East Kazakhstan Region
| |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
 Map of Kazakhstan, location of East Kazakhstan Region highlighted | |
| Coordinates: 49°57′N 82°37′E / 49.950°N 82.617°E | |
| Country | |
| Established | 1932 |
| Capital | Öskemen |
| Government | |
| • Akim | Ermek Kosherbayev[1] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 97,726 km2 (37,732 sq mi) |
| Population (2020)[2] | |
| • Total | 1,369,597 |
| • Density | 14/km2 (36/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Total | KZT 3,916.8 billion US$ 8.483 billion (2022) |
| • Per capita | KZT 5,353,800 US$ 11,595 (2022) |
| Time zone | UTC+6 (East) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+6 (not observed) |
| Postal codes | 070000 |
| Area codes | +7 (722), +7 (723) |
| ISO 3166 code | KZ-VOS |
| Vehicle registration | 16, F, U |
| Districts | 15 |
| Cities | 10 |
| Townships | 30 |
| Villages | 870 |
| Website | akimvko |
East Kazakhstan Region (Kazakh: Шығыс Қазақстан облысы, romanized: Şyğys Qazaqstan oblysy; Russian: Восточно-Казахстанская область, romanized: Vostochno-Kazakhstanskaya oblast) is a region of Kazakhstan. It occupies the easternmost part of Kazakhstan, and includes parts of the Irtysh River, Lake Markakol, and Lake Zaysan.[4] Its administrative center is Öskemen (also known as Ust'-Kamenogorsk).[4] The region borders Altai Krai and Altai republic in Russia in the north and northeast and the People's Republic of China, via Xinjiang, in the south and southeast. The easternmost point of the Oblast is within about 50 kilometres of the westernmost tip of Mongolia; however, Kazakhstan and Mongolia do not share a common border, the two countries being separated by a small part of Russia and China.
The region was created by the merger of two Soviet-era Kazakhstan oblasts: the old Vostochno-Kazakhstanskaya (East Kazakhstan) Oblast and Semipalatinsk Oblast. On 17 March 2022, it was announced that East Kazakhstan region would be divided, creating the Abai Region. This came into force on 8 June 2022, with eight districts of East Kazakhstan Region being transferred to the new region. The new border dividing Abai Region and East Kazakhstan region roughly corresponds to the border that existed between the two Soviet-era Oblasts.
Geography
East Kazakhstan Region borders the Kazakh regions of Pavlodar Region to the northwest, Karaganda Region to the west, Almaty Region to the south, Russia's Altai Krai and Altai Republic to the north and China's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region to the east. However, since Abai Region became a different region than East kazakhstan region, the western part of this region borders Abai Region now and not Karaganda region[4]
The region occupies a very diverse range of geographic and climatic regions with the Altai Mountains in the east and the eastern margins of the Kazakh Steppe in the west of the region.
Demographics

As of 2020, the East Kazakhstan Region has a population of 1,369,597.[2]
Ethnic groups (2020):[5]
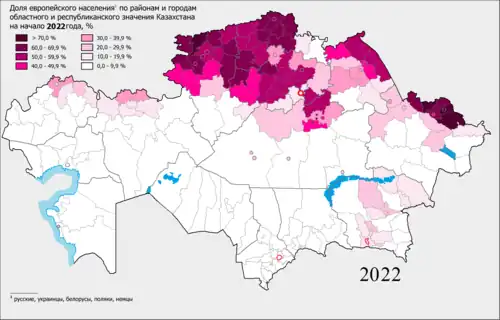
The share of the European population by districts and cities of regional and republican subordination Kazakhstan in 2022
> 70٪
60.0 – 69.9 %
50.0 - 59.9 %
40.0 - 49.9 %
30.0 - 39.9 %
20.0 - 29.9 %
10.0 - 19.9 %
0.0 - 9.9 %
|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1979 | 1,657,403 | — |
| 1989 | 1,767,225 | +0.64% |
| 1999 | 1,531,024 | −1.42% |
| 2009 | 1,396,593 | −0.91% |
| 2021 | 1,363,656 | −0.20% |
| Source: Citypopulation[6] | ||
Administrative divisions
The region is administratively divided into fifteen districts and the cities of Öskemen (Ust-Kamenogorsk), Ayagoz, Kurchatov, Ridder, Semey (Semipalatinsk), and Zyryanovsk.[7]
- Abai District, with the administrative center in the selo of Karauyl;
- Altai District, the town of Altai;
- Ayagoz District, the town of Ayagoz;
- Beskaragay District, the selo of Beskaragay;
- Borodulikha District, the selo of Borodulikha;
- Glubokoye District, the settlement of Glubokoye;
- Katonkaragay District, the selo of Ulken Narym;
- Kokpekti District, the selo of Kokpekti;
- Kurshim District, the selo of Kurshim;
- Shemonaikha District, the town of Shemonaikha;
- Tarbagatay District, the selo of Aksuat;
- Ulan District, the settlement of Molodyozhny;
- Urzhar District, the selo of Urzhar;
- Zaysan District, the town of Zaysan;
- Zharma District, the selo of Kalbatau (Georgiyevka).
* The following ten localities in East Kazakhstan Region have town status: Öskemen (Ust-Kamenogorsk), Ayagoz, Charsk (Shar), Kurchatov, Ridder, Semey (Semipalatinsk), Serebryansk, Shemonaikha, Zaysan, and Zyryanovsk.
Economy
East Kazakhstan Region's economy is dominated by industry, particularly the metallurgy industry, although the region also has a significant energy industry, forestry industry, food industry, and various light industries.[4]
₸619.4 billion was invested in the regional economy, an increase of 23.0%. A significant increase in investment was observed in industry (30.6%), transport and warehousing (36.2%), agriculture (13.8%), and construction (7.2%). Investments in fixed assets increased by 5.4% to ₸59.7 billion.
