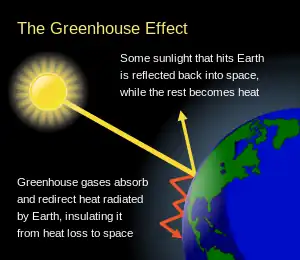
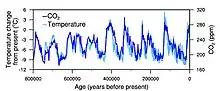
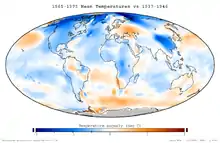
The Climate Change Portal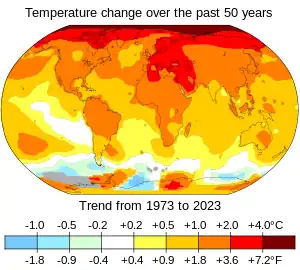 Surface air temperature change over the past 50 years.[1] In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices add to greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Climate change has an increasing impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causing more intense storms, droughts, and other weather extremes. Rapid environmental change in mountains, coral reefs, and the Arctic is forcing many species to relocate or become extinct. Even if efforts to minimise future warming are successful, some effects will continue for centuries. These include ocean heating, ocean acidification and sea level rise. Climate change threatens people with increased flooding, extreme heat, increased food and water scarcity, more disease, and economic loss. Human migration and conflict can also be a result. The World Health Organization (WHO) calls climate change the greatest threat to global health in the 21st century. Societies and ecosystems will experience more severe risks without action to limit warming. Adapting to climate change through efforts like flood control measures or drought-resistant crops partially reduces climate change risks, although some limits to adaptation have already been reached. Poorer communities are responsible for a small share of global emissions, yet have the least ability to adapt and are most vulnerable to climate change. Many climate change impacts are already felt at the current 1.2 °C (2.2 °F) level of warming. Additional warming will increase these impacts and can trigger tipping points, such as the melting of the Greenland ice sheet. Under the 2015 Paris Agreement, nations collectively agreed to keep warming "well under 2 °C". However, with pledges made under the Agreement, global warming would still reach about 2.7 °C (4.9 °F) by the end of the century. Limiting warming to 1.5 °C will require halving emissions by 2030 and achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. Strategies to phase out fossil fuels involve conserving energy, generating electricity cleanly, and using electricity to power transportation, heat buildings, and operate industrial facilities. The electricity supply can be made cleaner and more plentiful by vastly increasing deployment of wind, and solar power, alongside other forms of renewable energy and nuclear power. Carbon can also be removed from the atmosphere, for instance by increasing forest cover and farming with methods that capture carbon in soil. (Full article...) Selected article – Surface air temperature change over the past 50 years. In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global average temperature is more rapid than previous changes, and is primarily caused by humans burning fossil fuels. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices add to greenhouse gases, notably carbon dioxide and methane. Greenhouse gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight. Larger amounts of these gases trap more heat in Earth's lower atmosphere, causing global warming. Climate change has an increasing impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has contributed to melting permafrost, glacial retreat and sea ice loss. Higher temperatures are also causing more intense storms, droughts, and other weather extremes. Rapid environmental change in mountains, coral reefs, and the Arctic is forcing many species to relocate or become extinct. Even if efforts to minimise future warming are successful, some effects will continue for centuries. These include ocean heating, ocean acidification and sea level rise. Climate change threatens people with increased flooding, extreme heat, increased food and water scarcity, more disease, and economic loss. Human migration and conflict can also be a result. The World Health Organization (WHO) calls climate change the greatest threat to global health in the 21st century. Societies and ecosystems will experience more severe risks without action to limit warming. Adapting to climate change through efforts like flood control measures or drought-resistant crops partially reduces climate change risks, although some limits to adaptation have already been reached. Poorer communities are responsible for a small share of global emissions, yet have the least ability to adapt and are most vulnerable to climate change. (Full article...)Selected picture –Measuring snowpack in a crevasse on the Easton Glacier, North Cascades, USA. The two-dimensional nature of the annual layers is apparent. Crucial to the survival of a glacier is its mass balance, the difference between accumulation and ablation (melting and sublimation). Climate change may cause variations in both temperature and snowfall, causing changes in mass balance.
WikiProjects
In the newsAdditional News
Selected biography – Regina McCarthy (born May 3, 1954) is an American air quality expert who served as the first White House national climate advisor from 2021 to 2022. She previously served as the thirteenth Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency from 2013 to 2017. A Massachusetts native, McCarthy holds degrees from the University of Massachusetts Boston and Tufts University. She was a civil servant in the Massachusetts state government, holding various environmental roles and serving as an environmental advisor to the Governor of Massachusetts. She served as commissioner of the Connecticut Department of Environmental Protection from 2004 to 2009 before joining the EPA in 2009. On March 4, 2013, President Barack Obama nominated McCarthy to replace Lisa Jackson as EPA administrator. Confirmation hearings started on April 11, 2013. On July 18, 2013, she was confirmed after a record 136-day confirmation process, becoming the face of Obama's global warming and climate change initiative. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various climate-related articles on Wikipedia.
Did you know –Related portalsSelected panorama –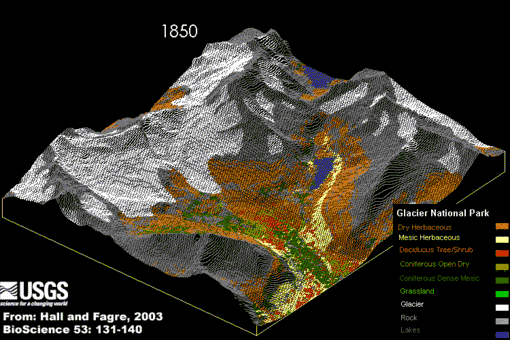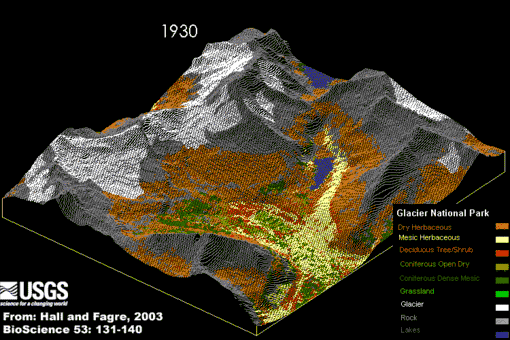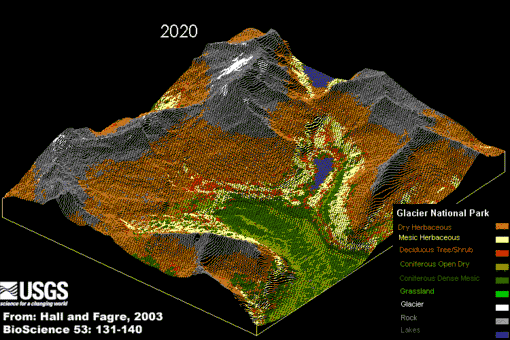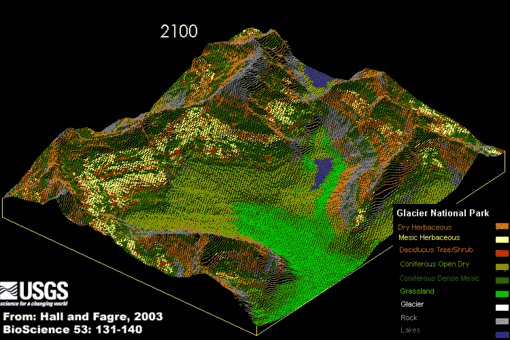 Credit: U.S. Geological Survey – Northern Rocky Mountain Science Center (NOROCK) Authors: Myrna H. P. Hall and Daniel B. Fagre, 2003 Animation of Modeled Climate-Induced Glacier Change in Glacier National Park, 1850- 2100. The simulation reflects the predicted exponential rise in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations, a 2xCO2 "global warming" scenario, with a concurrent warming of 2-3 degrees centigrade (4-5 degrees Fahrenheit) by the year 2050. In addition it assumes that precipitation, primarily in the form of rain, will increase over the same time period about 10 percent (based on the research of Dr. Steven Running, University of Montana).
TopicsCategoriesCategory puzzle Climate change Climate change by country and region Climate change and society Climate change-related lists Climate change assessment and attribution Climate change and the environment Climate change feedbacks Greenhouse gases Climate change journals Climate change litigation Climate change mitigation Climate change stubs Web resources
Things to do
WikimediaReferences
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|




