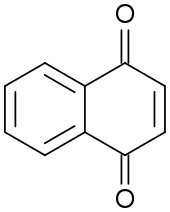
Chemical structure of 1,4-naphthoquinone
Naphthoquinones constitute a class of organic compounds structurally related to naphthalene. Two isomers are common for the parent naphthoquinones:
Natural products

Chemical structure of juglone, a compound produced by black walnut trees.
- Alkannin
- Hexahydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione
- Juglone
- Lapachol
- Lawsone
- Menatetrenone
- 2-Methoxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, a compound found in Impatiens species
- Nigrosporin B
- 2,3,5,6,8-Pentahydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione
- Phylloquinone
- Plumbagin
- 2,3,5,7-Tetrahydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione
- Vitamin K and related compounds
- Phylloquinone
- Vitamin K2
- Menadione (2-Methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone)
Synthetic naphthoquinones
- 5,8-Dihydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone and dihydroxynaphthoquinones
- Atovaquone
- Buparvaquone, an antiprotozoal drug used in veterinary medicine
- Diazonaphthoquinone, a diazo derivative of naphthoquinone
- 1,2-Naphthoquinone, from the biodegradation of naphthalene.
See also
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.