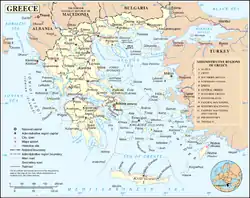
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Greece:
Greece – sovereign country located on the southern end of the Balkan Peninsula in Southern Europe.[1] Greece borders Albania, Bulgaria, and North Macedonia to the north, and Turkey to the east. The Aegean Sea lies to the east and south of mainland Greece, while the Ionian Sea lies to the west. Both parts of the Eastern Mediterranean basin feature a vast number of islands.
Greece lies at the juncture of Europe, Asia and Africa. It is heir to the heritages of ancient Greece, the Roman and Byzantine Empires,[2] and nearly four centuries of Ottoman rule.[3] Greece is the birthplace of democracy,[4] Western philosophy,[5] the Olympic Games (for this reason, unless it is the host nation, it always leads the Parade of Nations in accordance with tradition begun at the 1928 Amsterdam Olympics), Western literature and historiography, political science, major scientific and mathematical principles, and Western drama[6] including both tragedy and comedy.
Greece is a developed country, a member of the European Union since 1981,[7] a member of the Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union since 2001, NATO since 1952,[8] the OECD since 1961,[9] the WEU since 1995 and ESA since 2005.[10] Athens is the capital; Thessaloniki, Patras, Heraklion, Volos, Ioannina, Larissa and Kavala are some of the country's other major cities.
General reference
- Pronunciation: /ˈɡriːs/
- Common English country name: Greece
- Official English country name: The Hellenic Republic
- Common endonym(s): Ελλάς (Ellas, archaic); Ελλάδα (Ellada)
- Official endonym(s): Ελληνική Δημοκρατία (Elliniki Dimokratia)
- Adjectives: Greek, Grecian, Hellenic
- Demonym: Greek
- Etymology: Name of Greece
- International rankings of Greece
- ISO country codes: GR, GRC, 300
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:GR
- Internet country code top-level domain: .gr
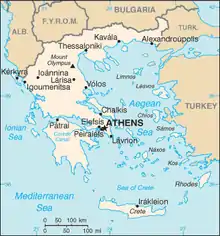
Geography of Greece

- Greece is: a country
- Location:
- Northern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
- Eurasia
- Europe
- Southern Europe
- Balkans (also known as "Southeastern Europe")
- Western Europe
- Southern Europe
- Europe
- Time zone: Eastern European Time (UTC+02), Eastern European Summer Time (UTC+03)
- Extreme points of Greece
- High: Mount Olympus 2,919 m (9,577 ft)
- Low: Mediterranean Sea 0 m
- Land boundaries: 1,228 km
 Bulgaria 494 km
Bulgaria 494 km Albania 282 km
Albania 282 km North Macedonia 246 km
North Macedonia 246 km Turkey 206 km
Turkey 206 km
- Coastline: 13,676 km
- Population of Greece: 11,306,183 (January 1, 2010) - 73rd most populous country
- Area of Greece: 131,990 km2
- Atlas of Greece
Environment of Greece

- Climate of Greece
- Environmental issues in Greece
- Renewable energy in Greece
- Protected areas of Greece
- Wildlife of Greece
- Fauna of Greece
Natural geographic features of Greece



Regions of Greece
Ecoregions of Greece
Administrative divisions of Greece
Administrative divisions of Greece
Administrative regions of Greece
Regional units of Greece
Municipalities of Greece
Municipalities and communities of Greece
- Capital of Greece: Athens (outline)
- Cities of Greece
Traditional geographic divisions of Greece
Demography of Greece
Government and politics of Greece
- Form of government: parliamentary representative democratic republic
- Capital of Greece: Athens
- Elections in Greece
- Greek government-debt crisis
- Greek withdrawal from the eurozone
- Political parties in Greece
- Taxation in Greece
Branches of the government of Greece
Executive branch of the government of Greece
Legislative branch of the government of Greece

