Placenames in Normandy have a variety of origins. Some belong to the common heritage of the Langue d'oïl extension zone in northern France and Belgium; this is called "Pre-Normanic". Others contain Old Norse and Old English male names and toponymic appellatives. These intermingle with Romance male names and place-name elements to create a very specific superstratum, typical of Normandy within the extension zone of the Langue d'oïl. These are sometimes called "Normanic".[1]
Pre-Normanic placenames
There are still a significant number of Celtic (Gaulish) names, as there are throughout France and western Europe. These names, partly mixed with Latin elements, follow the Late Latin phonetic changes that led to Langue d'oïl.
Traditional large cities
Almost all the main cities kept a Romanized Celtic name, that produced the modern toponym.
BC era
- Rouen: from the Gallo-Romance ROTOMAGU (Latin Rotomagus),[2] in turn from the Gaulish Ratumacos (sometimes Ratómagos, on the coins of the Veliocassi tribe). The first part of the name might refer to roto-, the word for "wheel" or "race", cf. Old Irish roth or Welsh rhod ("wheel" or "race"). The meaning of the second part, Magos, is much clearer: "field", "plain", or later "market" cf. Old Irish mag (gen. maige), meaning "field" or "plain"; Old Breton ma, meaning "place". Taken together, the whole could mean "hippodrome", "racecourse", or "wheel market".[3]
- Caen: probably *Catumagus, from the Old Celtic catu-, meaning "battle", "fight", or "combat"; or the Old Irish cath (gen. catho), meaning "combat", "battalion", or "troop"; the Breton -kad /-gad and the Welsh cad, both meaning "combat" or "troop". As a whole, the name could mean "battlefield".
- Carentan: attested as Carentomagus.[4]
- Vernon: probably *Vernomagus,[5] meaning "plain of the alder-trees", derived from uernā, meaning "alder-tree"; or, in Old Irish, fern; and in Breton and Welsh, gwern.
AD era
In the following examples, a Gaulish toponym was replaced by the name of the local tribe, according to a process well known in the later Roman Empire:
- Bayeux: rooted in the civitas named Bajocassensis; which was formerly known as Augustodurum, meaning "forum dedicated to Augustus".
- Evreux: rooted in the civitas named Eburovicensis, formerly known as Mediolanum.
- Lisieux: rooted in the civitas named Lexoviensis, formerly known as Noviomagus,[6] meaning "new market", from the Old Celtic noviios, meaning "new".
- Avranches: rooted in the civitas named Abrincatii; formerly known as Ingena or Legedia.
There were exceptions to this practice, such as:
- Coutances: derived from Constantia, meaning "dedicated to Emperor Constantius Chlorus".
- Lillebonne: derived from Juliobona, where Julio meant "dedicated to Julius", and bona, from the Old Celtic, meant "foundation" or "spring". (Also see Ratisbona or Vindobona).
Some of these would disappear later, replaced by Normanic names; thus Coriovallum became Cherbourg and Caracotinum became Harfleur. Such changes indicate that the older inhabitants who used the earlier name were displaced by newcomers, either leaving completely or becoming a small minority.
Some cities' Pre-Normanic names are not known, such as Honfleur or Dieppe.
Common northern French toponymic types
The most common suffix in northern France is -acum (written -acum, -acus or -aco in early Medieval Latin documents, pronounced in Vulgar Latin as -acu), that means "place of" or "property". Its origin is the Celtic -āko(n). Originally, it was used to as the location of either a god or a people. Examples include Anualonacu, meaning "sanctuary of Anualō [a god]" and nautae Parisiaci, meaning "sailors of the Parisii [tribe]".[7]
In northern France and southern Belgium, –(i)acum became -ay, -ai, -ey, -é or -y. All of these variations are found in Normandy. Places with this suffix include Gournay, Bernay, Cernay, and Andilly.
Another, generally later, variation is composed of masculine names that can be either Gaulish or Latin, for example: Massy from Gaulish Mascius; Marcilly from Roman Marcellus; Fleury from Roman Florius; and Montigny from Roman Montanius.
However, the latest -acum formations are combined with a Christian or a Germanic masculine name, such as Repentigny, from the Christian name Repentin(i)us or with a Romance placename element. The most common -acum place-name in Normandy is Glatigny, of which more than 40 exist.
Romance place-name elements
These come from the Vulgar Latin, but began only about 100 years after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, in the 6th century AD. In this province, it is sometimes difficult to know if these formations (-ville, -val, -mont, -mesnil, etc.) are Pre-Normanic or Normanic, due to similarities between the two.
The main romance appellatives are the following:
- -ville or Ville-, meaning "farm", and later "village"
- -court, Cour-, or Cor-, meaning "farm with a courtyard"
- -val or Val-, meaning "small valley"
- -mont or Mont-, meaning "hill"
- -mesnil, -menil or Mesnil-, meaning "property"
General description
In Northern France, including Normandy, the extension of -court, -ville, and -mesnil (including its variant spellings -maisnil and -ménil) corresponds generally to Frankish and other Germanic settlements. This is the most likely reason why the common word order is also from the Germanic: determinative (adjective, appellative or owner's name) plus determined (romance element). Examples include: Neuville, meaning "new village"; Bourville (Bodardi villa, 8th century) meaning "Bodard's farm"; Harcourt (Herolcurt, 11th century) meaning "Herulf's farm"; and Attemesnil (Ademesnil, 13th century) meaning "Adda's property".[8] Less than one-third of France, the north, makes use of the Germanic ordering.
