 | |
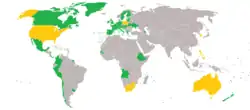 Map of members | |
| Formation | 16 November 2017[1] |
|---|---|
| Type | International environmental organization |
Region served | Worldwide |
| Website | poweringpastcoal |

The Powering Past Coal Alliance (PPCA) is a group of 170 countries, cities, regions and organisations aiming to accelerate the fossil-fuel phase out of coal-fired power stations, except the very few which have carbon capture and storage.[2][3][4] It has been described as a "non-proliferation treaty" for fossil fuels.[5] The project was undertaken with financial support from the Government of Canada, through their environmental department known as Environment and Climate Change Canada.[6]
History

The Alliance was launched by Canada and the UK at the COP23 climate summit in November 2017. Announcing the launch, Climate Action Network-Canada Executive Director Catherine Abreu said:
"Canada and the UK are right to kick-start the Alliance, as science tells us that OECD countries need to phase out coal by 2030 at the latest”.[1][7]
By the end of the summit, membership had grown to include over 20 countries, regions and organizations.[8] Within a month membership had grown to over 50 .[9] Its purpose is to establish a new international norm, or “standard of appropriate behaviour”, that coal should not be burned for power.[2]
In April 2018 a research partnership was announced with Bloomberg Philanthropies.[10]
In October 2018 the South Korean province of South Chungcheong became the first jurisdiction in Asia and the largest user of coal power to join the Alliance.[11][12] In December 2018 Sydney, Melbourne, Scotland, Scottish Power, Senegal and Israel also joined[13] and in September 2019 seven new members joined including Germany and Slovakia.[5][14]
In June 2020 6 global finance organisations joined including Desjardins Group, the first major North American financial institution to join.[15]
During 2021 at least 38 new members joined including Hungary, Uruguay,[16] Chile, Estonia, Singapore, Slovenia and Ukraine.[17]
Aims
Alliance members agree that:[9]
- Governments/states will phase out existing traditional coal power.
- Governments/states will create a moratorium on any new traditional coal power stations without operational carbon capture and storage.
- Businesses/organisations will power operations without coal.
- Members will ensure policies and investments support clean power.
- Members will restrict financing for traditional coal power without carbon capture and storage.
Reaction
Reacting to the launch, Tracy Carty of Oxfam said the Alliance:
"represents real and tangible progress in the fight against climate change."[18]
Business change organisation The B Team welcomed the Alliance, and argued that exiting coal must happen as a just transition that protects vulnerable workers and communities such as coal mining communities.[19]
Members
Members of the Powering Past Coal Alliance as of December 2023 were:[20]
Nations
- Albania
- Angola
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belgium
- Canada
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Denmark
- El Salvador
- Estonia
- Ethiopia
- Fiji[21]
- Finland
- France
- Germany[22]
- Greece
- Hungary
- Ireland
- Israel
- Italy
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Kosovo
- Marshall Islands
- Mauritius
- Mexico
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- Niue
- North Macedonia
- Panama
- Peru
- Portugal
- Senegal
- Singapore[23]
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Tuvalu
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- Uruguay
- Vanuatu
Sub-national entities
- Alberta, Canada
- Australian Capital Territory, Australia
- Baden-Württemberg, Germany
- Balearic Islands, Spain
- British Columbia, Canada
- California, USA
- Colorado, USA
- Connecticut, USA
- Daegu, South Korea
- Durban, South Africa
- Eastern Wielkopolska, Poland
- Gangwon, South Korea
- Guimaras, Philippines
- Gyeonggi, South Korea
- Hawaii, USA
- Honolulu, USA
- Ilocos Norte, Philippines
- Incheon, South Korea
- Jeju, South Korea
- Jeollanam, South Korea
- Kaohsiung City
- Koszalin, Poland
- Kyoto City
- Los Angeles, USA
- Masbate, Philippines
- Melbourne, Australia
- Minnesota, USA
- Negros Occidental, Philippines
- Negros Oriental, Philippines
- New Jersey, USA
- New Mexico, USA
- New Taipei City
- New York, USA
- Ontario, Canada
- Oregon, USA
- Ormoc, Philippines
- Philadelphia, USA
- Puerto Rico
- Quebec, Canada
- Rotterdam, Netherlands
- Scotland, UK
- Seoul, South Korea
- South Chungcheong, South Korea
- Sydney, Australia
- Taichung City, Taiwan
- Vancouver, Canada
- Wales, UK
- Wałbrzych, Poland
- Washington, USA
Businesses and other organisations
- Aberdeen Standard Investments
- Alterra Power
- Amundi
- ArcTern Ventures
- Autodesk
- Avant Garde Innovations
- Aviva[24]
- Axa Investment Managers
- BT
- Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec
- Caisse des dépôts et consignations
- CalPERS
- Capital Power
- CCLA Investment Management Limited
- Central Finance Board of the Methodist Church and Epworth IM
- Church Commissioners for England
- Church of England Pensions Board
- Desjardins Group
- Diageo
- Drax
- DSM
- DTEK
- Econet Group
- EcoSmart
- EDP[25]
- Electricité de France (EDF)
- Eneva
- Engie
- Ethos Foundation
- Export Development Canada
- Fidelity International
- GAM
- Generation Investment Management
- GeoExchange Coalition
- GreenScience
- Hermes Investment Management[24]
- HSBC
- Iberdrola
- Impax Asset Management
- Indika Energy
- Kering
- Legal & General
- Lloyds Bank
- M&G Plc
- Marks and Spencer
- Mott MacDonald
- National Grid
- National Grid (ESO)[26][27]
- Natura Cosmetics
- NatWest
- Ontario Power Generation
- Ørsted
- Pacific Islands Development Forum
- PensionDanmark
- Robeco
- Salesforce
- Schroders
- SCOR Global Investments
- Scottish Power
- SSE
- Stichting Pensioenfonds ABP
- Storebrand
- Swiss Re
- TransAlta
- Unilever
- United Church of Canada
- Vancity
- Varma Mutual Pension Insurance Company
- Virgin Group
- XPND Capital
- ZE PAK
See also
References
- 1 2 Beer, Mitchell (26 November 2017). "BREAKING: 25 JURISDICTIONS JOIN CANADA, UK IN COAL PHASEOUT ALLIANCE". The Energy Mix. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- 1 2 Blondeel, Mathieu; Van de Graaf, Thijs; Haesebrouck, Tim (January 2020). "Moving beyond coal: Exploring and explaining the Powering Past Coal Alliance". Energy Research & Social Science. 59: 101304. doi:10.1016/j.erss.2019.101304.