Judicial branch of the government of Greece
Judicial system of Greece There are three Supreme Courts in Greece. They are:
- Court of Cassation (Greek: Άρειος Πάγος)
- Council of State (Greek: Συμβούλιο της Επικρατείας)
- Chamber of Accounts (Greek: Ελεγκτικό Συνέδριο)
Foreign relations of Greece
International organization membership
The Hellenic Republic is a member of:[1]
Law and order in Greece
_March_2016.jpg.webp)

- Law of Greece
- Crime in Greece
- Human rights in Greece
- Law enforcement in Greece
Military of Greece


Local government in Greece
Local government in Greece
History of Greece


.jpg.webp)
By period
By subject
Culture of Greece









- Architecture of Greece
- Cuisine of Greece
- Greek dress
- Greek nationalism
- Languages of Greece
- Media in Greece
- Monuments of Greece
- Acropolis of Athens
- Ancient Agora of Athens
- Ancient Theatre of Epidaurus
- Arch of Galerius and Rotunda
- Erechtheion
- Greek pyramids
- Knossos Minoan palace complex
- Lion Gate
- Odeon of Herodes Atticus
- Palaestra at Olympia
- Stadium of Delphi
- Temple of Hephaestus
- Temple of Olympian Zeus, Athens
- Terrace of the Lions
- Theatre of Dionysus
- Tholos of Delphi
- Museums in Greece
- National symbols of Greece
- People of Greece
- Philhellenism
- Public holidays in Greece
- World Heritage Sites in Greece
Art in Greece
Religion in Greece


Sports in Greece
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)
- Baseball in Greece
- Basketball in Greece
- Cricket in Greece
- Football in Greece
- Greece at the Olympics
- Greece at the Paralympics
- Hockey in Greece
- Rugby in Greece
- Sports venues in Greece
Economy and infrastructure of Greece




- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 27th (twenty-seventh)
- Agriculture in Greece
- Banking in Greece
- Communications in Greece
- Companies of Greece
- Currency of Greece: Euro (see also: Euro topics)
- Former currency: Greek drachma
- ISO 4217: EUR
- Economic history of Greece
- Energy in Greece
- Maritime industry
- Science and technology
- Tourism in Greece
- Transport in Greece
- Water supply and sanitation in Greece
Education in Greece
- Academic grading in Greece
- Higher education in Greece
- Universities in Greece
- Polytechnics
- Τechnological Universities-Technological educational institutes
- Vocational education
Health in Greece
See also
References
- 1 2 "Greece". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. July 2, 2009. Retrieved July 23, 2009.
- ↑ Sir Steven Runciman, Conclusion, The Fall of Constantinople
- ↑ "Greece." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2006. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 6 Sept. 2006 <http://search.eb.com/eb/article-9106266>.
- ↑ Finley, M. I. Democracy Ancient and Modern. 2d ed., 1985. London: Hogarth.
- ↑ History of Philosophy, Volume 1 by Frederick Copleston
- ↑ Brockett, Oscar G. History of the Theatre. sixth ed., 1991. Boston; London: Allyn and Bacon.
- ↑ "Member States of the EU: Greece". European Union. europa.eu. Retrieved 2007-04-07.
- ↑ On the 14 August 1974 Greek forces withdrew from the integrated military structure of NATO in protest at the Turkish occupation of northern Cyprus. Greece rejoined NATO in 1980.
- ↑ "Convention on the OECD". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. www.oecd.org. Retrieved 2007-04-07.
- ↑ "Greece becomes 16th ESA Member State". European Space Agency. www.esa.int. 2005-03-22. Retrieved 2007-04-07.
External links
- Government
- President of the Hellenic Republic
- Prime Minister of the Hellenic Republic
- Hellenic Parliament
- Greek News Agenda Newsletter
- Greece — information and links related to Greece from the ministry of foreign affairs
- Greek missions abroad (embassies, consulates, representations)
- Foreign missions in Greece
- Greek National Tourism Organisation
- National Statistical Service of Greece
- Other




.jpg.webp)