In Vulgar Latin, as in Celtic, the opposite word order prevailed: determined (Romance appellative) plus determinative (adjective). This order dominates in Occitan toponymy, as well as in western France.[9] Instead of Neuville, in the south we find Villeneuve, derived either from Occitan, Vielanova, or from a more modern name.
Similarly, northern Neuchâtel, Neufchâtel,[10] or Neufchâteau, meaning "new castle", corresponding to southern Châteauneuf or Châtelneuf, a translation of Castelnau in Occitan.[11]
Local specificity
In the Norman toponymy, the most widespread appellative is -ville or Ville-, with an estimated 20% of the French communes of Normandy containing this appellative. The oldest recorded instance is Bourville, as Bodardi villa in 715.[12] This is in contrast to the much less frequently used -court, which was not used anymore in the Viking Age.
The most widely used -ville toponyms are combined with either an Old Scandinavian or Anglo-Scandinavian male name or a Romance adjective: Amfreville (Ásfríðr′s farm), Auzouville (Osulf / Osolf′s farm), Beuzeville (Bosi′s farm), Colleville (Kolli′s farm), Épreville (*Sproti′s farm, cf. Faroese Sproti), Sotteville (Sóti′s farm), Tocqueville (Tóki′s farm), Touffreville (Þórfríðr′s farm), Tourville (Þórr's farm), Trouville (Thorold's farm), Grainville (Grímr / GrímR's farm), Bretteville (Briton's farm) and Englesqueville or Anglesqueville (English farm).[13] These toponyms do not exist in France outside of Normandy, because their first element is an Old Scandinavian or an Old Anglo-Scandinavian personal name and sometimes a romance adjective marking they came from Great-Britain, but were mainly Anglo-Scandinavian farmers. In addition some typical Gaelic male′s names can be found in Doncanville (Donnchadh> Duncan′s farm), Quinéville or Quenneville (Cináed > Kenneth′s farm), Néville (Niall > Njáll′s farm).
The -court appellative is usually combined with either a Germanic masculine name, as in Hébécourt, from Herbert > Norman-French Hebert (today the surname Hébert), as in Sébécourt, from Sigebert > Sebert (today the surname Sébert).[14] It almost never appears as a suffix in the western part of Normandy, but as a prefix (Cour-, Gour-, Col-, Coul-): Gourfaleur from falor, the name of a people; Coulvain, meaning "Laipwin's court"; and Coulimer, meaning "Lietmar's court".[15] François de Beaurepaire observed that -court and Cour- were never used with an Anglo-Scandinavian male's name or element.[16]
Another common appellative is -mesnil or Mesnil- (written as ménil in the Orne département). They are mainly combined with masculine anthroponyms as in Aubermesnil or Avremesnil, much like the -ville place-names, and were later built according to the Romance order, for example Mesnil-Hermant and Mesnil-Esnard.[17]
The appellative -bosc or Bosc- (pronounced [bo:] or [bɔk]), meaning "wood", corresponds to the French word bois, and is specific to this Province. In Normandy, it is usually combined with a masculine name: Auberbosc and Colbosc, when following the Germanic order; while the later Romance order gives numerous examples, such as Bosc-Roger, Bosc-Renoult, and Bosc-Robert.[18]
-vast is the only one that never appears as *Vast-, but autonomous as le Vast. The first element must be a personal name, like Gallo-Romance Martin in Martinvast, Old Norse Sóti in Sottevast (Sotewast, 12th century), and Old Norse Tóli in Tollevast (Toberwast and Tolewast, 12th century).[19] Véraval, now often misspelled as Ver-à-Val, became a -val ("valley") place-name by popular etymology. First recorded as Warelwast in 1024 (see William de Warelwast), utilizing the former appellative, -wast (meaning "bad land", or "unfertile or uncultivated land"),[20] which is now spelled -vast in the north and ga(s)t(te) in the south.[21] Its etymology is ultimately Latin vastus "bad land" mixed up with Old Low Franconian *wost "desert" (Old High German wuosti, Old English wēste).
