
Trees play multiple roles in J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy world of Middle-earth, some such as Old Man Willow indeed serving as characters in the plot. Both for Tolkien personally, and in his Middle-earth writings, caring about trees really mattered. Indeed, the Tolkien scholar Matthew Dickerson wrote "It would be difficult to overestimate the importance of trees in the writings of J. R. R. Tolkien."[4]
Tolkien stated that primaeval human understanding was communion with other living things, including trees. Treebeard, a tree-giant or Ent, herds trees including the Huorns which are halfway between Ents and trees, either becoming animated or reverting to becoming treelike.
Some specific kinds of tree are important in Tolkien's stories, such as the tall Mallorn trees at the heart of Lothlórien. In Tom Bombadil's Old Forest, Old Man Willow is a malign and fallen tree-spirit of great age, controlling much of the forest. Early in the creation, the Two Trees of Valinor, one silver, one gold, gave light to the paradisiacal realm of Valinor.
Commentators have written that trees gave Tolkien a way of expressing his eco-criticism, opposed to damaging industrialisation.
"A deep feeling for trees"

In a 1955 letter to his publisher, Tolkien wrote "I am (obviously) much in love with plants and above all trees, and always have been; and I find human mistreatment of them as hard to bear as some find ill-treatment of animals".[T 1]
Tolkien's biographer John Garth writes that "A deep feeling for trees is Tolkien's most distinctive response to the natural world."[5] The Tolkien scholars Shelley Saguaro and Deborah Cogan Thacker comment that Tolkien clearly loved trees; he was often photographed with them, such as with the large black pine in the Oxford Botanic Garden.[1][2] The "mythical mallorn" tree may be magical: but for Tolkien, all trees were, they write, in some sense "magical".[1] Dickerson adds that Tolkien used a tree as a picture of his own subcreation in Leaf by Niggle; and when his friend C. S. Lewis died, he applied the picture to himself, writing that he felt "like an old tree that is losing all its leaves one by one: this feels like an axe-blow near the roots".[4][T 2]
The flowers and plants of Middle-earth are used for the realistic subcreation of a secondary world. In Dinah Hazell's view, this at once serves a "narrative function, provides a sense of place, and enlivens characterization".[6]
Tree species in Middle-earth
Specific kinds of tree play a role, such as the tall Mallorn trees of Lothlórien; Galadriel gives Sam Gamgee a seed of the more or less magical Mallorn.[1] After "the Scouring of the Shire", he plants it in the party field, near the centre of the Shire, to replace the much-loved tree there cut down by Sharkey's men.[T 3][T 4] When Frodo enters Lothlórien and first acquaints himself with the Mallorn trees: "He felt a delight in wood and the touch of it, neither as forester nor as carpenter; it was the delight of the living tree itself."[T 5]

Tolkien's poem "Sing all ye joyful!" at the end of The Hobbit has in its last verse a mention of six kinds of tree:[T 6]
Lullaby! Lullaby! Alder and Willow!
Sigh no more Pine, till the wind of the morn!
Fall Moon! Dark be the land!