_at_the_top_of_the_atmosphere_(TOA).png.webp)





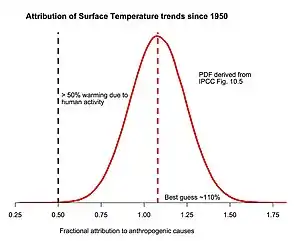


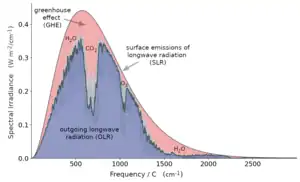
.png.webp)
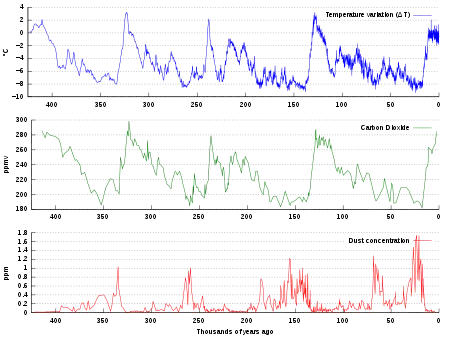




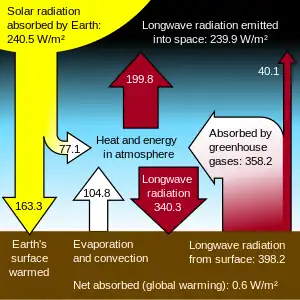





.png.webp)




%252C_the_El_Ni%C3%B1o_%E2%80%93_Southern_Oscillation%252C_the_Arctic_Oscillation%252C_and_the_North_Atlantic_Oscillation_(NOAA).png.webp)