Normanic place names
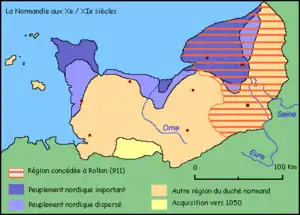
Description
Old Norse place names were given during the Norse settlement at the end of the ninth century, expanding in the tenth century with the creation of the Duchy of Normandy by Rollo in 911. Since the speakers of Old Norse were linguistically assimilated into the Old French dialect society within a few generations, these settlement names were given most likely date prior to the 11th century. Most of these settlers were coming from areas that are today most likely Danish and/or Norwegian. These languages were quite similar to each other, making it difficult to distinguish the origin of the appellatives and accompanying adjective or male name.[22]
Old Norse and Old English appellatives
- Acre, -acre "field" > "surface measure" (Norman acre) : Old Norse akr (Icelandic akur "field"). in Herboutacre, hamlet at Grainville-Ymauville (De campo Herboutacre 1209). First element Herbout- represents probably the Germanic personal name Herbold now found as patronymic as Herbout in pays de Caux (Valliquerville, etc.); Fouquelacre (Dieppe, Fulconis Acra 1244); l'Acre-Guérard (Saint-Valéry-en-Caux)
- Bec- or -bec, derived from beck, meaning "stream" or "brook". It can also be found alone as in, le Bec. Examples of its combination with an adjective would be: Houlbec, meaning "hollow beck"; Foulbec, meaning "dirty beck"; and Caudebec 'cold beck' (Caldebec, 11th century), etc.[23][24][25]
- -beuf or Boos, from Old Norse búð > Old Eastern Norse bóð and Old English bōth > English booth, meaning "booth, shed". Examples are: Elbeuf-sur-Andelle, Elbeuf (Seine-Maritime, Wellebuot 1070–1081), Criquebeuf-en-Caux, Lindebeuf (Seine-Maritime, Lindebeod 1142), and Boos (Seine-Maritime, Bodas 1030–1040, Bothas ab 1049) -similar to Booths, Yorkshire-, Daubeuf-la-Campagne (Eure, Dalbuoth 1011).[26][27] Two cases at least are doubtful: Criquebeuf-la-Campagne (Eure, Crichebu 1203) and Carquebut, which probably derive not from Old Eastern Norse bóð but from the Old Norse bú.[28] Sometimes -beuf has been misspelled -bœuf, meaning "ox" in French, as in Cricquebœuf (Calvados, Crikeboe 1198).[29] The other -bœuf place-names throughout France refer to "ox", and clearly allude to slaughterhouses, such as Écorchebœuf ("flay-ox"), Tubœuf ("kill-ox") or Tombebœuf ("fall-ox"). The -beuf, -bu, -bot element corresponds to the place-names ending with -by in Great Britain (though some of these may have influence from Norse byr). It explains the existence of parallel formations on both sides of the English Channel:[30]
| Normandy | Great Britain |
|---|---|
| Elbeuf (*Wellabóð) | Welby |
| Criquebeuf (*Kirkjubóð) | Kirkby |
| Daubeuf (*Dalbóð) | Dalby |
| Ribeuf (*Hrisbóð) | Risby |
A similar use can be found in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany : Haddeby (Hadæboth 1285).[31]
- Bre(c)q- or -bre(c)que (sometimes Bricque-), from the Old Norse brekka, meaning "slope", "incline", or "hill". Found in the following place-names: Houllebrecque in (Saint-Aubin-de-Crétot), Brecqhou (England : Norbreck, Warbreck, and Scarisbrick).[32][33]
- -cher or -quier, from the Old Norse kjarr meaning "marsh" or "swamp", which can be found in Villequier (combined with the Old English wiliġ, meaning "willow") and Orcher (Alrecher, 11th century, combined with the Old English alor, aler, meaning "alder").[34][35]
- -clives, -lif, Clé- or Cli-, from the Old Norse klif or Old English clif, meaning "cliff".[36][37][38] Examples of which are: Risleclif, Witeclif (now Côte-Blanche "white cliff" at Évreux), Verclives, Clitourps, Cléville, Carquelif, and Clairefougère (Clivefeugeriam, 12th century).[39]
- Crique- or -crique, from the Old Norse kirkja, meaning "church", but this should not be confused with the French term, la crique from Old Norse kriki, "creek". Examples of this appellative are la Crique, Criquetot-l'Esneval, Criquetot-le-Mauconduit or Yvecrique.[40]
- Dalle-, -dalle, -dal, or Dau-, from the Old Norse dalr, meaning "valley", or the Old English dæl, meaning "dale". It can be seen on its own with a romance article as in la Dalle or Le Dallet; or in combination with an adjective, as in Dieppedalle (with the Old Norse djupr[41][42][43] or Old English dēop, meaning "deep"[44]), Croixdalle (with the Old English crāwe, meaning "crow"), and Oudalle (from the Norman ouf, meaning "wolf").
- Escalle or -écal-, from either the Old Norse skali or Old English scale, meaning "shelter". Examples would be Touffrécal, Brecquécal, Écalles-Alix (Escales, 12th century), and Villers-Écalles (Escalis, 12th century).[45][46][47]
- Étain-, Étan- or Étenne-, from the Old Norse steinn or Old English stān, meaning "stone". Examples would be: Grestain (combined with the Old English grēat, meaning "big"),[48] Étainhus (Stone house), Étaintot, Étheintot, Étalondes, and Étangval (Stone valley).
