| Kyushu Shinkansen | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
 800 Series Shinkansen Tsubame at Shin-Minamata Station in November 2004 | |||
| Overview | |||
| Native name | 九州新幹線 | ||
| Owner | |||
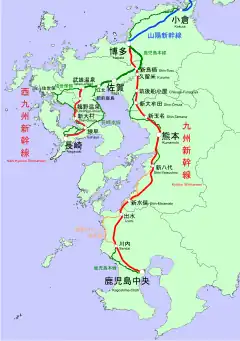
| Locale | Kyushu (Fukuoka, Saga, Nagasaki, Kumamoto, and Kagoshima Prefectures) | ||
| Termini |
| ||
| Stations |
| ||
| Color on map | Red (#FF0000) | ||
| Service | |||
| Type | High-speed rail | ||
| System | Shinkansen | ||
| Services | Mizuho, Sakura, Tsubame | ||
| Operator(s) | |||
| Depot(s) |
| ||
| Rolling stock | |||
| History | |||
| Opened |
| ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 256.8 km (159.6 mi) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Minimum radius | 4,000 m (2.5 mi; 13,000 ft) | ||
| Electrification | 25 kV 60 Hz AC (overhead line) | ||
| Operating speed | 260 km/h (162 mph) | ||
| |||
The Kyushu Shinkansen (九州新幹線, Kyūshū Shinkansen) is a Japanese Shinkansen high-speed railway network. It is an extension of the San'yō Shinkansen from Honshu connecting the city of Fukuoka (Hakata Station) in the north of Japan's Kyushu Island to the city of Kagoshima (Kagoshima-Chuo Station) in the south. The line runs parallel to the existing Kagoshima Main Line and is operated by Kyushu Railway Company (JR Kyushu).
The southernmost 127 km (79 mi) section of the track was constructed first, opening on 13 March 2004. The dual-track offered a significant improvement in transit time over the equivalent single-track section of the Kagoshima Main Line, despite the need for passengers to change to a Relay Tsubame narrow gauge train at Shin-Yatsushiro, and the remainder of the journey to Hakata Station. The northernmost 130 km (81 mi) section opened on 12 March 2011, enabling through-services to Shin-Osaka (and with an interchange, to Tokyo). However, opening ceremonies were cancelled due to the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami.[1]
The Nishi Kyushu Shinkansen route to Nagasaki (from Takeo-Onsen to Nagasaki) opened on 23 September 2022.[2][3] A cross-platform interchange to a relay service called 'Relay Kamome' at Takeo-Onsen station offers a connection to Hakata.[4][5][6]
Kagoshima Route
Construction of the Kagoshima Route (鹿児島ルート) began in 1991, and the first segment between Kagoshima and Shin-Yatsushiro opened on 13 March 2004. This initial section cut travel times between the two cities from 2 hours and 10 minutes to 35 minutes and reduced the time between Hakata and Kagoshima from 4 hours to 2 hours. When the entire line was completed, the travel time from Hakata to Kagoshima was further reduced to about an hour and 20 minutes. As of 2012, the maximum line speed is 260 km/h (160 mph) between Hakata and Kagoshima.[7] Like all Shinkansen lines, the Kyushu Shinkansen is standard gauge.
The line's Sakura and Mizuho services often operate through to Shin-Ōsaka Station via the San'yō Shinkansen. All-stop trains are named Tsubame ("Swallow"), the name of the former Hakata-Kagoshima limited express service, and are solely truncated to the Kyushu Shinkansen.
In September 2011, six months after the line's completion, JR Kyushu reported a year-over-year increase in ridership of 64% to the southern part of Kyushu (between Kumamoto and Kagoshima), easily surpassing the 40% increase projected by the company. By the first anniversary, ridership had increased, mainly from tourists from Kansai and Chugoku.[8] In northern Kyushu, where there is fierce competition with conventional JR rapid service, the private Nishi-Nippon Railroad, and expressway buses, Shinkansen ridership increased by only 38% (compared to the now-discontinued conventional express Relay Tsubame), falling short of estimates.[9]
Nishi Kyushu (Nagasaki) Route
A Shinkansen line from Fukuoka to Nagasaki, initially known as the Nagasaki Shinkansen (長崎新幹線), was laid out in the 1973 Basic Plan. Renamed as the Nagasaki Route (長崎ルート), then changed to the Nishi Kyushu Route (西九州ルート, Nishi Kyūshū rūto) in 1995, the segment between Takeo-Onsen and Nagasaki, Nishi Kyushu Shinkansen, opened for service on 23 September 2022.[10][11]
Other planned routes
According to the Shinkansen Basic Plan laid out in 1973, two other routes would accompany the Kagoshima and West Kyushu (Nagasaki) routes: the East Kyushu Shinkansen, from Hakata to Kagoshima-Chūō via Ōita and Miyazaki, paralleling the Nippō Main Line; and the Trans-Kyushu Shinkansen, linking Kumamoto and Ōita, and connecting with the also-planned Shikoku Shinkansen to Matsuyama, Takamatsu and Osaka. These plans have been shelved indefinitely and are unlikely to be reconsidered until the Shinkansen lines that are already under construction are completed.