Hush! Hush! Oak, Ash, and Thorn!— The Hobbit, "The Last Stage"
The last phrase naming three English trees echoes Rudyard Kipling's "A Tree Song", with its refrain:[7]
Of all the trees that grow so fair,
Old England to adorn,
Greater are none beneath the Sun,
Than Oak, and Ash, and Thorn.— Rudyard Kipling, "A Tree Song"
The Tolkien scholar Tom Shippey writes that while Tolkien does not mention Kipling, he shares the "theme of unchanging Englishness" seen in Kipling's writing.[8] Tolkien names the same three trees in Tree and Leaf: "Each leaf, of oak and ash and thorn, is a unique embodiment of the pattern..."; Saguaro and Thacker write that this is "a plea for the 'recovery fairy stories help us to make'".[1] Dale Nelson in the J.R.R. Tolkien Encyclopedia writes that the affinity of Kipling's Puck for these three trees "make him kin to Bombadil and Treebeard".[9]
Individual trees
Mythic symbols
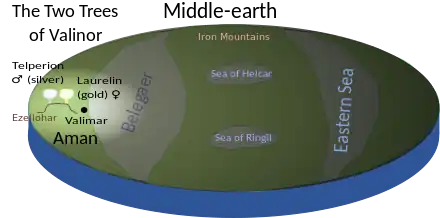
The Two Trees of Valinor, Telperion and Laurelin, one silver, one gold, gave light to the paradisiacal realm of Valinor,[T 7] where "Through long ages the Valar dwelt in bliss in the light of the Trees beyond the Mountains of Aman".[T 8] This continued until they were destroyed by the evil giant spider Ungoliant and the first Dark Lord, Melkor, leaving only a flower and a fruit which became the Moon and the Sun for Middle-earth.[T 9] The Tolkien scholar Matthew Dickerson writes that the Two Trees are "the most important mythic symbols in all of the legendarium".[4] Some of the light of the Trees was saved in the Silmarils, central to the mythology of The Silmarillion.[T 8][T 10]

Another tree, Galathilion, was created in the image of Telperion. One of its seedlings, Celeborn, was brought to the island of Tol Eressëa. One of its seedlings was given to the Men of Númenor, and it became Nimloth, the White Tree of Númenor. It was destroyed by the King, Ar-Pharazôn, who had come under Sauron's influence; but the hero Isildur had saved one of its fruits, and when he arrived in Middle-earth from the wreck of Númenor, he planted its seeds; one of these grew into the White Tree of Gondor. When the line of Kings of Gondor failed, the White Tree died, and stood dead and leafless, but still honoured, in the royal courtyard of the city of Minas Tirith throughout the centuries of rule by the Stewards of Gondor. When Aragorn returned as King, he fittingly found a seedling of the White Tree on the mountain behind the city.[T 11][4] He returns with it to the citadel and plants it in the court, where it quickly comes to flower.[T 11] Saguaro and Thacker call this "deliberately religious language and imagery".[1] Dickerson writes that it is the symbol of Aragorn's kingship, being descended from Nimloth, the White Tree of Numenor, itself descended from Telperion.[4]
The Tolkien translator and author Stéphanie Loubechine describes the opposing roles of the beneficial birch and the malign willow in Tolkien's tree symbolism, on the view that plants are not simply a green backdrop but consistently carry meaning.[10] Curry comments that Tolkien's trees are never just symbols, also being individuals in the narrative. He mentions a real-world instance, a "great-limbed poplar tree" that grew by Tolkien's house; when it was "suddenly lopped and mutilated by its owner", he notes that Tolkien described the event as a "barbarous punishment for any crimes it may have been accused of". Within Middle-earth, Curry quotes the Ent or tree-giant Treebeard's account of the traitorous wizard Saruman's destruction in Fangorn Forest: "Curse him, root and branch! many of those trees were my friends, creatures I had known from nut and acorn; many had voices of their own that are lost for ever now. And there are wastes of stump and bramble where once there were singing groves".[11]
Fallen nature
Old Man Willow is a malign tree-spirit of great age in Tom Bombadil's Old Forest, appearing physically as a large willow tree beside the River Withywindle, but spreading his influence throughout the forest, who as Tolkien explains[T 12][1]
But none was more dangerous than the Great Willow: his heart was rotten, but his strength was green; and he was cunning, and a master of winds, and his song and thought ran through the woods on both sides of the river. His grey thirsty spirit drew power out of the earth and spread like fine root-threads in the ground, and invisible twig fingers in the air, till it had under its dominion nearly all the trees of the Forest from the Hedge to the Downs.[T 13]

