 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
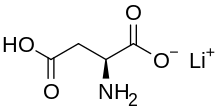
| Formula | C4H6LiNO4 |
| Molar mass | 139.04 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Lithium aspartate (C4H6LiNO4) is a salt of aspartic acid and lithium. It is sometimes marketed as a dietary supplement used in small doses to treat certain medical conditions; however, there are no systematic reviews supporting the efficacy, or safety, of lithium aspartate and it is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of any medical condition. Published research on lithium aspartate is sparse.[1][2][3]
Aspartatic acid stimulates the NMDA receptor.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Müller-Oerlinghausen B, Imiela M (June 1986). "Is lithium aspartate at low serum levels more effective than the usual lithium salts?". Nervenarzt. 57 (6): 370–3. PMID 3736729.
- ↑ Olbrich R, Watzl H, Völter M, Siedow H (March 1991). "Lithium in the treatment of chronic alcoholic patients with brain damage--a controlled study". Nervenarzt. 62 (3): 182–6. PMID 2052117.
- ↑ Daunderer M (September 1982). "Lithium aspartate in drug dependence". Fortschr. Med. 100 (33): 1500–2. PMID 7129311.
- ↑ Chen PE, Geballe MT, Stansfeld PJ, Johnston AR, Yuan H, Jacob AL, Snyder JP, Traynelis SF, Wyllie DJ (May 2005). "Structural features of the glutamate binding site in recombinant NR1/NR2A N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors determined by site-directed mutagenesis and molecular modeling". Molecular Pharmacology. 67 (5): 1470–84. doi:10.1124/mol.104.008185. PMID 15703381. S2CID 13505187.
External links
- Lithium – The Misunderstood Mineral Part 1 article on lithium compounds by Jonathan Wright, M.D.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.