Station list
- Tsubame trains stop at all stations. For Mizuho and Sakura, all trains stop at stations marked "●", while some trains stop at those marked "▲". All trains stop at Hakata, Kumamoto and Kagoshima-Chūō.
Legend:
| ● | All trains stop |
|---|---|
| ▲ | Some trains stop |
| | | All trains pass |
| Station | Japanese | Distance from Hakata (km) |
Distance from Shin-Ōsaka (km) |
Mizuho | Sakura | Tsubame | Transfers | Location | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kagoshima Route | ||||||||||
| Currently operational | ||||||||||
| ↑ Through services towards Shin-Ōsaka via the Sanyō Shinkansen[12] ↑ | ||||||||||
| Hakata | 博多 | 0.0 | 553.7 | ● | ● | ● | Hakata, Fukuoka City |
Fukuoka | ||
| Shin-Tosu | 新鳥栖 | 26.3 | 580.0 | | | ● | ● | Tosu | Saga | ||
| Kurume | 久留米 | 32.0 | 585.7 | ▲ | ● | ● | Kurume | Fukuoka | ||
| Chikugo-Funagoya | 筑後船小屋 | 47.9 | 601.6 | | | ▲ | ● |
|
Chikugo | ||
| Shin-Ōmuta | 新大牟田 | 59.7 | 613.4 | | | ▲ | ● | Ōmuta | |||
| Shin-Tamana | 新玉名 | 76.3 | 630.0 | | | ▲ | ● | Tamana | Kumamoto | ||
| Kumamoto | 熊本 | 98.2 | 651.9 | ● | ● | ● |
|
Nishi-ku, Kumamoto | ||
| Shin-Yatsushiro | 新八代 | 130.0 | 683.7 | | | ▲ | ● |
|
Yatsushiro | ||
| Shin-Minamata | 新水俣 | 172.8 | 726.5 | | | ▲ | ● | Minamata | |||
| Izumi | 出水 | 188.8 | 742.5 | | | ▲ | ● | Hisatsu Orange Railway Line | Izumi | Kagoshima | |
| Sendai | 川内 | 221.5 | 775.2 | ▲ | ● | ● |
|
Satsumasendai | ||
| Kagoshima-Chūō | 鹿児島中央 | 256.8 | 810.5 | ● | ● | ● |
|
Kagoshima | ||
Services
Kagoshima route
Services not leaving the Kyushu Shinkansen are operated by 6-car 800 Series trains, with a maximum speed of 260 km/h (160 mph).[7] The trains were developed by Hitachi, and based on the 700 series trains already in service on the Tokaido/Sanyo Shinkansen line.
8-car N700-7000 and N700-8000 series trains are used on through-running services between Shin-Osaka and Kagoshima-Chūō. The first set (S1) was delivered to Hakata Depot in October 2008.[13]
Three services operate on the line, in order of speed: Mizuho, Sakura, and Tsubame. The Mizuho makes two return trips between Shin-Osaka and Kagoshima-Chūō during the morning hours, and two return trips during the evening, with an end-to-end journey time of 3 hours 45 minutes. Sakura services run once per hour throughout the day between Shin-Osaka and Kagoshima-Chūō making additional stops, with an end-to-end travel time of 4 hours 10 minutes. There are also one to two Sakura services every hour between Hakata and either Kumamoto or Kagoshima-Chūō. Tsubame trains operate the all-stations shuttle service between Hakata and Kumamoto once to twice per hour, with some services operating to/from Kagoshima-Chūō.[14] Mizuho trains cannot be used by foreign passengers traveling with a Japan Rail Pass.