Saguaro and Thacker comment that critics have puzzled over this depiction, as it does not fit with Tolkien's image as an environmentalist "tree-hugger". They write that trees (like other creatures) are in Tolkien's world subject to the corruption of the Fall of Man, mentioning Tolkien's Catholicism. They state that while Tolkien's writings on the meaning of trees verges on the pagan, both the Old and the New Testament use trees as symbols, the Tree of Knowledge of Good and Evil in Genesis, the Cross, the tree of death in the Gospels, and the Tree of Life in Revelation (22:2); and that Tolkien succeeds in "bring[ing] all these elements together" in The Lord of the Rings: death, creation, sub-creation, re-creation.[1] Dickerson writes that Old Man Willow indicates both that nature, like Man, is fallen, and that it is actively hostile to Man.[4] The Tolkien critic Jared Lobdell compares the "treachery of natural things in an animate world" seen in the character of Old Man Willow to Algernon Blackwood's story "The Willows".[9][12]
Animated trees
Fangorn forest is the realm of Treebeard (also called Fangorn), a tree-giant or Ent (from the Old English for "giant"), one of the oldest living things, or actually the oldest living thing, in Middle-earth. The Ents are tree-herds; they are fully sentient but look much like trees: they have branch-like arms, root-like legs, faces, and the ability to move and speak. Among their charges are the Huorns, which are either trees in the process of becoming animated, or Ents that are reverting to becoming treelike.[T 14][T 15][13] The trees in the Old Forest are not so clearly sentient, but they too convey emotion, even vindictiveness, seeking to impede the intruding Hobbits.[14]
Eco-criticism
Dickerson comments that trees provide "a potent vehicle for [Tolkien's] eco-criticism."[4] The party tree in Hobbiton near the centre of the Shire appears at the beginning and the end of The Lord of the Rings: at the start, as the tree that just happens to be in the party field, a happy place; at the end, cut down by Saruman's ruffians to no useful purpose.[T 16][T 3] Dickerson writes that Saruman's "evil ways" are revealed exactly by his "wanton destruction" of Fangorn's trees, and notes that Treebeard calls Saruman an "accursed tree-slayer".[4][T 17] The Tolkien critic Paul Kocher notes that Treebeard says that ents have a far closer sympathy for trees than shepherds do for their sheep, because "ents are 'good at getting inside other things'". He also cites Treebeard's statement that he is "not altogether on anybody's side, because nobody is altogether on my side ... nobody cares for the woods as I care for them", but notes that all the same, he is driven by the knowledge that Saruman has taken sides in the War of the Ring to take action against him. He destroys Saruman's industrial Isengard, whose factories Saruman was fuelling by cutting down Treebeard's trees. After the destruction of the One Ring, Aragorn gives wide lands for new forest; but, Kocher writes, Tolkien gives "ominous hints that the wild wood will not prosper in the expanding Age of Man" that will follow.[15]
See also
References
Primary
- ↑ Carpenter (1981). Letters, #165 to Houghton Mifflin, June 1955
- ↑ Carpenter (1981). Letters, #251 to Priscilla Tolkien, 26 November 1963
- 1 2 Tolkien 1955, book 6, ch. 8 "The Scouring of the Shire"
- ↑ Tolkien 1955, book 6, ch. 9 "The Grey Havens"
- ↑ Tolkien 1954a, book 2, ch. 6 "Lothlorien"
- ↑ Tolkien 1937, ch. 19 "The Last Stage"
- ↑ Tolkien 1977, "Quenta Silmarillion", ch. 1 "Of the Beginning of Days"
- 1 2 Tolkien 1977, "Quenta Silmarillion", ch. 3 "Of the Coming of the Elves and the Captivity of Melkor"
- ↑ Tolkien 1977, "Quenta Silmarillion", ch. 8 "Of the Darkening of Valinor"
- ↑ The Silmarillion, "Quenta Silmarillion", ch. 8 "Of the Darkening of Valinor"
- 1 2 Tolkien 1955, book 6, ch. 5 "The Steward and the King"
- ↑ Tolkien 1954a, book 1, ch. 6 "The Old Forest"
- ↑ Tolkien 1954a, book 1, ch. 7 "In the House of Tom Bombadil"
- ↑ Tolkien 1954, book 3, ch. 4 "Treebeard"
- ↑ Tolkien 1954, book 3, ch. 9 "Flotsam and Jetsam"
- ↑ Tolkien 1954a, book 1, ch. 1 "A Long-Expected Party"
- ↑ Tolkien 1955, book 6, ch. 6 "Many Partings"
Secondary
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Saguaro, Shelley; Thacker, Deborah Cogan (2013). Chapter 9. Tolkien and Trees J. R. R. Tolkien The Hobbit and the Lord of the Rings. Palgrave Macmillan (New Casebooks). pp. 138–154. ISBN 978-1-137-26399-5.
- 1 2 Townshend, Emma (6 August 2014). "Tolkien's black pine: Why do we love old trees?". The Independent.
