 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
nitronium fluoroborate, NO 2BF 4 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.107 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BNO2F4 | |
| Molar mass | 132.81 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
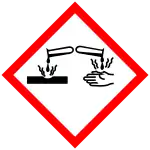   | |
| Danger | |
| H314, H317, H334 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P272, P280, P285, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P304+P341, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P333+P313, P342+P311, P363, P405, P501 | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations |
Nitrosonium tetrafluoroborate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
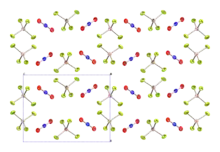
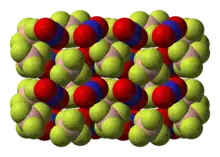
Nitronium tetrafluoroborate is an inorganic compound with formula NO2BF4. It is a salt of nitronium cation and tetrafluoroborate anion. It is a colorless crystalline solid, which reacts with water to form the corrosive acids HF and HNO3. As such, it must be handled under water-free conditions. It is sparsely soluble in many organic solvents.
Preparation
Nitronium tetrafluoroborate can be prepared by adding a mixture of anhydrous hydrogen fluoride and boron trifluoride to a nitromethane solution of nitric acid or dinitrogen pentoxide.[1]
Applications
Nitronium tetrafluoroborate is used as a nitration agent.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.