Nishi Kyushu route
Services are operated by 6-car N700S series trains with a service type named Kamome.[15]
Incidents
2016 Kumamoto earthquakes
On the evening of 14 April 2016, the entire length of the Kagoshima Route was shut down after the first of two powerful earthquakes struck Kumamoto prefecture. There was extensive damage along the route, including cracks in elevated support structures at 25 locations[16] and collapsed sound insulation walls in nearly 80 locations.[17]
An 800 series train was derailed near Kumamoto Station after the first tremor, while the train was deadheading. On 18 April, JR Kyushu began attempts to return the derailed train to the tracks.[16]
On 27 April 2016, the line reopened with reduced speed and service frequency.[18]
2021 Attempted arson
On the morning of 8 November 2021, a 69-year old man from Fukuoka attempted to set a Sakura Shinkansen service on fire.[19] The train, Sakura #401, was travelling between Kumamoto and Shin-Yatsuhiro stations at the time of the attempted arson. No casualties were reported. According to the perpetrator, the motive of the incident was to replicate the October 2021 Tokyo attack.
References
- ↑ 九州新幹線全線開通 博多-鹿児島中央 計画決定から38年 / 西日本新聞 [The entire Kyushu Shinkansen line opens Hakata-Kagoshima Chuo 38 years after the plan was decided]. nishinippon.co.jp (in Japanese). 13 March 2011. Archived from the original on 14 March 2011. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ↑ "Construction of new bullet train route starts in Kyushu : National : …". Daily Yomiuri Online. 18 February 2013. Archived from the original on 18 February 2013. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ↑ 建設計画・ルート [Construction plan / route] (in Japanese). Pref.nagasaki.jp. Archived from the original on 27 January 2012. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ↑ "Shorter N700S to serve Nagasaki". railwaygazette.com. 29 October 2020. Archived from the original on 1 November 2020. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ↑ 2022年度秋頃に西九州新幹線が開業します!列車名「かもめ」 [The West Kyushu Shinkansen will open in the fall of 2022! Train name "Kamome"]. jrkyushu.co.jp (in Japanese). Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ↑ "JR初の新型特急「783系」は型破りな異端児だった 「ハイパーサルーン」の愛称でJR九州の主力担う" [JR's first new limited express "783 series" is the mainstay of JR Kyushu under the nickname of "Hyper Saloon", which was an unconventional heretic.]. Toyokeizai Online (in Japanese). 30 July 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- 1 2 "300km/hのトップランナー" [300 km/h Top Runners]. Japan Railfan Magazine (in Japanese). Vol. 52, no. 612. Japan: Kōyūsha Co., Ltd. April 2012. p. 14.
- ↑ "Shinkansen spurs Kyushu Business". japantimes.co.jp. 13 March 2012. Archived from the original on 14 March 2012. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ↑ Tsuchiya, Ryō (12 September 2011), "南部好調、北部で苦戦 九州新幹線、全線開通から半年" 南部好調、北部で苦戦 九州新幹線、全線開通から半年, The Asahi Shimbun (in Japanese), archived from the original on 26 September 2011, retrieved 12 September 2011
- ↑ 九州新幹線長崎ルート [Kyushu Shinkansen Nagasaki route]. nagasaki-np.co.jp. 9 October 2007. Archived from the original on 1 February 2012. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ↑ 西九州新幹線の開業日について [About the opening date of the West Kyushu Shinkansen] (PDF). jrkyushu.co.jp (in Japanese). 2 February 2022. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 May 2022. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ↑ Only Mizuho and Sakura services run through to the Sanyō Shinkansen.
- ↑ 山陽・九州新幹線直通用車両 量産先行車 [Sanyo / Kyushu Shinkansen direct train vehicle mass production precedent vehicle] (in Japanese). Japan. 2008. pp. 64–67.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ↑ 平成23年春ダイヤ改正 (Press release) (in Japanese). JR Kyushu. 17 December 2010. Archived from the original on 20 December 2010. Retrieved 19 December 2010.
- ↑ 西九州新幹線の最高速度、開通後の時短効果は? もしかして料金が高くなってしまうのでは……? [What is the maximum speed of the West Kyushu Shinkansen and the time saving effect after opening? Maybe the price will be higher?]. nlab.itmedia.co.jp (in Japanese). 25 August 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- 1 2 "Pictures reveal serious damage to Shinkansen in Kyushu". asahi.com. The Asahi Shimbun. 18 April 2016. Archived from the original on 2 September 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ↑ "Reopening of Kyushu Shinkansen still a long way off". Mainichi Daily News. Mainichi Japan. 19 April 2016. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- ↑ "Kyushu Shinkansen resumes after quakes- News – NHK WORLD – English". NHK WORLD. NHK. Archived from the original on 30 April 2016. Retrieved 11 June 2022.
- ↑ "Man Arrested after Setting Fire on Kyushu Shinkansen Train". nippon.com. 8 November 2021. Retrieved 6 September 2022.
External links
- Official website (in Japanese)