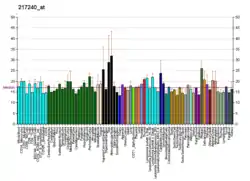
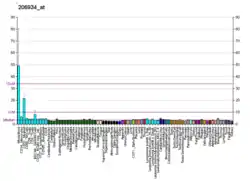
| SIRPB1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | SIRPB1, CD172b, SIRP-BETA-1, signal regulatory protein beta 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 603889 MGI: 3779828 HomoloGene: 82993 GeneCards: SIRPB1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Signal-regulatory protein beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIRPB1 gene.[5][6][7] SIRPB1 has also recently been designated CD172B (cluster of differentiation 172B).
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the signal-regulatory-protein (SIRP) family, and also belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. SIRP family members are receptor-type transmembrane glycoproteins known to be involved in the negative regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-coupled signaling processes. This protein was found to interact with TYROBP/DAP12, a protein bearing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs. This protein was also reported to participate in the recruitment of tyrosine kinase SYK. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene.[7]
Interactions
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000101307 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000095028 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Kharitonenkov A, Chen Z, Sures I, Wang H, Schilling J, Ullrich A (April 1997). "A family of proteins that inhibit signalling through tyrosine kinase receptors". Nature. 386 (6621): 181–6. Bibcode:1997Natur.386..181K. doi:10.1038/386181a0. PMID 9062191. S2CID 4259314.
- ↑ van den Berg TK, van Beek EM, Buhring HJ, Colonna M, Hamaguchi M, Howard CJ, Kasuga M, Liu Y, Matozaki T, Neel BG, Parkos CA, Sano S, Vignery A, Vivier E, Wright M, Zawatzky R, Barclay AN (December 2005). "A nomenclature for signal regulatory protein family members". J Immunol. 175 (12): 7788–9. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.175.12.7788. PMID 16339511. S2CID 41479985.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: SIRPB1 signal-regulatory protein beta 1".
- ↑ Dietrich J, Cella M, Seiffert M, Bühring H J, Colonna M (January 2000). "Cutting edge: signal-regulatory protein beta 1 is a DAP12-associated activating receptor expressed in myeloid cells". J. Immunol. UNITED STATES. 164 (1): 9–12. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.1.9. ISSN 0022-1767. PMID 10604985.
- ↑ Tomasello E, Cant C, Bühring H J, Vély F, André P, Seiffert M, Ullrich A, Vivier E (August 2000). "Association of signal-regulatory proteins beta with KARAP/DAP-12". Eur. J. Immunol. GERMANY. 30 (8): 2147–56. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(2000)30:8<2147::AID-IMMU2147>3.0.CO;2-1. ISSN 0014-2980. PMID 10940905. S2CID 84258013.
Further reading
- Dietrich J, Cella M, Seiffert M, et al. (2000). "Cutting edge: signal-regulatory protein beta 1 is a DAP12-associated activating receptor expressed in myeloid cells". J. Immunol. 164 (1): 9–12. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.1.9. PMID 10604985.
- Tomasello E, Cant C, Bühring HJ, et al. (2000). "Association of signal-regulatory proteins beta with KARAP/DAP-12". Eur. J. Immunol. 30 (8): 2147–56. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(2000)30:8<2147::AID-IMMU2147>3.0.CO;2-1. PMID 10940905. S2CID 84258013.
- Deloukas P, Matthews LH, Ashurst J, et al. (2002). "The DNA sequence and comparative analysis of human chromosome 20". Nature. 414 (6866): 865–71. Bibcode:2001Natur.414..865D. doi:10.1038/414865a. PMID 11780052.
- Cannon JP, Haire RN, Litman GW (2002). "Identification of diversified genes that contain immunoglobulin-like variable regions in a protochordate". Nat. Immunol. 3 (12): 1200–7. doi:10.1038/ni849. PMID 12415263. S2CID 19367972.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Suzuki Y, Yamashita R, Shirota M, et al. (2004). "Sequence Comparison of Human and Mouse Genes Reveals a Homologous Block Structure in the Promoter Regions". Genome Res. 14 (9): 1711–8. doi:10.1101/gr.2435604. PMC 515316. PMID 15342556.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Liu Y, Soto I, Tong Q, et al. (2006). "SIRPbeta1 is expressed as a disulfide-linked homodimer in leukocytes and positively regulates neutrophil transepithelial migration". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (43): 36132–40. doi:10.1074/jbc.M506419200. PMID 16081415.
- Liu T, Qian WJ, Gritsenko MA, et al. (2006). "Human Plasma N-Glycoproteome Analysis by Immunoaffinity Subtraction, Hydrazide Chemistry, and Mass Spectrometry". J. Proteome Res. 4 (6): 2070–80. doi:10.1021/pr0502065. PMC 1850943. PMID 16335952.
- Laplana M, Royo JL, Aluja A, López R, Heine-Sunyer H, Fibla J (September 2014). "SIRPB1 copy-number polymorphism as candidate quantitative trait locus for impulsive-disinhibited personality". Genes, Brain and Behavior. 13 (7): 653–62. doi:10.1111/gbb.12154. hdl:10486/667487. PMID 25039969.
External links
- SIRPB1 human gene location in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- SIRPB1 human gene details in the UCSC Genome Browser.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.