Tanohata
田野畑村 | |
|---|---|
 Tanohata Village Hall | |
 Flag  Seal | |
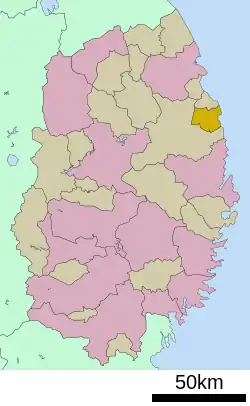 Location of Tanohata in Iwate Prefecture | |
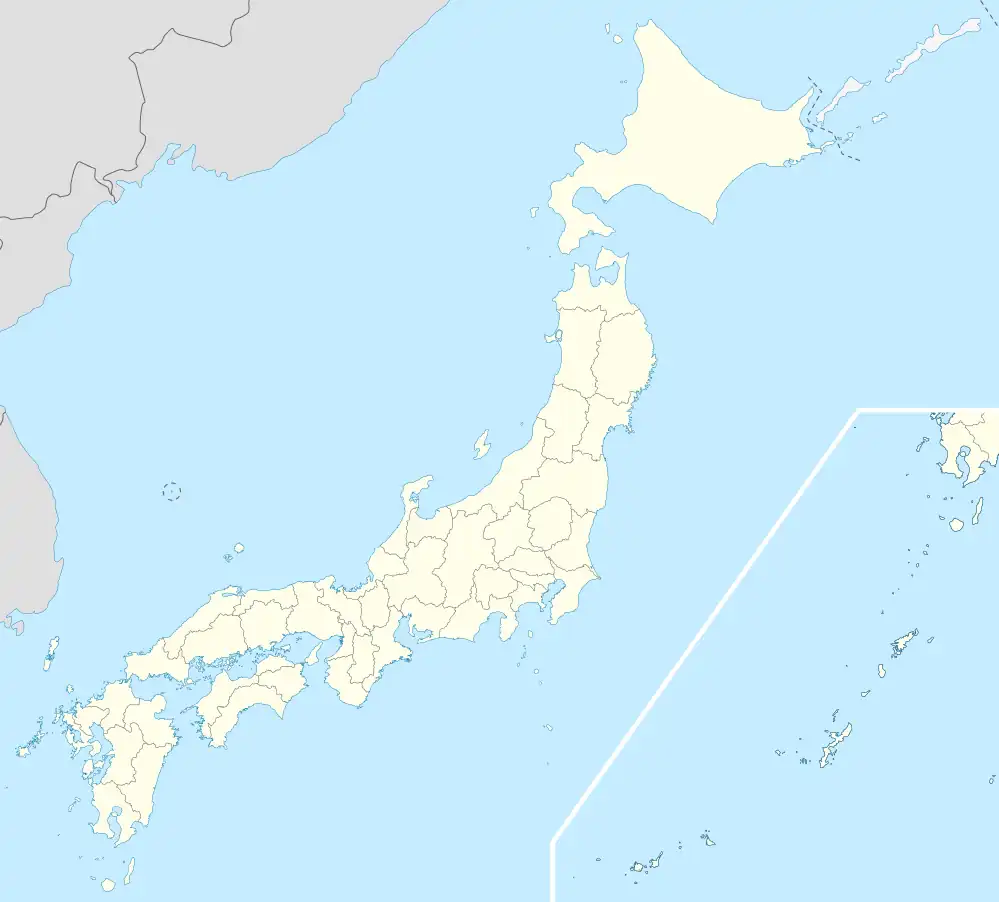 Tanohata | |
| Coordinates: 39°55′49.7″N 141°53′20.1″E / 39.930472°N 141.888917°E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Tōhoku |
| Prefecture | Iwate |
| District | Shimohei |
| Area | |
| • Total | 156.19 km2 (60.31 sq mi) |
| Population (May 1, 2020) | |
| • Total | 3,244 |
| • Density | 21/km2 (54/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| City symbols | |
| • Tree | Kiri |
| • Flower | Rhododendron subg. Hymenanthes |
| • Bird | Copper pheasant |
| Phone number | 0194-34-2111 |
| Address | 143-1 Tanohata, Tanohata-mura, Shimohei-gun, Iwate-ken 028-8407 |
| Website | Official website |

Tanohata (田野畑村, Tanohata-mura) is a village located in Iwate Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 May 2020, the village had an estimated population of 3,244, and a population density of 21 persons per km² in 1,398 households.[1] The total area of the village is 156.19 square kilometres (60.31 sq mi).
