 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Cyanic dithioperoxyanhydride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2N2S2 | |
| Molar mass | 116.16 g mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
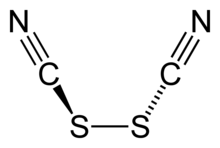
Thiocyanogen, (SCN)2, is a pseudohalogen derived from the pseudohalide thiocyanate, [SCN]−. This hexatomic compound exhibits C2 point group symmetry and has the connectivity NCS-SCN.[1] The oxidation ability is greater than bromine. It reacts with water:[2]
- 3(SCN)2 + 4H2O → H2SO4 + HCN + 5SCN− + 5H+
Thiocyanogen was originally prepared by the reaction of iodine with a suspension of silver thiocyanate in diethyl ether,[3] but this reaction suffers from competing equilibria attributed to the weak oxidizing power of iodine. These same investigations led Söderbäck to the isolation of sulfur dicyanide. An improved method for generating thiocyanogen entails oxidation of plumbous thiocyanate, which precipitates when aqueous solutions of lead(II) nitrate and sodium thiocyanate are combined. A suspension of anhydrous Pb(SCN)2 is treated with bromine in glacial acetic acid to afford a 0.1M solution of thiocyanogen that is stable for days.[4] Alternatively, a solution of bromine in methylene chloride is added to a suspension of Pb(SCN)2 in methylene chloride at 0 °C.[5]
- Pb(SCN)2 + Br2 → (SCN)2 + PbBr2
Thiocyanogen adds to alkenes to give 1,2-bis(thiocyanato) compounds and reacts with titanacyclopentadienes giving (Z,Z)-1,4-bis(thiocyanato)-1,3-butadienes, which in turn can be converted to 1,2-dithiins.[5] Selenocyanogen, (SeCN)2, prepared from reaction of silver selenocyanate with iodine in tetrahydrofuran at 0 °C,[6] reacts in a similar manner to thiocyanogen.[5]
References
- ↑ Jensen, James (2005). "Vibrational frequencies and structural determination of thiocyanogen". Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM. 714 (2–3): 137–141. doi:10.1016/j.theochem.2004.09.046.
- ↑ Stedman, G.; Whincup, P. A. E. (1969). "Oxidation of metal thiocyanates by nitric and nitrous acids. Part I. Products". Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical: 1145. doi:10.1039/j19690001145. ISSN 0022-4944.
- ↑ Söderbäck, Erik (1919). "Studien über das freie Rhodan". Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie. 419 (3): 217–322. doi:10.1002/jlac.19194190302. hdl:2027/uc1.$b133351.
- ↑ Gardner, William Howlett; Weinberger, Harold (1939). "Chapter 29: Thiocyanogen Solution, in Inorganic Syntheses". Inorganic Syntheses. 1: 84–86. doi:10.1002/9780470132326.ch29. ISBN 978-0-470-13232-6.
- 1 2 3 Block, E; Birringer, M; DeOrazio, R; Fabian, J; Glass, RS; Guo, C; He, C; Lorance, E; Qian, Q; Schroeder, TB; Shan, Z; Thiruvazhi, M; Wilson, GC; Zhang, Z (2000). "Synthesis, Properties, Oxidation, and Electrochemistry of 1,2-Dichalcogenins". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122 (21): 5052–5064. doi:10.1021/ja994134s.
- ↑ Meinke, PT; Krafft, GA; Guram, A (1988). "Synthesis of selenocyanates via cyanoselenation of organocopper reagents". J. Org. Chem. 53 (15): 3632–3634. doi:10.1021/jo00250a047.