- ↑ Shrestha, Priyanka (15 July 2019). "National Grid ESO joins Powering Past Coal Alliance". Energy Live News. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- ↑ Rabson, Mia (17 November 2017). "Canada and U.K. form alliance to phase out coal to combat climate change". CBC. Retrieved 20 January 2020.
- 1 2 Blondeel, Thijs; Van de Graaf, Mathieu (10 February 2019). "Growing anti-coal alliance could become non-proliferation treaty for fossil fuel". Climate Home News. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- ↑ "Our mission | Powering Past Coal Alliance". Powering Past Coal Alliance (PPCA). Retrieved 2020-01-21.
- ↑ "Canada & UK launch coal phaseout plan". Retrieved 29 September 2018.
- ↑ "Powering Past Coal Alliance: 20 countries sign up to phase out coal power by 2030". ABC News. 2017-11-17. Retrieved 29 September 2018.
- 1 2 Hill, Joshua (17 December 2017). "Powering Past Coal Alliance Membership Blows Out Past 50". CleanTechnica. Retrieved 29 September 2018.
- ↑ Cochran, Lee. "Bloomberg Philanthropies Announces Partnership with Powering Past Coal Alliance to Strengthen Global Efforts to Phase Out Coal". Bloomberg Philanthropies. Retrieved 12 January 2020.
- ↑ Sauer, Natalie (10 March 2018). "South Korean province joins international coal phase-out club". Climate Home News. Retrieved 21 January 2020.
- ↑ Chen, Han (2 October 2018). "Korean Province to Phase Out Coal: Implications for Asia". Natural Resources Defense Council. Retrieved 4 October 2018.
- ↑ Sauer, Natalie (13 December 2018). "Sydney and Melbourne vow to ditch coal power". Climate Home News. Retrieved 15 December 2018.
- ↑ "Germany and Slovakia head list of new Alliance members at UN Climate Action Summit". poweringpastcoal.org. Retrieved 6 October 2019.
- ↑ "Canada to celebrate Clean Air Day with new members of the Powering Past Coal Alliance, including Quebec-based Desjardins Group". bloomberg.com. 2 June 2020. Retrieved 7 March 2022.
- ↑ "Hungary becomes member of Powering Past Coal Alliance". bbj.hu. Retrieved 7 March 2022.
- ↑ "Powering Past Coal Alliance Expands at COP26, Adds New Mexico". newsdata.com. Retrieved 7 March 2022.
- ↑ Hernandez-Arthur, Simon (8 December 2017). "Reaction to launch of 'Powering Past Coal' Alliance". Oxfam International. Retrieved 15 December 2018.
- ↑ Burrow, Sharan; Robinson, Mary (2020). "Powering past coal is right move, but we can't do it without a just transition". The B Team. Retrieved December 15, 2019.
- ↑ "Members". Retrieved 2 December 2022.
- ↑ "Fiji Joins "Powering Past Coal Alliance" to Accelerate Clean Growth". 16 November 2017. Retrieved 12 January 2020.
- ↑ "Deutschland tritt Allianz der Kohleausstiegsländer bei". Neue Zürcher Zeitung. 22 September 2019. Retrieved January 20, 2020.
- ↑ Leo, Lakeisha. "COP26: Singapore commits to phasing out unabated coal power by 2050". CNA. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- 1 2 "PPCA Finance Principles launched at Green Finance Summit 2019". Powering Past Coal Alliance (PPCA). Retrieved 2019-07-27.
- ↑ https://steelguru.com/coal/edp-joins-powering-past-coal-alliance-to-end-coal-power-generation/563368#:~:text=Coal%20News%20%2D%20Published%20on%20Mon%2C%2021%20Sep%202020&text=EDP%20is%20one%20of%20the,from%20unabated%20coal%20power%20generation.
- ↑ "National Grid Electricity System Operator joins Powering Past Coal Alliance | Powering Past Coal Alliance". Powering Past Coal Alliance (PPCA). Retrieved 2019-07-15.
- ↑ "National Grid ESO joins Powering Past Coal Alliance". BusinessGreen. 2019-07-15. Retrieved 2019-07-15.