 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
lithium azide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.039.237 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| LiN3 | |
| Molar mass | 48.96 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 115 °C (239 °F; 388 K) |
| 36.12 g/100 g (10 °C) 62.07 g/100 g (15.5 °C) 66.41 g/100 g (16 °C)[2] | |
| Solubility | 20.26 g/100 g (16 °C, ethanol)[2] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External SDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
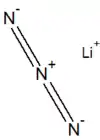
Lithium azide is the lithium salt of hydrazoic acid. It is an unstable and toxic compound that decomposes into lithium and nitrogen when heated.
Preparation
It can be prepared by metathesis reaction between sodium azide and lithium nitrate or lithium sulfate solutions:
- NaN3 + LiNO3 → LiN3 + NaNO3
- 2 NaN3 + Li2SO4 → 2 LiN3 + Na2SO4[3]
It can also be prepared by reacting lithium sulfate with barium azide.
- Ba(N3)2 + Li2SO4 → 2 LiN3 + BaSO4[2]
References
- ↑ Pringle, G. E.; Noakes, D. E. (February 1968). "The crystal structures of lithium, sodium and strontium azides". Acta Crystallogr. B. 24 (2): 262–269. doi:10.1107/S0567740868002062.
- 1 2 3 Hála, Jiri. "IUPAC-NIST Solubility Data Series. 79. Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metal Pseudohalides" (PDF). nist.gov. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 February 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2018.
- ↑ "Λ » LambdaSyn – Darstellung von Lithiumazid".
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.