- -gard, from the Old Norse garðr, meaning "yard" or "garden", found in the names: Auppegard (Appelgart ab. 1160) combined with æppel, meaning "apple") and Figard (Figart 1238, combined with fiskr, meaning "fish").[49]
- -gate or -gathe, meaning "way", as in Houlgate, la Houlgate, Hôrgate (meaning "hollow way"), Hiégathe, etc.[50][51]
- Hague, -hague, from the Old Norse or Old English haga, meaning "enclosure". Examples are: la Hague, le Tohague, Étauhague, and le Haguedic (combined with the Anglo-Norse dik).[52][53]
- Hogue or Hougue from the Old Norse haugr, meaning "hill", found in names like Les Hogues, Saint-Vaast-la-Hougue, and la Hougue-Bie (Jersey).[54][55][56]
- Houlme, Hom(me) or -homme, from the Old Norse word holmr, meaning "islet". The appellative, homme, is identical to the French word meaning, "man", but is pronounced differently: French [ɔm] (l'homme) versus Norman [χɔm] or [hɔm] (le homme). It is found in place-names such as Le Houlme, Robehomme, Saint-Quentin-sur-le-Homme, and les Échommes.[57][58][59]
- -hus or -hurs from the Old Norse hús or Old English hūs, meaning "house". As found in: Sahurs (Salhus ab 1024, maybe from Sálúhús "kind of inn" like Salhus (disambiguation), Norway) and Étainhus (″stone house″).[60][61][62]
- Londe, -lon or -ron, from the Old Norman londe, meaning "forest" or "wood". There are over 45 municipalities and hamlets named La Londe in Normandy, as well as several Les Londes (plural). It is also used in combination with other adjectives, such as Bouquelon (Eure, Buculun ab 1040), Bois de Boclon (Seine-Maritime, Bocolunda silva 1032), la Bouquelonde, combined with bók(i), meaning "beech tree"; Yquelon, Yclon (Seine-Maritime, Iquelont 1404), Iclon (Seine-Maritime, Ichelunt 1088) combined with eik(i), meaning "oak tree"; Écaquelon (Eure, Schacherlon 1174), Écaquelon (Eure, Escakerlon 1169), combined with the Old English sċeaċere, meaning "thief" or "brigand"; Catelonde (Calvados, Cathelunde 12th century) with personal name Káti; Yébleron (Seine-Maritime, Eblelont ab 1210); Ablon (Calvados, Eblelont w. d.) with epli "apple".[63][64][65]
- Thuit or -tuit, from the Old Norse thveit, meaning "assart", English Thwaite (placename element). Several le Thuit exist, as well as other combined examples, such as Bracquetuit, Vautuit, and Bliquetuit.[66][67][68]
- Torp, Torps, Tourp, Tourps, -tourp or -tour, from the Old Norse torp or the Old English thorp, meaning "settlement". There are several stand alone towns named either Torps or le Torp. Other examples are: le Torp-Mesnil, Clitourps, Saussetour (Sauxetorp end 12th century), Sauxtour (Sauxetourp 1292), similar as Saustrup (Schleswig-Holstein, Saxtorppe, 15th century[69]), meaning "Saxi's Torp".[70][71][72]
- Tot or -tot, meaning "property", is the most common suffix of Old Norse origin, with more than 300 locations ending with -tot in Normandy. It is derived from the Old Norse topt (similar to the Old English toft, and Old Danish -toft[e]), meaning "site of a house". In later usages of the 11th century, it can also be found alone as in, le Tot. It can be combined with a male name, as in Yvetot, Routot, Martintot or Létantot, (respectively Yvo (Germanic), Hrolfr (Norse), Martin (Romance) and Lestan (Anglo-Saxon)); or a tree-name, as in Bouquetot (from boki, meaning "beech-tree"), and Ectot or Ecquetot (from eski, meaning "ash-tree") and Plumetot (from Old English plūme "plum tree"); or with another appellative or adjective, examples of which would be Martot (from marr or mere, meaning "pond"), Életot (from sletta, meaning "flat land"), and Hautot, Hottot or Hotot (from the Old English hōh, meaning "slope" or "incline").[73][74][75]
- Veules or El-, from the Old Norse vella or OE wella, meaning "spring" or "stream", which can be found in place-names such as: Veules-les-Roses (Seine-Maritime, Wellas 1025), Elbeuf (Wellebuoth 1070–1081), Elbeuf-sur-Andelle, and Elbeuf-en-Bray.[76][77][78]
- -vic or -vy, meaning "bay" or "beach", as in: le Vicq (Manche), Sanvic (Seine-Maritime, Sanwic 1035) see Sandwich or Sandvik, Brévy (Manche, see Breivik, Breidvik, and Breivika), Vasouy (Calvados, Wasewic w. d.), Cap-Lévi (Kapelwic 12th century).[79][80][81]
Old English appellatives
Old English appellatives:[82][83][84]
- -bourg or -bury, meaning "borough": Cabourg, Wambourg, and Cherbourg.
- Bruque- or -broc, from brōc, meaning brook: le Fouillebroc (recorded as Fulebroc in the Domesday book), and Bruquedalle.[85][86][87]
- -crot, -croc or -crocq, meaning croft: Vannecrocq and Bec-de-Croc. The difference in spelling with either a -c or a -cq is the result of confusion with the French croc, meaning "fang" or "tooth".[88][89][90]
- -fleur, from either flōd or flēot, meaning "run of water" or "river going into the sea": Honfleur, Barfleur, Harfleur, Vittefleur, Crémanfleur, Vicqfleur, and la Gerfleur.[91][92][93] This appellative is similar to -fleet found in place-names in the North of England, such as Adingfleet, Marfleet, and Ousefleet.
- -ham, meaning "home": Ouistreham, Étréham, and le Ham.
- -land or -lan, meaning land: Heuland and Ételan.[94][95][96]
Old Norse masculine names
Old Norse -i names
The names in parentheses are the earlier forms of the place-names, with the century in which they appeared.
