40°36′48″N 74°02′53″W / 40.61333°N 74.04806°W
| The Narrows | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | |
 A TERRA satellite image of New York Harbor with The Narrows (in red), connecting Upper New York Bay to Lower New York Bay | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | New York |
| Municipality | New York City |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Upper New York Bay |
| Mouth | Lower New York Bay |
The Narrows is the tidal strait separating the boroughs of Staten Island and Brooklyn in New York City. It connects the Upper New York Bay and Lower New York Bay and forms the principal channel by which the Hudson River empties into the Atlantic Ocean. It has long been considered to be the maritime "gateway" to New York City and historically has been one of the most important entrances into the harbors of the Port of New York and New Jersey.
History
Pre-history
The Narrows was most likely formed after deposition of the Harbor Hill Moraine about 18,000 years prior to the end of the last ice age. Previously, Staten Island and Brooklyn were connected and the Hudson River emptied into the Atlantic Ocean through the Raritan River, taking a more westerly course through parts of present-day northern New Jersey, along the eastern side of the Watchung Mountains to Bound Brook, New Jersey, and then on into the Atlantic via Raritan Bay. A build-up of water in the Upper Bay allowed the river to break through to form The Narrows less than 12,000 to 13,000 years ago as it exists today.[1]
Post-European contact
The first recorded European entrance into The Narrows was in 1524 by Giovanni da Verrazzano, who set anchor in the strait and was greeted by a group of Lenape, who paddled out to meet him in the strait.
In August 1776, the British forces under William Howe on Staten Island undertook an amphibious operation across the Narrows and landed in Brooklyn, where they routed Washington's Army at the Battle of Long Island.
The Staten Island Tunnel, carrying the New York City Subway across the Narrows, was partially built during the 1920s but was never completed.[2] The Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge was completed across the Narrows in 1964.[3] The longest suspension bridge in the world at the time, it is still the longest suspension bridge in the United States (by length of the main span).[4]
.jpg.webp)
_under_the_Verrazano_Narrows_Bridge.jpg.webp) The Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge, shown with USS Leyte Gulf passing underneath it, spans The Narrows
The Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge, shown with USS Leyte Gulf passing underneath it, spans The Narrows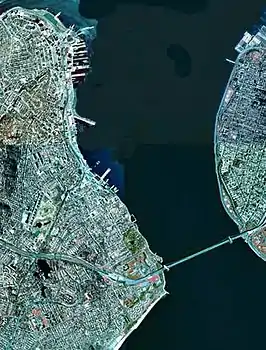 A satellite view of The Narrows with Staten Island (on the left) and Brooklyn (on the right) connected by the Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge
A satellite view of The Narrows with Staten Island (on the left) and Brooklyn (on the right) connected by the Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge
See also
References
Notes
- ↑ Charles Merguerian (2003): The Narrows, Flood – Post-Woodfordian Meltwater Breach of the Narrows Channel, NYC (pdf; 1,5 MB)
- ↑ Raskin, Joseph B. (2013). The Routes Not Taken: A Trip Through New York City's Unbuilt Subway System. New York, New York: Fordham University Press. doi:10.5422/fordham/9780823253692.001.0001. ISBN 978-0-82325-369-2.
- ↑ "Verrazano Bridge Opened to Traffic; New Landmark Greeted With Fanfare in Harbor". The New York Times. November 22, 1964. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved November 28, 2022.
- ↑ McCauley, J. K. (November 25, 2014). "The Verrazano-Narrows Bridge at 50". City Room. Retrieved November 28, 2022.
Bibliography
- Merguerian, Charles. "The Narrows, Flood – Post-Woodfordian Meltwater Breach of the Narrows Channel, NYC" (2003)
- Waldman, John. Heartbeats in the Muck The Lyons Press; (2000). ISBN 1-55821-720-7
External links
 Media related to The Narrows at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to The Narrows at Wikimedia Commons