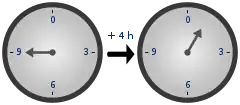Portal maintenance status: (August 2018)
|
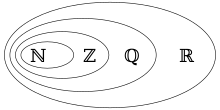
The Arithmetic Portal The main arithmetic operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Arithmetic is an elementary branch of mathematics that studies numerical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. In a wider sense, it also includes exponentiation, extraction of roots, and taking logarithms. Arithmetic systems can be distinguished based on the type of number they operate on. Integer arithmetic restricts itself to calculations with positive and negative whole numbers. Rational number arithmetic involves operations on fractions that lie between integers. Real number arithmetic includes calculations with both rational and irrational numbers and covers the complete number line. Another distinction is based on the numeral system employed to perform calculations. Decimal arithmetic is the most common. It uses the basic numerals from 0 to 9 and their combinations to express numbers. Binary arithmetic, by contrast, is used by most computers and represents numbers as combinations of the basic numerals 0 and 1. Some arithmetic systems operate on mathematical objects other than numbers, such as interval arithmetic and matrix arithmetic. (Full article...) The Egyptians and Babylonians used all the elementary arithmetic operations as early as 2000 BC. Later Roman numerals, descended from tally marks used for counting. The continuous development of modern arithmetic starts with ancient Greece, although it originated much later than the Babylonian and Egyptian examples. Euclid is often credited as the first mathematician to separate study of arithmetic from philosophical and mystical beliefs. Greek numerals were used by Archimedes, Diophantus and others in a positional notation not very different from ours. The ancient Chinese had advanced arithmetic studies dating from the Shang Dynasty and continuing through the Tang Dynasty, from basic numbers to advanced algebra. The ancient Chinese used a positional notation similar to that of the Greeks. The gradual development of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system independently devised the place-value concept and positional notation, which combined the simpler methods for computations with a decimal base and the use of a digit representing zero (0). This allowed the system to consistently represent both large and small integers. This approach eventually replaced all other systems. In the Middle Ages, arithmetic was one of the seven liberal arts taught in universities. The flourishing of algebra in the medieval Islamic world and in Renaissance Europe was an outgrowth of the enormous simplification of computation through decimal notation. Selected general articles
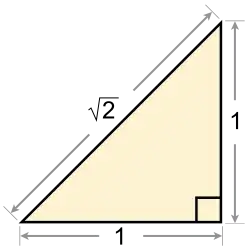
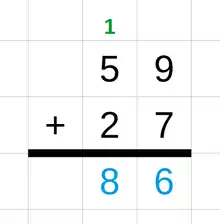
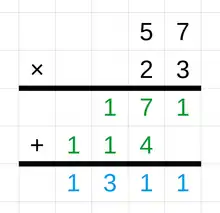
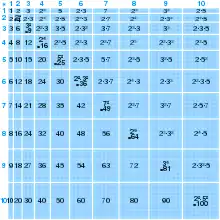
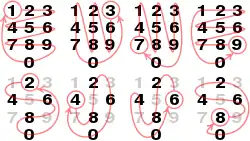
General imagesThe following are images from various arithmetic-related articles on Wikipedia.
Need help?Do you have a question about Arithmetic that you can't find the answer to? Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk. Selected biography
SubcategoriesCategory puzzle
Arithmetic Numbers Binary arithmetic Comparison (mathematical) Computer arithmetic Elementary arithmetic Factorization Formal theories of arithmetic Fractions (mathematics) Mental calculation Modular arithmetic Operations on numbers Quotients Ratios Related portalsRelated topics
Associated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Discover Wikipedia using portals
|

_mess_tent_still_does_not_break_out_of_the_sub-freezing_temperatures.jpg.webp)

.svg.png.webp)







.jpg.webp)