- Ámundi or Old Danish Amundi:[97] Émondeville, Mondeville[98][99][100] and probably Amontot
- Agi or Old Danish Aghi:[101] Acqueville[102][103]
- Áki or Old Danish Aki:[104] Achelunda and Acqueville[105][106]
- Api:[107] Aptot, Aptuit, Appeville, Appeville-Annebault, Appeville (Denmark : Aptrup)[108][109]
- Baggi:La Baguelande (Bagalunda and Baguelonde, 13th century)[110]
- Barki (or Barkr) in Berquetot (Yébleron, Berketot 12th). In Normandy [a] tends regularly to [e] before [r] cf. French argent > Norman ergent
- Barni: Barneville-sur-Seine and Barneville-Carteret[111][112][113]
- Bondi: Notre-Dame-de-Bondeville, Sainte-Hélène-Bondeville and Bonderup[114][115][116]
- Bosi: Beuzeville, Beuzeville-la-Grenier (Boseville, 12th century), Beuzebosc, Beuzemouchel, and Beuzeval (This appellative is sometimes confused with the Frankish name Boso)[117]
- Bóli (Old Danish Bole) : Bolbec, Bolleville, and Boulleville
- Bolli, other possibility, for Bolbec / Bolleville et Boulleville
- Bulli (variant form of Bolli) in Bultot (Seine-Maritime, Buletot 1236; Bulletot 1412) et Bolleville (Seine-Maritime, Bullevilla ab 1025)
- Brámi or Bráma : Brametot (Bramatot ab 1025)
- Brandi (or Old Danish Brande) : Branville (Calvados, Dozulé, hamlet), former Brandeville like Brandeville (Seine-Maritime, Vattetot-sur-Mer).
- Galli : Galleville (Seine-Maritime) et Fontaine Galleville (Calvados)
- Geiri / GæiRi : Gerville (Criquetot-le-Mauconduit, Geyrivilla ab 1040)
- Geri (Old Danish variant form of Geiri) in Gerville-la-Forêt (Manche, Gerivilla 1080) et Gréville-Hague better than West Germanic Gero
- Ginni in Gennetot et Genetot (hamlet at Hautot-Saint-Sulpice). cf. Domesday Book : Ghinius, Genius. cf. Gintoft (Germany, Schleswig-Holstein)
- Goti in Gauville (Seine-Maritime, Got villa 1025–1026; Gothvilla 1074)
- Gulli: from the Old Swedish Golle: Golleville
- Hnakki (or Old Danish Nakke) : Urville-Nacqueville (Nakevilla 1148)
- Hófi / Hofi or Old Danish Hovi in le Navetot (Hovetot 1077)
- Helgi: Heuqueville (Heuguevilla, 12th century), Heugueville-sur-Sienne (Helgevilla, 12th century), Heugon
- Hnakki: Urville-Nacqueville (Nakevilla, c. 12th century), Necqueville
- Holti: Houtteville (Hultivilla and Holtavilla, 11th century)
- Hunni or Húni: Honfleur (Hunefleth and Hunefloth, 11th century), Honneville, and Honaville
- Kappi, meaning "warrior": Wanchy-Capval (Capeval, 12th century), Captot at Étoutteville
- Kari: Cartot, Carbec-Grestain (Carebec, 12th century), Carville, Carville-la-Folletière, (Carevilla, 13th century)
- Karli: Cailletot, Calletot, Caltot, and Calleville-les-Deux-Églises (Carlevilla, 12th century)
- Kati: Catelon and Catteville
- Kǣrandi: Carneville (Chernetvilla, Carnanvilla and Kiernevilla, 12th century)
- Knapi: Canapville (Kenapevilla, 12th century), Canappeville
- Koli: Colletot, Colleville, Colmesnil, and Colbosc
- Korni: Cornemare, Corneville-la-Fouquetière, and Corneville-sur-Risle
- Malti: Motteville (Maltevilla, 11th century), Mautheville (Mautevilla, 12th century)
- Múli or Muli, meaning "muzzle", "mouth", or "mountain spur": Le Mulambec and Muneville-le-Bingard
- Ottar (Old Danish): Octeville (Otteville, 12th century), Octeville-l'Avenel (Otheville, 13th century), and Octeville-sur-Mer
- Rúmfari: Saint-Romphaire
- Rúni or Runi (Old Danish): Runetot and Runeville, Reigneville-Bocage (Runevilla, 12th century)
- Saxi: Saussetour (Sauxetorp, 12th century), Sauxtour (Sauxetourp, 13th century), Sassetot-le-Mauconduit, Sasseville, and Saussemesnil
- Sibbi (the Old Danish diminutive for Sighbiorn): Sébeville (Sebevilla, 12th century)
- Silli or Sild(i): Cidetot (Silletot, 12th century), Silleron, Sideville (Sildeville, 13th century)
- Skalli, meaning "bald head": Écausseville (Escaullevilla or Escallevilla, 12th century), Écolleville (from Escauleville, 15th century)
- Skeggi: Ecuquetot (Eskeketot, 13th century) and Equiqueville (Schechevilla, 12th century)
- Skrauti: Écretteville-lès-Baons (Scrotivilla, 11th century) and Écretteville-sur-Mer (Escrutevilleta, 13th century)
- Skúli or Skuli (Old Danish): Écultot (Esculetot, 13th century) and Éculleville (Esculleville, 16th century)
- Soti: Sottevast, Sotteville-les-Rouen (Sotavilla, 11th century), Sotteville-sous-le-Val (Sotevilla, 11th century)
- Stáli or Stali (Old Danish): Etalleville (Stalavilla, 12th century)
- Svarti: Surville (Souarville and Soarvilla, 13th century)
- Svarthofdi: Surtauville (Sortovilla, 13th century) and Sortosville
- Toki: Tocqueville (Tokevilla, 11th century), Tocqueville-sur-Eu (Toche villa, 11th century)
- Tofi: Le Mesnil-Tove
- Tommi or Tummi: Tonneville (Tommevilla or Thommevilla, 13th century),
