| Colonial India | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
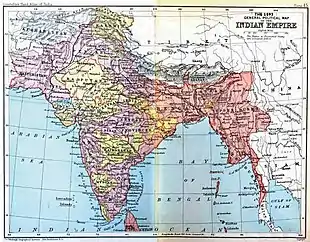
For administrative purposes British India was subdivided into the following units:
Main administrative units
Political units
While British India did administratively not include the princely states, which remained nominally outside the British Raj,[1] under the administration of their own rulers, the relationship of the British with these states was managed by:
Still, the British authorities recurred to the doctrine of lapse when they decided to interfere in the internal matters of a princely state.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Great Britain India Office. The Imperial Gazetteer of India. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1908.
- ↑ William Cooke Taylor, A Popular History of British India
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.