| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N,N-Dinitronitramide | |||
| Other names
Trinitroamine | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| N4O6 | |||
| Molar mass | 152.022 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
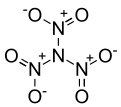
Trinitramide is a compound of nitrogen and oxygen with the molecular formula N(NO2)3. The compound was detected and described in 2010 by researchers at the Royal Institute of Technology (KTH) in Sweden.[1] It is made of a nitrogen atom bonded to three nitro groups(-NO2).
Earlier, there had been speculation whether trinitramide could exist. Theoretical calculations by Montgomery and Michels in 1993 showed that the compound was likely to be stable.[2]
Preparation
Trinitramide is prepared by the nitration reaction of either potassium dinitramide or ammonium dinitramide with nitronium tetrafluoroborate in acetonitrile at low temperatures.[1]
- NH4N(NO2)2 + NO2BF4 → N(NO2)3 + NH4BF4
Uses
Trinitramide has a potential use as one of the most efficient and least polluting of rocket propellant oxidizers, as it is chlorine-free.[3] This is potentially an important development, because the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation implies that even small improvements in specific impulse yields a similar change in delta-v, which can make large improvements in the size of practical rocket launch payloads. The density impulse (impulse per volume) of a trinitramide based propellant could be 20 to 30 per cent better than most existing formulations,[4] however the specific impulse (impulse per mass) of formulations with liquid oxygen is higher.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 Rahm Martin (2010). "Experimental Detection of Trinitramide, N(NO2)3". Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 50 (5): 1145–1148. doi:10.1002/anie.201007047. PMID 21268214. S2CID 32952729.
- ↑ J. A. Montgomery Jr. & H. H. Michels (July 1993). "Structure and stability of trinitramide". Journal of Physical Chemistry. 97 (26): 6774–6775. doi:10.1021/j100128a005.
- ↑ Discovery of New Molecule Could Lead to More Efficient Rocket Fuel, Science Daily, 2010-12-22, accessed 2011-01-03.
- ↑ "New molecule could propel rockets".