| Nezelof syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Thymic dysplasia with normal immunoglobulins[1]: 85 |
 | |
| Autosomal recessive is the manner in which this condition is inherited | |
| Specialty | Immunology |
| Symptoms | Hepatosplenomegaly[2] |
| Causes | Currently unknown[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Blood test[3][4] |
| Treatment | Antimicrobial therapy, IV immunoglobulin[5] |
Nezelof syndrome is an autosomal recessive[6] congenital immunodeficiency condition due to underdevelopment of the thymus. The defect is a type of purine nucleoside phosphorylase deficiency with inactive phosphorylase, this results in an accumulation of deoxy-GTP which inhibits ribonucleotide reductase. Ribonucleotide reductase catalyzes the formation of deoxyribonucleotides from ribonucleotides, thus, DNA replication is inhibited.
Symptoms and signs
This condition causes severe infections. it is characterized by elevated immunoglobulins that function poorly.[7][8] Other symptoms are:[2]
Cause
Genetically speaking, Nezelof syndrome is autosomal recessive. the condition is thought to be a variation of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID).[8] However, the precise cause of Nezelof syndrome remains uncertain[3]
Mechanism
In the mechanism of this condition, one first finds that the normal function of the thymus has it being important in T-cell development and release into the body's blood circulation[9] Hassal's corpuscles[10] absence in thymus(atrophy) has an effect on T-cells.[3]
Diagnosis
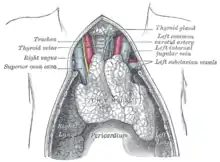
The diagnosis of Nezelof syndrome will indicate a deficiency of T-cells,[11] additionally in ascertaining the condition the following is done:[3][4]
- Blood test (B-cells will be normal)
- X-ray of thymus (atrophy present)
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for this condition consists of acquired immune deficiency syndrome and severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome[3][8]
Treatment
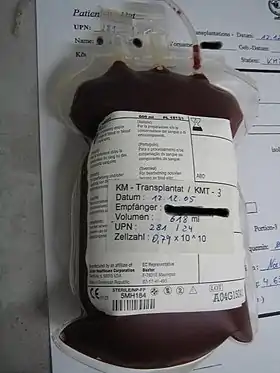
In terms of treatment for individuals with Nezelof syndrome, which was first characterized in 1964,[12] includes the following(how effective bone marrow transplant is uncertain[4]) :
See also
References
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
- 1 2 "Immune defect due to absence of thymus | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Retrieved 2017-06-02.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Lavini, Corrado; Moran, Cesar A.; Uliano, Morandi; Schoenhuber, Rudolf (2009). Thymus Gland Pathology: Clinical, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Features. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 35 & 22. ISBN 9788847008281. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- 1 2 3 Mosby (2016-04-28). Mosby's Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing & Health Professions - eBook. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1226. ISBN 9780323414197.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Smeltzer, Suzanne C. O'Connell; Bare, Brenda G.; Hinkle, Janice L.; Cheever, Kerry H. (2010). Brunner & Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-surgical Nursing (12 ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 1563. ISBN 9780781785891. Retrieved 6 June 2017.
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 242700
- ↑ Cantani, Arnaldo (2008-01-23). Pediatric Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 1298. ISBN 9783540333951.
- 1 2 3 Disorders, National Organization for Rare (2003). NORD Guide to Rare Disorders. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 408. ISBN 9780781730631.
- ↑ Pearse, Gail (2006-08-01). "Normal Structure, Function and Histology of the Thymus". Toxicologic Pathology. 34 (5): 504–514. doi:10.1080/01926230600865549. ISSN 0192-6233. PMID 17067941.
- ↑ Kierszenbaum, Abraham L.; Tres, Laura (2015-05-04). Histology and Cell Biology: An Introduction to Pathology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 339. ISBN 9780323313353.
- ↑ Wallach, Jacques Burton (2007). Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 504. ISBN 9780781730556.
Nezelof syndrome diagnosis.
- ↑ Nezelof, C.; Jammet, M. L.; Lortholary, P.; Labrune, B.; Lamy, M. (October 1964). "Hereditary Thymic Hypoplasia: ITS Place and Responsibility in a Case of Lymphocytic, Normoplasmocytic and Normoglobulinemic Aplasia in an Infant". Archives Françaises de Pédiatrie. 21: 897–920. ISSN 0003-9764. PMID 14195287.
Further reading
- Lavini, Corrado; Moran, Cesar A.; Uliano, Morandi; Schoenhuber, Rudolf (2009-05-08). Thymus Gland Pathology: Clinical, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Features. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9788847008281.