Geography
Tanohata is a coastal mountainous community situated on the rocky ria Sanriku Coast along the Pacific coast of Iwate. Parts of the village are within the borders of the Sanriku Fukkō National Park.[2]
Neighboring municipalities
Iwate Prefecture
Climate
Tanohata has a cold humid climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa) characterized by mild summers and cold winters. The average annual temperature in Tanohata is 10.1 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1201 mm with September as the wettest month and February as the driest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 22.6 °C, and lowest in January, at around -1.1 °C.[3]
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[4] the population of Tanohata peaked around the year 1960 and has declined steadily over the past 60 years.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 4,084 | — |
| 1930 | 4,314 | +5.6% |
| 1940 | 4,678 | +8.4% |
| 1950 | 5,757 | +23.1% |
| 1960 | 6,585 | +14.4% |
| 1970 | 5,412 | −17.8% |
| 1980 | 5,225 | −3.5% |
| 1990 | 5,019 | −3.9% |
| 2000 | 4,529 | −9.8% |
| 2010 | 3,843 | −15.1% |
| 2020 | 3,244 | −15.6% |
History
The area of present-day Tanohata was part of ancient Mutsu Province, dominated by the Nambu clan during the Edo period, who ruled Hachinohe Domain under the Tokugawa shogunate. With the Meiji period establishment of the modern municipalities system, the village of Tanohata was created within Kitahei District on April 1, 1889. Kitahei, Nakahei and Higashihei Districts were all merged into Minamihei District on March 29, 1896.
The area is prone to tsunami, with damage recorded as early as the 869 Sanriku earthquake. The 1611 Sanriku earthquake also caused major damage and the 1896 Sanriku earthquake destroyed most of the village, as did the 1933 Sanriku earthquake.
In 1953, the national and prefectural governments targeted Fudai for consolidation with its southern neighbor, Tanohata, following the Law for the Consolidation of Cities, Towns and Villages ("the great Shōwa mergers").[5] Merger talks continued intermittently between 1955 and 1960. The Tanohata delegation was not in favor of the merger, but because of the pressure from the prefecture to implement the government directive, they felt they were not at liberty to directly reject the proposal. At a party in May 1960 to celebrate the end of the long merger negotiations, the mayor of Tanohata drunkenly insulted the delegates from Fudai in a final effort to scuttle the negotiations.[5] The party was abandoned, and no further serious attempts were made to continue with the merger.[5]
The tsunami following the March 11 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami completely destroyed more than 200 buildings in the village, killing 39 residents and also destroying 512 of the 565 vessels in the local fishing cooperative.[6] The height of the tsunami was estimated at more than 10 meters at Shimanokoshi Station, which was completely washed away.[7] In October 2013, a sign from the village was found washed up on Kahuku Beach, Hawaii.[8]
Government
Tanohata has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral village council of 10 members. Tanohata, together with the city of Miyako, town of Iwaizumi and the villages of Fudai and Yamada, collectively contributes three seats to the Iwate Prefectural legislature. In terms of national politics, the village is part of Iwate 2nd district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy
The local economy is based on commercial fishing and to a lesser extent on agriculture.
Education
Tanohata has one public elementary school and one public junior high school operated by the village government. The village does not have a high school.
Transportation
Railway
Highway
Local attractions
References
- ↑ Tanohata Village official home page
- ↑ "Introducing places of interest: Rikuchukaigan National Park". Ministry of the Environment (Japan). Archived from the original on 8 February 2012. Retrieved 17 May 2011.
- ↑ Fudai climate data
- ↑ Tanahata population statistics
- 1 2 3 Bailey, Jackson H. (1991). Ordinary people, extraordinary lives : political and economic change in a Tōhoku village. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. pp. 272. ISBN 978-0-8248-1299-7.
- ↑ "東日本大震災 図説集". 毎日jp. 毎日新聞社. 2011-04-10. Archived from the original on 2011-06-22. Retrieved 2011-04-17.
- ↑ "三陸鉄道「国の支援なければ、もはや何も…」". YOMIURI ONLINE. 読売新聞社. 2011-04-05. Retrieved 2011-04-05.
- ↑ "Japan's tsunami debris: Five remarkable stories". BBC News. March 9, 2015. Retrieved March 9, 2015.
External links
![]() Media related to Tanohata, Iwate at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Tanohata, Iwate at Wikimedia Commons
- Official Website (in Japanese)