- Thori: Tourville
- Vakri (ou Vakr) dans Vacqueville [?], hamlet at Vierville-sur-Mer. Compare with Blacqueville for the phonetics Vakr- > Vacque- similar to Blakkr > Blacque- Blac(h)revilla 11th century). Vacqueville (Meurthe-et-Moselle, Episcopi villa, Vaskeville, Vesqueville) has another etymology and means "farm, village of the bishop"
- Vígi (or VígR) or better, variant Old Danish form Wigh : Prétot-Vicquemare (Wiguemare, 13th century), Victot-Pontfol (Wigetot, 12th century)[118][119][120] cf. Wigtoft (GB, Lincolnshire)
- Wari (Old Danish) or Varr in Varaville (Waravilla 1155); Varreville (Neuilly, Calvados, Varvilla 1294)
- Viði or Old Danish Withi dans Vitot (Witot 1035–1047)
Old Norse simple and combined names
Old Norse simple and combined names:[121][122][123]
- Arnketill: Saint-Pierre-d'Arthéglise (Sancti Petri de Archetiglise, 12th century)
- Ásbjǫrn or Ásbiǫrn: Auzouville-Auberbosc (Osber boscus, 12th century), Aubermesnil-Beaumais (Osberni mesnil, 11th century), Auberville-la-Manuel (Osberni villa, 11th century)
- Ásgautr: Angoville
- Ásfriðr: Amfreville (Ansfrevilla 12th century), Amfreville-les-Champs (Anfridivilla, 11th century), Amfreville-la-Campagne (Ansfredville, 11th century)
- Ásketill: Anquetot, Ancteville (Ansketevilla, 12th century), Anctoville-sur-Boscq (Anschitilvilla, 12th century), Ancourteville-sur-Héricourt (Anschetilvilla, 11th century), Ancretteville-sur-Mer (Anschetevilla, 12th century)
- Ásleikr: Anneville (Anslecville, 11th century)
- Ásmundr or Osmundr: Omonville-la-Foliot (Osmundi villa, 12th century), Omonville (Osmundivilla, 12th century), Saint-Martin-Osmonville (Osmundi villam, 12th century)
- Ásulfr: Auzouville and Ozeville
- Blakkr: Blactot, Blacqueville (Blacrevilla, 11th century), Chamblac (Campus Blaque, 12th century)
- Brandr: Branville-Hague, Brainville, Branvill
- Bretakollr: Brectouville (Britecolvilla, 12th century)
- Farmaðr, from the Old Danish Farman, meaning "wayfarer" or "traveller": Fermanville (Farmanville, 12th century), Fermanbreuil, Saint-Denis-le-Ferment (Sanctus Dyonisus de Farman, 12th century)
- Fastulfr: Fatouville-Grestain (Fastovilla, 12th century)
- Fotr: Fauville (Fodvilla, 13th century), Fauville (Foville, 12th century)
- Grimr: Grainval (Grinval, 11th century), Mesnil-Grain, Grainville, Grainville-la-Teinturière (Grinvillam, 11th century), Grainville-sur-Ry (Grinvilla, 11th century)
- Gunnulfr: Gonnetot / Gonneville-la-Mallet, etc.; Norman surnames: Gounout, Gounouf
- Gunnfriðr: Gonfreville-l'Orcher (Gonfrevilla, 12th century), Gonfreville-Caillot (Gunfredi villa, 11th century), Gonfreville, Mesnil-Gonfroy
- Hals: Hauville (Halsvilla, 11th century)
- Hasteinn: Hattentot, Hattenville (Hastingi villa, 11th century), Hatainville
- *Helgimaðr: Hecmanville (Heuguemanville, 14th century)
- Holmgeirr: Hougerville
- Hugleikr: Hugleville-en-Caux and Heugleville-sur-Scie
- Ingulfr: Ingouville (Ingulfi villam, 10th century), Digosville (Ingulvilla, 11th century)
- Ketill, meaning "(sacrificial) cauldron, helmet": Quettehou, Quettetot, Quetteville, Cretteville
- Klakkr or KlakkR: Mesnil-Claque, Claville-Motteville and Clasville
- Krákr: Crasville
- Kolbeinn: Compainville (Cobeinvilla and Cobbenivilla, 13th century)
- Krókr: Cropus, Crosville-sur-Scie (Crocvilla, 11th century), Crosville-sur-Douve, Crosville-la-Vieille
- Morfar: Montfarville (Morfarvilla, 13th century)
- Njáll or Njál, from the Old Irish Niall: Néville (Nevilla, 11th century), Néville-sur-Mer (Neevilla or Nigevilla, 12th century), Néhou (Neauhou, 12th century)
- Ospakr: Le Mesnil-Opac
- *Sigbrandr (Old Swedish Sigbrand): Cibrantot (Terre de Sibrantot)
- *Sigfríðr: Chiffretot, Chiffreville (Sigefridisvilla, 11th century), Chiffrevast, Cheffreville-Tonnencourt (Sigefredivilla, 12th century)
- Skammhals, from the Old Danish Skammel: Équemauville (Scamelli Villae, 11th century), Scamelbec, Cannetot (Scameltot)[124]
- *Snægeir: Négreville (Esnegervilla, 12th century)
- Smiðr: Émiéville (Esmitvilla, 12th century) and Émainville (Smit villa, 11th century)
- Sprot: Épretot (Espretot, 12th century) and Épreville (Sprovilla, 11th century)
- Starr: Éterville (Starvilla, 11th century)
- Styrr or Styr (Old Danish): Étretat (Strutat, 11th century), Étréville (Sturivilla, 11th century), Éturville (Sturvilla, 12th century)
- Styrkárr (Old Danish Styrkar): Turcaville (Sturgarvilla, 11th century)
- Summarliði: Summerleevilla
- Svartingr: Surtainville (Sortinvilla, 11th century)
- Teitr: Théville (Tedvilla, Teivilla, Téville, Theyvilla, and Villa Teth, 11th century)
