 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
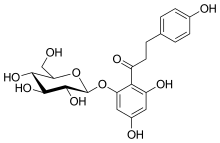
| IUPAC name
1-[2-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-4,6-dihydroxyphenyl]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
1-(2,4-Dihydroxy-6-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}phenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one | |
| Other names
Isosalipurposide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.443 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H24O10 | |
| Molar mass | 436.413 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 106 to 109 °C (223 to 228 °F; 379 to 382 K) |
| Boiling point | 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) decomposition |
| water, low MW alcohols | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Phlorizin is a glucoside of phloretin, a dihydrochalcone. A white solid, samples often appear yellowing to impurities. It is of sweet taste and contains four molecules of water in the crystal. Above 200 °C, it decomposes to give rufin. It is poorly soluble in ether and cold water, but soluble in ethanol and hot water. Upon prolonged exposure to aqueous solutions phlorizin hydrolyzes to phloretin and glucose. [1]
Occurrence
Phlorizin is found primarily in unripe Malus (apple)[2] root bark of apple,[3] and trace amounts have been found in strawberry.[4] In Malus, it is most abundant in vegetative tissues (such as leaves and bark) and seeds. Closely related species, such as pear (Pyrus communis), cherry, and other fruit trees in the Rosaceae do not contain phlorizin.[5] Phlorizin is a phytochemical that belongs to the class of polyphenols. In natural sources, it may occur with other polyphenols such as quercetin, catechin, epicatechin, procyanidins, and rutin.
Pharmacology
Phlorizin is an inhibitor of SGLT1 and SGLT2 because it competes with D-glucose for binding to the carrier; this action reduces renal glucose transport, lowering the amount of glucose in the blood.[6][7] Phlorizin was studied as a potential pharmaceutical treatment for type 2 diabetes, but has since been superseded by more selective and more promising synthetic analogs, such as empagliflozin, canagliflozin and dapagliflozin.[8] Phlorizin is not an effective drug because when orally consumed, it is nearly entirely converted into phloretin by hydrolytic enzymes in the small intestine.[9][10]
References
- ↑ Ehrenkranz, Joel R. L.; Lewis, Norman G.; Ronald Kahn, C.; Roth, Jesse (2005). "Phlorizin: A review". Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews. 21 (1): 31–38. doi:10.1002/dmrr.532. PMID 15624123. S2CID 37909306.
- ↑ Makarova, Elina; Górnaś, Paweł; Konrade, Ilze; Tirzite, Dace; Cirule, Helena; Gulbe, Anita; Pugajeva, Iveta; et al. (2015). "Acute anti-hyperglycaemic effects of an unripe apple preparation containing phlorizin in healthy volunteers: A preliminary study". Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 95 (3): 560–568. doi:10.1002/jsfa.6779. PMID 24917557.
- ↑ Bays, Harold (2013). "Sodium glucose co-transporter type 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: Targeting the kidney to improve glycemic control in diabetes mellitus". Diabetes Therapy. 4 (2): 195–220. doi:10.1007/s13300-013-0042-y. PMC 3889318. PMID 24142577.
- ↑ Hilt, Petra; Schieber, Andreas; Yildirim, Caner; Arnold, Gabi; Klaiber, Iris; Conrad, Jürgen; Beifuss, Uwe; et al. (2003). "Detection of phloridzin in strawberries (Fragaria x ananassa Duch.) by HPLC–PDA–MS/MS and NMR spectroscopy". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 51 (10): 2896–2899. doi:10.1021/jf021115k. PMID 12720368.
- ↑ Gosch, Christian; Halbwirth, Heidi; Stich, Karl (2010). "Phloridzin: Biosynthesis, distribution and physiological relevance in plants". Phytochemistry. 71 (8–9): 838–843. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.03.003. PMID 20356611.
- ↑ Rossetti, Luciano; Smith, Douglas; Shulman, Gerald I.; Papachristou, Dimitrios; DeFronzo, Ralph A. (1987). "Correction of hyperglycemia with phlorizin normalizes tissue sensitivity to insulin in diabetic rats". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 79 (5): 1510–1515. doi:10.1172/JCI112981. PMC 424427. PMID 3571496.
- ↑ Tatoń, Jan; Piątkiewicz, Paweł; Czech, Anna (2010). "Molecular physiology of cellular glucose transport – A potential area for clinical studies in diabetes mellitus". Endokrynologia Polska. 61 (3): 303–310. PMID 20602306.
- ↑ Chao, Edward C.; Henry, Robert R. (2010). "SGLT2 inhibition – A novel strategy for diabetes treatment". Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 9 (7): 551–559. doi:10.1038/nrd3180. PMID 20508640.
- ↑ Idris, Iskandar; Donnelly, Richard (2009). "Sodium–glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors: An emerging new class of oral antidiabetic drug". Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism. 11 (2): 79–88. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.00982.x. PMID 19125776.
- ↑ Crespy, Vanessa; Aprikian, Olivier; Morand, Christine; Besson, Catherine; Manach, Claudine; Demigné, Christian; Rémésy, Christian (2001). "Bioavailability of phloretin and phloridzin in rats". The Journal of Nutrition. 131 (12): 3227–3230. doi:10.1093/jn/131.12.3227. PMID 11739871.