| River Ingol | |
|---|---|
 River Ingol at Snettisham | |
 Location within Norfolk | |
| Location | |
| Country | England |
| County | Norfolk |
| Region | East of England |
| District | King's Lynn and West Norfolk |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Shernborne |
| • coordinates | 52°51′43″N 0°32′38″E / 52.8620°N 0.5438°E |
| • elevation | 28 m (92 ft) |
| Mouth | The Wash |
• location | Wolferton Creek |
• coordinates | 52°50′40″N 0°27′10″E / 52.8444°N 0.4529°E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 10.4 km (6.5 mi) |
| Basin size | 34.4 km2 (13.3 sq mi) |
The River Ingol is a small river in the west of the English county of Norfolk.[1]
Sources
The source of the river can be found a little to the west of the village of Shernborne, about 30 metres (98 ft) above sea level. It flows in a westerly direction across agricultural land towards Snettisham, and north of the hamlet of Ingoldisthorpe.
Watermill at Snettisham
.JPG.webp)
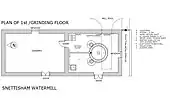
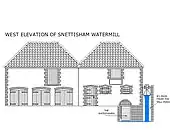
On the river at Snettisham stands a watermill TF68083346 52°52′21″N 0°29′45″E / 52.8724°N 0.4959°E. This was built in 1800 for £800 at a time when bread was scarce and it was built by the community of Snettisham for the people of the village. It is believed that the present mill was built on an existing site although virtually no records have so far been found apart from the fact that Thomas Stonne was a Snettisham miller in 1626. At the time of Domesday, there were seven mills in Snettisham more than in any other Norfolk village. Today's mill is very small and originally consisted of a single small structure built of local dark brown carrstone with a pantiled roof. In 1877, machinery was improved and a granary and wagon store were added to the complex. The mill had three pairs of stones and unusually the larger two pairs were driven from above and the smaller pair from below, the latter pair required less power and was used when water levels were low. The mill worked on until 1940 producing flour and after that was used for animal feed production until 1960. The mill was restored, and brought back to working order by 1984. It was sold in 2008, and a planning application lodged to part convert it to holiday accommodation.[2] Permission was refused. 1 September 2008.[3]
Snettisham to the Sea
From Snettisham the river flows again across open agricultural land. The river's course has been modified but there are no embankments or flood defence structures to date. The lowermost reaches of the river run parallel to the coastline where the river backs up into a series of ponds and tidal flaps, discharging into the sea at low tide. These brackish lagoons, intertidal mudflats, and salt marshes all host a selection of birds, plants, and rare invertebrates. On Faden’s map of Norfolk of 1797, the tidal ponds of today were part of what was then Snettisham harbour and salt marshes, which was also then the mouth of the river Ingol
References
- ↑ "Ingol". Catchment Data Explorer. Environment Agency. Retrieved 30 November 2016.
- ↑ Norfolk Mills, Snettisham Watermill.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2009.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)