- Thorfriðr: Touffrécale (Torfrescalis, 12th century), Touffreville (Turfreivilla, 12th century), Touffreville-la-Corbeline (Turfreitvilla, 11th century)
- Thorgautr: Turgauville
- Thorgisl: Tourgéville and Torgisval[125]
- Thorketill: Teurthéville-Hague (Torquetevilla, 12th century), Teurthéville-Bocage (Torquetelvilla, 12th century)
- Thorlakr: Tourlaville (Torlachvilla, 11th century), Tout-la-ville (Torlavilla, 12th century), Tous-les-Mesnil (Toulamesnil, 14th century)
- Þormóðr or Thormoth (Old Danish) : Trémauville (Fauville-en-Caux), Tourmauville (Tormovilla, 12th century), Turmauville (Tormotville, 12th century)
- Thorsteinn: Toutainville (Turstini villa), 11th century
- Thorvaldr: Turretot, Trouville (Thorouvilla, 13th century), and Bourgtheroulde
- Tolir (diminutive of Thórleifr): Tollevast (Toberwast, 11th century) and Tolleville
- Ulfr: Oudalle (Hulvedala, 11th century), Ouville, Ouville-la-Bien-Tournée (Ulvilla, 12th century)
- Valr: Vautuit, Valletot and Valleville
- Vigautr or Old Danish Wigot: Igoville (Vigovilla, 13th century), Le Mesnil-Vigot (Maisnillum Vigot, 12th century)
- *Ysteinn: Inthéville (Usteinvilla, 12th century)
Anglo-Saxon -a names
Anglo-Saxon -a names:[126]
- Boia: Buglise (Buiglise, 13th century), Biville-la-Baignarde (Buivilla, 13th century)
- Huna: Honfleur, Honaville, and Honneville
- Lufa: Louvetot (Luvetoth, 11th century) and Leesthorpe (Luvestorp, 11th century)
- Hwita: Vitot (Witoth, 11th century), Vittefleur (Witeflue, 12th century), Quittebeuf (Witeboe, 12th century), Ymare (Wimara, 13th century), Yville-sur-Seine (Witvilla, 11th century), and Iville
- Peola: Pelletot (Peletot, 12th century)
- Smala: Émalleville (Esmaleville, 12th century) and Saint-Sauveur-d'Émalleville (Esmaleville, 11th century)
- Cuda: Coudeville (Coudevilla, 13th century)
- Watta: Vattetot-sur-Mer (Watetot, 12th century), Vattetot-sous-Beaumont (Watetot, 12th century), and Vatteville-la-Rue
- Willa: Illeville-sur-Montfort (Willevilla, 13th century)
Anglo-Saxon simple and combined names[127]
- Æðel-wine (Alwin): Alvintot, Alvimare, and Alvimbuc
- Æðel-wold: Allouville-Bellefosse (Adelolvilla, 11th century)
- Æðel-stān (Alestan): L'Étantot (Alestantot) and Lestanville (Alestanvilla, 12th century)
- Bæling: Notre-Dame-de-Bliquetuit (Belinguetuith, 11th century)
- Beornwulf (Old Norse Björnúlfr): Cambernon (Campo Bernulfi and Campbernolf, 13th century)[128]
- Beorh-stān: Brétantot and Brestanville
- *Blacward: Saint-Mards-de-Blacarville (Blacuardi villa, 11th century)
- Blein or Bleyn (Old Norse Blæingr): Blainville-sur-Mer (Blainvilla, 10th century and Bleinvilla, 12th century)
- Broc: Brosville (Broovilla, 12th century) and Brosville (Brochvilla, 11th century)
- Burning: Bournainville-Faverolles (Burnenvilla, 12th century), Bourneville (Burnenvilla, 12th century), Bonneville-sur-le-Bec (Burnencvilla, 11th century)
- Calvert: Cauverville-en-Roumois (Calvervilla, 13th century)
- Culvert: Cuverville (Culvertivilla, 11th century)
- Dun-stān: Dénestanville (Donestanvilla, 11th century and Dunestanvilla, 12th century)
- Flot-mån(n): Flottemanville-Hague (Flotemanvilla, 12th century), Flottemanville-Bocage (Flotemanvilla, 12th century)
- Hard-kin: Harcanville (Harkenvilla, 12th century)
- Kine-wald or Kine-wold: Canouville (Kenualdi villa, 11th century)
- Lēōd-grim or Lēōf-grim: Lingreville (Legrinvilla, 11th century)
- Lēōf-rēd or Levred: Linverville (Livervilla, 12th century)
- Mōrcǣr (see Morcar): Montcarville (Moncarvilla, 12th century, and Moncarvilla, 13th century)
- Ōs-wid (Old Norse Asvidr): Anvéville (Ovevillam and Onvéville, 13th century)
- Sæwald or Siwold: Saumont-la-Poterie (Seiwaltmont, 11th century), Siouville (Seolvilla, 13th century), Sciotot
- Sideman: Septimanville (Sedemanvilla, 11th century)
- Scarding: Écardenville-sur-Eure (Scherdanvilla, 11th century) and Écardenville-la-Campagne (Esquardenville, 14th century)
- Skelder (Old Norse Skialdari): Équeurdreville-Hainneville (Sceldrevilla, 11th century)
- Snuter: Sainte-Opportune-la-Mare (Esnutrivillam, 11th century) and Nètreville (Esnetrevilla, 12th century)
- Swart-kin: Sorquainville (Soartichin villa, 11th century)
- Wifel: Veauville-les-Baons (Wivelvilla, 11th century) and Veauville-les-Quelles (Wiauvilla, 14th century)
- Win-stān: Vénestanville (Wenestanvillam, 12th century)
- Wivar (Old Norse Vidhfari): Viertot and Virville (Wivarevilla, 13th century), Vierville-sur-Mer (Wiarevilla, 12th century)
See also
Notes
- ↑ French normanique cf. RENAUD Jean, La toponymie normanique: Reflet d'une colonisation in FLAMBARD HÉRICHER Anne-Marie, La progression des Vikings, des raids à la colonisation, Publications de l'Université de Rouen, 2003.