- ↑ O'Byrne 2019.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Dickerson 2013.
- ↑ Garth 2020, pp. 112–131.
- ↑ Hazell 2015, Introduction.
- ↑ Kipling, Rudyard. "A Tree Song". Kipling Society. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- ↑ Shippey 2005, p. 397.
- 1 2 Nelson, Dale (2013) [2007]. "Literary Influences: Nineteenth and Twentieth Centuries". In Drout, Michael D. C. (ed.). J.R.R. Tolkien Encyclopedia. Routledge. pp. 372–377. ISBN 978-0-415-86511-1.
- ↑ Loubechine, Stéphanie "Le Saule et le Bouleau — Symbolique de l'arbre chez Tolkien" [The Birch and the Willow – Tolkien's Tree Symbolism] in Willis 2011, Chapter 1
- ↑ Curry 2000, p. 283.
- ↑ Lobdell, Jared (2004). The World of the Rings: Language, Religion, and Adventure in Tolkien. Open Court. p. 9. ISBN 978-0-8126-9569-4. OCLC 54767347.
- ↑ Hammond, Wayne G.; Scull, Christina (2005). The Lord of the Rings: A Reader's Companion. HarperCollins. pp. 372–373. ISBN 978-0-00-720907-1.
- ↑ Cohen 2009, pp. 91–125.
- ↑ Kocher 1974, pp. 102–103.
Sources
- Carpenter, Humphrey, ed. (1981). The Letters of J. R. R. Tolkien. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0-395-31555-2.
- Cohen, Cynthia M. (2009). "The Unique Representation of Trees in 'The Lord of the Rings'". Tolkien Studies. Project MUSE. 6 (1): 91–125. doi:10.1353/tks.0.0041. ISSN 1547-3163.
- Curry, Patrick (2000). "Defending Middle-earth". In Coupe, Laurence (ed.). The Green Studies Reader: From Romanticism to Ecocriticism. Psychology Press. pp. 282ff (chapter 47). ISBN 978-0-415-20406-4.
- Dickerson, Matthew T. (2013) [2007]. "Trees". In Drout, Michael D. C. (ed.). J.R.R. Tolkien Encyclopedia. Routledge. pp. 678–679. ISBN 978-0-415-96942-0.
- Garth, John (2020). "Tree-woven Lands". The Worlds of J.R.R. Tolkien: The Places that Inspired Middle-earth. London: Frances Lincoln Publishers. pp. 112–131. ISBN 978-0-71124-127-5.
- Hazell, Dinah (2015). The Plants of Middle-earth: Botany and Sub-creation (Paperback ed.). Kent State University Press. ISBN 978-1-60635-265-6.
- Kocher, Paul (1974) [1972]. Master of Middle-earth: The Achievement of J.R.R. Tolkien. Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14003-877-4.
- O'Byrne, Damian (2019). "9. The Fiendish Forests of Middle-earth: Tolkien's Trees as Ominous Adversaries". In Hackett, Jon; Harrington, Sean (eds.). Beasts of the Forest: Denizens of the Dark Woods. Indiana University Press. pp. 133–146. ISBN 978-0-8619-6959-3.
- Shippey, Tom (2005) [1982]. The Road to Middle-Earth (Third ed.). HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0261102750.
- Tolkien, J. R. R. (1937). Douglas A. Anderson (ed.). The Annotated Hobbit. Boston: Houghton Mifflin (published 2002). ISBN 978-0-618-13470-0.
- Tolkien, J. R. R. (1954a). The Fellowship of the Ring. The Lord of the Rings. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. OCLC 9552942.
- Tolkien, J. R. R. (1954). The Two Towers. The Lord of the Rings. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. OCLC 1042159111.
- Tolkien, J. R. R. (1955). The Return of the King. The Lord of the Rings. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. OCLC 519647821.
- Tolkien, J. R. R. (1977). Christopher Tolkien (ed.). The Silmarillion. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0-395-25730-2.
- Willis, Didier, ed. (2011). Tolkien, le façonnement d'un monde – volume 1, Botanique et Astronomie [Tolkien, the Shaping of a World – volume 1, Botany and Astronomy] (in French). Le Dragon de Brume. ISBN 978-2-9539896-0-1.
