 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium tetrachloridoplatinate(2–) | |
| Other names
Potassium chloroplatinite | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.034 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| K2PtCl4 | |
| Molar mass | 415.09 g/mol |
| Appearance | reddish solid |
| Density | 3.38 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 265 °C (509 °F; 538 K) |
| 0.93 g/100 mL (16 °C) 5.3 g/100 mL (100 °C) | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
    | |
| Danger | |
| H301, H315, H317, H318, H334 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P272, P280, P285, P301+P310, P302+P352, P304+P341, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P330, P332+P313, P333+P313, P342+P311, P362, P363, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Nonflammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Potassium hexachloroplatinate |
Other cations |
Sodium chloroplatinate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
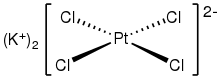
Potassium tetrachloroplatinate(II) is the chemical compound with the formula K2PtCl4. This reddish orange salt is an important reagent for the preparation of other coordination complexes of platinum. It consists of potassium cations and the square planar dianion PtCl42−. Related salts are also known including Na2PtCl4, which is brown-colored and soluble in alcohols, and quaternary ammonium salts, which are soluble in a broader range of organic solvents.
Preparation
Potassium tetrachloroplatinate is prepared by reduction of the corresponding hexachloroplatinate salt with sulfur dioxide.[1] K2PtCl4 is one of the salts that is most easily obtained from platinum ores. The complex is appreciably soluble only in water. Treatment with alcohols, especially in the presence of base, causes reduction to platinum metal. Organic tetrachloroplatinate salts, such as [PPN]2PtCl4 are soluble in chlorocarbons.[2]
Reactions
The chloride ligands on [PtCl4]2− are displaced by many other ligands. Upon reaction with triphenylphosphine, [PtCl4]2− converts to cis-bis(triphenylphosphine)platinum chloride:
- PtCl42− + 2 PPh3 → cis-PtCl2(PPh3)2 + 2 Cl−
The anti-cancer drug Cisplatin can similarly be prepared:[1]
- PtCl42− + 2 NH3 → cis-PtCl2(NH3)2 + 2 Cl−
Enedithiolates displace all four chloride ligands to give bis(dithiolene) complexes.[3] Reduction gives colloidal platinum of potential interest for catalysis.[4]
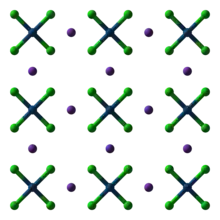
Historically, an important reaction involves ammonia and [PtCl4]2−. This reaction affords a deep green precipitate with empirical formula PtCl2(NH3)2. This material, known as Magnus' green salt, is a semiconducting coordination polymer consisting of chains of alternating [PtCl4]2− and [Pt(NH3)4]2+ centres.[5]
References
- 1 2 Keller, R. N.; Moeller, T. (2007). "Potassium Tetrachloroplatinate(II): (Potassium Chloroplatinite)". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 7. pp. 247–250. doi:10.1002/9780470132333.ch79. ISBN 9780470132333.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ↑ Elding, L. I.; Oskarsson, A.; Kukushkin, V. Yu (2007). "Platinum Complexes Suitable as Precursors for Synthesis in Nonaqueous Solvents". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 31. pp. 276–279. doi:10.1002/9780470132623.ch47. ISBN 9780470132623.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ↑ Scott D. Cummings; Richard Eisenberg (1995). "Acid-Base Behavior of the Ground and Excited States of Platinum(II) Complexes of Quinoxaline-2,3-dithiolate". Inorg. Chem. 34 (13): 3396–3403. doi:10.1021/ic00117a005.
- ↑ Ahmadi, T. S.; Wang, Z. L.; Green, T. C.; Henglein, A.; El-Sayed, M. A. (1996). "Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Colloidal Platinum Nanoparticles". Science. 272 (5270): 1924–6. Bibcode:1996Sci...272.1924A. doi:10.1126/science.272.5270.1924. PMID 8662492. S2CID 34481183.
- ↑ Caseri, W. (2004). "Derivatives of Magnus' green salt; from intractable materials to solution-processed transistors". Platinum Metals Review. 48 (3): 91–100. doi:10.1595/147106704X1504.