- ↑ Toponymic type that exists everywhere in France, for example Ruan (Rothomago 1233 / Rotomagus 5th century), Rom.
- ↑ Xavier Delamarre, Dictionnaire de la langue gauloise, éditions errance 2003, p. 261 – 262.
- ↑ Idem Charenton, etc.
- ↑ There are other Vernon in France, but they come from Vernō 'place of the alder-trees'.
- ↑ See Noviomagus and Lexovii.
- ↑ Pierre-Yves Lambert, La Langue gauloise, édition errance 1994, p.39.
- ↑ François de Beaurepaire, Les noms des communes et anciennes paroisses de l'Eure, éditions Picard 1981.
- ↑ François de Beaurepaire, op. mentioned.
- ↑ Neufchâtel-en-Bray is a former Neufcastel 13th century → 15th century, with the Old Norman spelling of the word "castle": castel, that gave birth to the Mod. Norman câtel (sometimes written catel). For instance: Old Norman Castel, Guernsey, known in Modern Norman as Sainte-Marie-du-Câtel (Guernsey), le Câtel (Jersey), Manoir du Catel (Pays de Caux), Radicatel (Pays de Caux), etc. corresponding to French château. There are many derived words such as Le Catelier, etc.
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Fournier
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ LAUR (Wolfgang), Historisches Ortsnamenlexicon von Schelswig-Holstein, K. Wachtholtz Verlag, Neuműnster, 1992, p. 298.
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ Jean Adigard des Gautries & Fernand Lechanteur, « Les noms de communes de Normandie », in Annales de Normandie XIX (juin 1969), § 715.
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Ridel
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ Laur
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Guinet
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ Nordic Names: Amundi
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ Nordic Names: Aghi
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Nordic Names: Aki
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Nordic Names: Api
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ Fournier
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Dauzat et Rostaing
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ Renaud
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ De Beaurepaire
- ↑ Renaud
References
- François de Beaurepaire, Les noms des communes et anciennes paroisses de la Seine-Maritime, éditions Picard 1979.
- François de Beaurepaire, Les noms des communes et anciennes paroisses de l'Eure, éditions Picard 1981.
- François de Beaurepaire, Les noms des communes et anciennes paroisses de la Manche, éditions Picard 1986.
- Albert Dauzat and Charles Rostaing, Dictionnaire étymologique des noms de lieu en France, Librairie Guénégaud, Paris, 1979.
- Albert Hugh Smith, English Place-names Elements, 2 volumes, Cambridge, 1972.
- Eilert Ekwall, The Concise Oxford Dictionary Of English Place-names, Oxford, 1947.
- Åse Kari H. Wagner, Les noms de lieux issus de l'implantation scandinave en Normandie: le cas des noms en -tuit, in Les fondations scandinaves en occident et les débuts du duché de Normandie, actes publiés sous la direction de Pierre Bauduin. Caen: Publications du CRAHM 2005.
- W. Laur, Historisches Ortsnamenlexikon von Schleswig-Holstein, Karl Wachholtz Verlag, 1992.
- L'Héritage maritime des Vikings en Europe de l'ouest, Colloque international de la Hague, sous la direction d'Elisabeth Ridel, Presses Universitaires de Caen, 2002.
- René Lepelley, Dictionnaire étymologique des noms de communes de Normandie, Charles Corlet éditions / Presses universitaires de Caen 1994.
- Jean Renaud, Les Vikings et la Normandie, éditions Ouest-France Université 1989.
- Jean Renaud, Vikings et noms de lieux de Normandie, OREP éditions 2009.
- Georges Bernage, Vikings en Normandie, Éditions Copernic, 1979.
- Jean Adigard des Gautries, Les noms de personnes scandinaves en Normandie de 911 à 1066, C. Bloms Boktryckeri, Lund, 1954.
- Marie-Thérèse Morlet, Les noms de personnes sur le territoire de l’ancienne Gaule du VIe au XIIe siècle, Paris, CNRS, t. III (les noms de personnes contenus dans les noms de lieux), 1985.
- Dominique Fournier, Dictionnaire des noms de rues et noms de lieux de Honfleur, éditions de la Lieutenance, Honfleur 2006.
- Louis Guinet, Les Emprunts gallo-romans au germanique: du Ier à la fin du Ve siècle, éditions Klincksieck, 1982.
- T. F. Hoad, English Etymology, Oxford University Press, 1993.