Since 2010, 74 investment projects have been implemented, at a value of ₸1.3 trillion, creating 17,600 jobs, including 3 projects of national significance.
For the period from 2010 to 2019, 50 projects were commissioned for a total of ₸731.4 billion, creating 8,600 jobs, including 4 projects in 2019 for a total of ₸24.1 billion, creating 164 jobs.
In 2020, the region plans to implement 5 projects totaling ₸16.0 billion, creating 610 jobs.
From 2021 to 2025, the region plans to implement 19 projects with a total investment of ₸555.0 billion and the creation of 8.4 thousand new jobs.
Significant industrial projects planned by the region include the construction of an automobile plant and industrial park for the production of automotive components in Öskemen under the joint-stock company "Asia Auto Kazakhstan" in 2021, and the expansion of processing capacities of Aktogay GOK by duplicating the existing sulfide factory run by KAZ Minerals Aktogay LLP in 2021.
In January–February 2020, ₸59.7 billion was invested in the regional economy, with an increase of 105.4%.
Agriculture
During the first half of 2020, the region's agricultural output totaled ₸157.1 billion, of which, ₸155.9 billion came from cattle breeding, and ₸1.1 billion came from crop growing.[8] Investments in agricultural fixed assets in the first half of 2020 totaled to ₸14.7 billion.[8]
In the first half of 2020, 1.371. million hectares of crops were sown.[8] During that time, the region recorded 1.2777 million heads of cattle, 477.4 thousand heads of horses, and 2.1759 million heads of sheep and goats.[8]
Industry
In the first half of 2020, the region's industrial output totaled ₸1.0973 trillion.[9] During this period, the region's mining industry accounted for ₸286.7 billion in output, the metallurgy industry accounted for ₸489.5 billion, the machine-building industry accounted for ₸120.4 billion, the chemicals industry accounted for ₸10.9 billion, woodworking accounted for ₸2.5 billion, light industry accounted for ₸2.3 billion, and another ₸185 billion came from other industries.[9]
The bulk of the region's metallurgical products are exported.[9]
The region's machine-building industry mostly produces mining equipment, equipment for mineral processing, oil and gas production, industrial capacitors, cables and wires, and vehicles.[9]
Education
As of 2019, the region has 312 libraries, 10 museums, and 1 "institution for the protection of historical and cultural heritage".[10]
Culture
As of 2019, the region has 301 culture clubs, 2 theaters, a zoo, 9 "houses of friendship", 6 cinemas, and 3 parks.[10]
In 2018, the Kazakhstan Ministry of Culture has funded archaeological excavations into the Shilikty Mounds and other nearby sites in the region to uncover cultural artifacts.[10]
Tourism
The East Kazakhstan Region and neighboring Almaty Region share Lake Alakol, a major domestic tourist site. In 2013, UNESCO established the Alakol Biosphere Reserve, stating that the lake and its surroundings are an important part of the Central Asian Flyway.[11] Birds native to the lake include the Dalmatian Pelican, the Eurasian Spoonbill, the Greater Flamingo, and the Ferruginous Duck.[11] The lake's color changes during the day, from azure-blue in the morning to purple at sunset. On sunny days the lake has a notably bright color, and on cloudy days the water is dark grey. The improvement of infrastructure near the lake, as well as its alleged medicinal properties, have led to increased tourism in recent years.
The Altai Alps ski resort, in the town of Tawlı Ülbi approximately 24 kilometres east of Öskemen, serves as a popular skiing destination.[12]
The Raxman Spring Sanatorium and the Katon-Karagay National Park are both located in the Katonkaragay District in the northeastern part of the region.
Sport
The region sent a bandy team to the Spartakiade 2009 and finished third.[13]
See also
References
- ↑ "Ермек Кошербаев стал акимом Восточно-Казахстанской области" (in Russian). 2023-06-16.
- 1 2 "Численность населения Республики Казахстан по отдельным этносам на начало 2020 года". Stat.kz. Retrieved 2020-08-06.
- ↑ DOSM. "Department of Statistics Kazakhstan". stat.gov.kz. Archived from the original on 2 January 2024. Retrieved 2023-03-01.
- 1 2 3 4 "East Kazakhstan Region". The Office of the Prime Minister of Kazakhstan. 2017. Archived from the original on 2017-03-07. Retrieved 2020-08-14.
- ↑ "Численность населения Республики Казахстан по отдельным этносам на начало 2020 года". Stat.kz. Retrieved 2020-08-06.
- ↑ "Kazakhstan: Regions".
- ↑ "Akimats of cities and districts". East Kazakhstan Region's Akimat. Retrieved 12 December 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 Сельское хозяйство [Agriculture] (in Russian). Akimat of the East Kazakhstan Region. Archived from the original on 2020-08-14. Retrieved 2020-08-14.
- 1 2 3 4 Промышленность и бизнес [Industry and Business]. Akimat of the East Kazakhstan Region. Archived from the original on 2020-08-14. Retrieved 2020-08-14.
- 1 2 3 Культура [Culture] (in Russian). Akimat of the East Kazakhstan Region. Archived from the original on 2020-08-14. Retrieved 2020-08-14.
- 1 2 "Alakol". UNESCO. July 2013. Archived from the original on 2020-08-14. Retrieved 2020-08-14.
- ↑ Shayakhmetova, Zhanna (2017-12-14). "Altai Alps ski resort welcomes visitors to enjoy winter activities, improve skills". The Astana Times. Archived from the original on 2020-08-14. Retrieved 2020-08-14.
- ↑ "Команда Восточно-Казахстанской области". Archived from the original on 2014-06-10. Retrieved 2014-06-10.



