| Trichomonasvirus | |
|---|---|
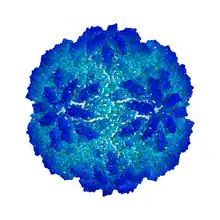 | |
| Cryo-EM image of protein surface of Trichomonas vaginalis virus 1 | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Duplornaviricota |
| Class: | Chrymotiviricetes |
| Order: | Ghabrivirales |
| Family: | Totiviridae |
| Genus: | Trichomonasvirus |
Trichomonasvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Totiviridae. The protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis serves as the natural host. There are four species in this genus.[1][2]
Taxonomy
The following four species are assigned to the genus:[2]
- Trichomonas vaginalis virus 1
- Trichomonas vaginalis virus 2
- Trichomonas vaginalis virus 3
- Trichomonas vaginalis virus 4
Structure
Viruses in Trichomonasvirus are non-enveloped, with icosahedral geometries, and T=2 symmetry. The diameter is around 36 nm. Genomes are linear and non-segmented, around 4.6-4.9kb in length. The genome has 2 open reading frames.[1]
| Genus | Structure | Symmetry | Capsid | Genomic arrangement | Genomic segmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trichomonasvirus | Icosahedral | T=2 | Non-enveloped | Linear |
Life cycle
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment to host receptors, which mediates endocytosis. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. Protozoan parasite trichomonas vaginalis serve as the natural host.[1]
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trichomonasvirus | Protozoa | Endocytosis | Unknown | Unknown | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Unknown |
References
- 1 2 3 "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 13 August 2015.
- 1 2 "Virus Taxonomy: 2020 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). March 2021. Retrieved 13 May 2021.