Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Charge-neutral
- Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2), nitrogen(IV) oxide
- Nitrogen trioxide (NO3), or nitrate radical
- Nitrous oxide (N2O), nitrogen(0,II) oxide
- Dinitrogen dioxide (N2O2), nitrogen(II) oxide dimer
- Dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3), nitrogen(II,IV) oxide
- Dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4), nitrogen(IV) oxide dimer
- Dinitrogen pentoxide (N2O5), nitrogen(V) oxide, or nitronium nitrate [NO2]+[NO3]−
- Nitrosyl azide (N4O), nitrogen(−I,0,I,II) oxide
- Nitryl azide (N4O2)
- Oxatetrazole (N4O)
- Trinitramide (N(NO2)3 or N4O6), nitrogen(0,IV) oxide
Anions
| Name | Formula |
|---|---|
| Nitroxide | O=N− |
| Nitrite | O=N−O− or NO−2 |
| Nitrate | NO−3 |
| Peroxynitrite | O=N−O−O− or NO−3 |
| Peroxynitrate | O2N−O−O− or NO−4 |
| Orthonitrate | NO3−4, analogous to phosphate PO3−4 |
| Hyponitrite | −O−N=N−O− or N2O2−2 |
| Trioxodinitrate or hyponitrate | [O2NNO]2− or [N2O3]2− |
| Nitroxylate | (−O−)2N−N(−O−)2 or N2O4−4 |
| Dinitramide | O2N−N−−NO2 or N3O−4 |
Cations
- Nitrosonium (N≡O+ or [NO]+)
- Nitronium (O=N+=O or [NO2]+)
Atmospheric sciences
- NOx (or NOx) refers to the sum of NO and NO2.[1][2]
- NOy (or NOy) refers to the sum of NOx and all oxidized atmospheric odd-nitrogen species (e.g. the sum of NOx, HNO3, HNO2, etc.)
- NOz (or NOz) = NOy − NOx
- Mixed Oxides of Nitrogen ("MON"): solutions of nitric oxide in dinitrogen tetroxide/nitrogen dioxide.
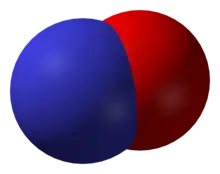 Nitric oxide, NO
Nitric oxide, NO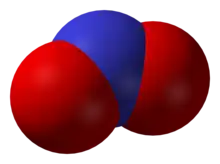 Nitrogen dioxide, NO2
Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 Nitrous oxide, N2O
Nitrous oxide, N2O Dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3
Dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3 Dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4
Dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O4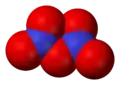 Dinitrogen pentoxide, N2O5
Dinitrogen pentoxide, N2O5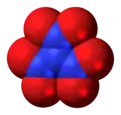 Trinitramide, N4O6
Trinitramide, N4O6
Stability
Due to relatively weak N–O bonding, all nitrogen oxides are unstable with respect to N2 and O2, which is the principle behind the catalytic converter, and prevents the oxygen and nitrogen in the atmosphere from combusting.
See also
- Nitrate
- Nitrogen oxide sensor
- Sulfur nitrides, which are valence isoelectronic with nitrogen oxides
References
- ↑ United States Clean Air Act, 42 U.S.C. § 7602
- ↑ Seinfeld, John H.; Pandis, Spyros N. (1997), Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, Wiley-Interscience, ISBN 0-471-17816-0
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.