1648–1814
- International relations (1814–1919)
- Aftermath of World War I
- International relations (1919–1939)
- Diplomatic History of World War II
- Cold War
- International relations since 1989
International organization membership
The French Republic is a member of:[3]
Law of France

- Adoption in France
- Cannabis in France
- Capital punishment in France
- Census in France
- Constitution of France
- Crime in France
- Law enforcement in France
- National law enforcement agencies
- National Police ("Police Nationale")
- National Gendarmerie ("Gendarmerie Nationale")
- Mobile Gendarmerie ("Gendarmerie Mobile")
- Local law enforcement agencies
- Police municipale (Municipal police) – may be maintained by local governments (communes), but have very limited law enforcement powers outside of traffic issues and local ordinance enforcement
- Garde champetre or Police Rurale (Rural police) – may be formed by Rural communes, and are responsible for limited local patrol and protecting the environment
- Équipes régionales d’intervention et de sécurité (SWAT teams) – are operated by The Department of Corrections (the prison system or Administration pénitentiaire)
- In Wallis and Futuna, there is a territorial guard as well as royal police.
- National law enforcement agencies
- Human rights in France
Historical law
Military of France

- Command
- French Armed Forces
- French Army (Armée de Terre)
- French Navy (Marine Nationale)
- French Air Force (Armée de l'Air)
- National Gendarmerie (Gendarmerie Nationale)
- Military history of France
History of France
General topics

By period
|
|
|
Culture of France

- Architecture of France
- Art in France
- Cuisine of France
- Cultural icons of France
- Languages of France
- Media in France
- Mythology in France
- National symbols of France
- People of France
- Ethnic minorities in France
- Public holidays in France
- Racism in France
- Scouting and Guiding in France
- World Heritage Sites in France (See also Transboundary sites)
Religion and belief systems in France
- Belief systems
- Religion in France
Sports in France


Sport articles specific to France:
- Fédération Française de Basket-Ball
- Football in France
- France at the Olympics: the modern Olympics were invented in France, in 1894
- Grand Prix de France
- French Open (tennis)
- Open de France
- Pétanque
- Parkour ('urban running')
- Rugby in France:
- Tour de France
- Alps Tour
- France men's national handball team
Economy and infrastructure of France

France is the most visited country in the world, receiving over 79 million foreign tourists annually (including business visitors, but excluding people staying less than 24 hours in France).[4]
- Economic rank
- Nominal GDP: 6th (sixth)
- GDP (PPP): 8th (eighth)
- Agriculture in France
- Banking in France
- Communications in France
- Companies of France

Education in France
The three stages of the education process in France:
- Primary education (enseignement primaire)
- Secondary education (enseignement secondaire)
- Collèges – cater for the first four years of secondary education from the ages of 11 to 15
- Lycées – provide a three-year course of further secondary education for children between the ages of 15 and 18, during which pupils are prepared for the baccalauréat (commonly referred to as le bac).
- Higher education (enseignement supérieur)
Health in France
See also
- All pages with titles beginning with France
- All pages with titles containing France
- All pages with titles beginning with French
- All pages with titles containing French
- List of international rankings
- Member state of the European Union
- Member state of the Group of Twenty Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors
- Member state of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of Europe
- Outline of geography
Notes
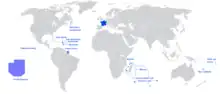
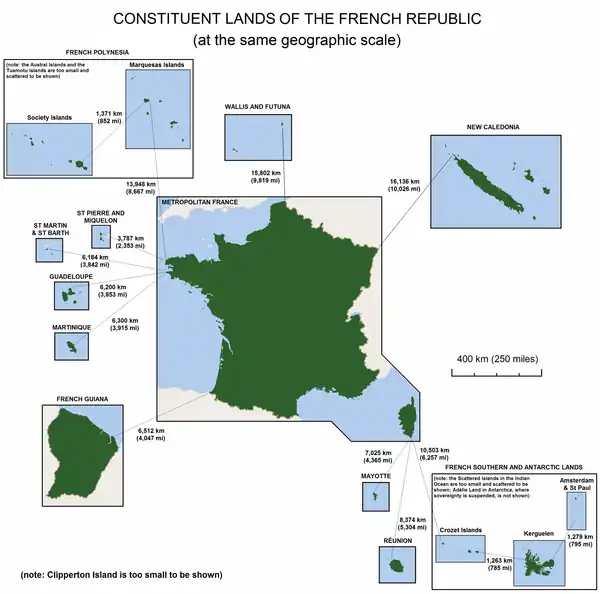
- ↑ French Guiana is located in South America; Guadeloupe and Martinique are in the Caribbean; and Réunion and Mayotte are in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of Africa. All five are considered integral parts of the republic.
References
- ↑ Overcoming barriers: Human mobility and development. Human Development Report 2009. the United Nations Development Programme. New York. ISBN 978-0-230-23904-3
- ↑ Map of France, SitesAtlas.com, 2009, webpage: SitA-507.
- ↑ "France". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. July 2, 2009. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Government of France, Directorate of Tourism. "79 millions d'arrivées de touristes internationaux en 2006" (PDF) (in French). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-08-08. Retrieved 2007-07-31.
External links
French government
- Official site of the French Embassy in the United Kingdom
- Official site of the French public service – Contains many links to various administrations and institutions
- Frenchculturenow.com: French society, culture, politics news
Country profiles
- France, from the Encyclopædia Britannica
- France, from the CIA World Factbook
 France travel guide from Wikivoyage
France travel guide from Wikivoyage- France, from the BBC
Culture
- Cocorico! French culture
- Contemporary French Civilization, journal, University of Illinois.
- Radio France Internationale in English culture pages
- Radio France Internationale in English Visiting France page



.jpg.webp)
