 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium selenide | |
| Other names
Dipotassium selenide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.817 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| K2Se | |
| Molar mass | 157.16 |
| Appearance | clearish wet crystal[1] |
| Density | 2.29 g/cm3[2] |
| reacts | |
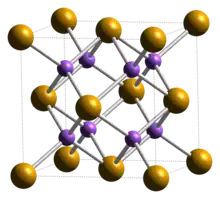
| Structure | |
| cubic: antifluorite | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
toxic |
| GHS labelling: | |
   | |
| Danger | |
| H301, H331, H373, H410 | |
| P260, P262, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P284, P301+P310, P304+P340, P310, P314, P320, P321, P330, P361, P363, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Potassium oxide Potassium sulfide Potassium telluride Potassium polonide |
Other cations |
Lithium selenide Sodium selenide Rubidium selenide Caesium selenide |
Related compounds |
Potassium selenate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Potassium selenide (K2Se) is an inorganic compound formed from selenium and potassium.
Production
It can be produced by the reaction of selenium and potassium. If the two are combined in liquid ammonia, the purity is higher.
Crystal structure
Potassium selenide has a cubic, antifluorite crystal structure.
References
- ↑ Jean D'Ans, Ellen Lax: Taschenbuch für Chemiker und Physiker. 3. Elemente, anorganische Verbindungen und Materialien, Minerale, Band 3. 4. Auflage, Springer, 1997, ISBN 978-3-5406-0035-0, S. 692 (, p. 692, at Google Books).
- ↑ Dale L. Perry, Sidney L. Phillips: Handbook of inorganic compounds. CRC Press, 1995, ISBN 978-0-8493-8671-8, S. 336 (, p. 336, at Google Books).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.