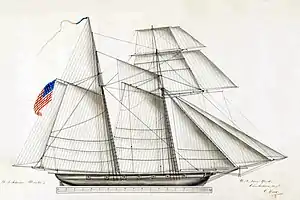
 Alligator | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | USS Alligator |
| Builder | Boston Navy Yard |
| Laid down | 26 June 1820 |
| Launched | 2 November 1820 |
| Commissioned | March 1821 |
| Fate | Wrecked, 23 November 1822 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type | Schooner |
| Tonnage | 198 |
| Length | 86 ft (26 m) |
| Beam | 24 ft 7 in (7.49 m) |
| Depth | 10 ft 4 in (3.15 m) |
| Propulsion | Sail |
| Speed | 8 knots (15 km/h; 9.2 mph) |
| Armament | 12 × 6-pounder guns |
The third USS Alligator was a schooner in the United States Navy.
Alligator was laid down on 26 June 1820 by the Boston Navy Yard; launched on 2 November 1820; and commissioned in March 1821 – probably on the 26th – with Lieutenant Robert F. Stockton in command. On 6 June 1996, the site of her wreck was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.
First anti-slavery patrol
When Alligator put to sea from Boston, Massachusetts on 3 April, she embarked upon a twofold mission. Lt. Stockton had been given command of Alligator as a result of his dogged efforts to persuade the Secretary of the Navy, Smith Thompson, to pass over several officers senior to him so that, in addition to cruising the west African coast to suppress the slave trade, he might also search for and acquire a stretch of the coast of Africa for the American Colonization Society. The Society had previously established a colony of former American slaves on the coast, but the climate in that area was so debilitating and unhealthy that the colony had disintegrated. Representatives of the Society therefore had approached Stockton to aid them in the acquisition of a more suitable parcel of land.
After a stop at New York to complete her crew, the warship sailed for waters off the west coast of Africa where she cruised from Cape Verde south to the equator in an effort to stem the illegal exportation of slaves from Africa to the Americas. Though she captured several slavers, among which were the schooners Mathilde, L'Eliza, and Daphne, perhaps her greatest contribution was the selection and acquisition of the territory around Cape Mesurado by her commanding officer and a representative of the American Colonization Society, Dr. Eli Ayers, who was embarked in Alligator for that purpose. The negotiations with the primary native chieftain, King Peter, involved great danger since his people were noted slavers themselves. Initial negotiations went well, but King Peter failed to appear at the appointed time to conclude the treaty. Instead, he repaired to a place some 20 miles inland leaving Stockton with the challenge to follow him to his retreat inland "if he dare." Thereupon, Stockton and Ayres took up the figurative gauntlet and headed inland. The result of their efforts – the parcel of coast around Cape Mesurado – was the germ from which the Republic of Liberia grew.
With that mission concluded, Alligator set sail to return to the United States and reentered Boston sometime in July. She remained there into the fall.
Second anti-slavery patrol
On 4 October 1821, Alligator put to sea from Boston again bound for the west coast of Africa. On 5 November, she encountered a strange sail ahead steering a perpendicular course. On sighting Alligator, the newcomer, instead of continuing on her way, lay to and awaited Alligator's approach. Lookouts on the American schooner soon reported that the stranger was wearing a distress flag, and Alligator moved in to offer assistance. However, when the warship entered gun range, the supposedly endangered vessel opened fire upon her and hoisted the Portuguese flag. Since the malefactor possessed guns of longer range than those mounted in Alligator, Lt. Stockton was obliged to load his guns and then to have his crew lie flat on the deck while he steered his ship in on her. The wind was slight that day, and Alligator weathered several hours of bombardment and suffered several casualties before she had the enemy within range of her own guns. When she succeeded, though, the issue was resolved rapidly. Her first volley sent the stranger's entire crew below for shelter. The American ship then poured broadside after broadside into her for about 20 minutes. At that point, Alligator's adversary struck her colors. Stockton hailed her, and her captain came on deck. He claimed her to be a Portuguese letter of marque.
Records of this action have identified this vessel by two slightly different names, Mariano Faliero and Marianna Flora, Stockton deemed her to be a pirate, put a prize crew on board, and sent her back to the United States to be condemned by an admiralty court. However, she was returned to her owners in response to the request of the Portuguese Government. During the remainder of the cruise, Alligator captured several slavers off the coast of Africa before returning to Boston.
Anti-piracy patrol
Early in 1822, Alligator sailed from Boston to the West Indies to combat the piracy then rampant in the Caribbean. In April, she took the pirate schooner Cienega off Nuevitas, Cuba. Alligator remained on the West Indian station for the remainder of her career.

While at Matanzas in November of that year, she got word that an American schooner and brig had been taken by a group of pirates and were located about 45 mi (72 km) east of Matanzas. She took the master and mate of the captured schooner on board and set sail to reclaim the American ships. She arrived at her destination at dawn on 9 November and found the pirates in possession of one ship, two brigs, and five schooners. Alligator launched armed boats which gave chase to a heavily armed schooner that opened fire with five of her guns and commenced a battle. The boats from Alligator pressed home their attack and soon overhauled the schooner which they boarded in a mad rush. In the short, but sharp, fight, Alligator lost her commanding officer, Lieutenant William H. Allen, wounded mortally by two musket balls. The captured vessel, of 80 tons (bm), was armed with one long 18-pounder gun on a pivot, and with four smaller guns. US casualties amounted to eight men killed and wounded.[1]
Soon thereafter, boats from Alligator captured all the pirate vessels except one schooner that managed to escape.[lower-alpha 1] Most of the pirates fled ashore.
Alligator recaptured William and Henry, which had been on her way from New York to New Orleans when captured, the brigs Iris and Sarah, from Boston to New Orleans, the schooner Argo, from Salem, and Nancy and Mary, of Boston.[1]
On 18 November 1822, Alligator, Lieutenant Dale, commanding, departed Matanzas for Norfolk, while escorting a convoy.[1]
Before dawn the following morning, she ran hard aground on what is now known as Alligator Reef off the coast of Florida.[3] After working desperately to refloat their ship, officers and crewmen gave up on a hopeless task. On 21 November they spied a vessel, and made signals of distress. The vessel took the survivors off.[1] On 23 November 1822, before they left, they set fire to Alligator, which soon blew up.
The wreck was initially thought to be located at 24°51′05″N 80°37′06″W / 24.85139°N 80.61833°W,[4] although a 1996 expedition proved this false, and the location of the Alligator remains unknown.[5]
See also
- List of historical schooners
- USS Ferret (1822) (Anti piracy schooner)
Notes
- ↑ The pirate vessel may have been Zaragozana. Her captain, Cayatano Arogonez (or Cayetano Aragonés), boasted after his capture that it was he who had killed Lieutenant Allen.[2]
Citations
- 1 2 3 4 Allen (1823), pp. 263–265.
- ↑ "By the sloop Providence, we have files of Jamaica papers to the 13th ult", 8 May 1823, Fayetteville Observer (Fayetteville, NC, United States) Volume: 6 , Issue: 49.
- ↑ Barnette, Michael C. (2008). Florida's Shipwrecks. Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7385-5413-6.
- ↑ Allen, Tony (1 February 2015). "Shipwrecks of Florida". Electric Blue Fishing. Retrieved 4 August 2016.
References
- Allen, William (1823). Accounts of shipwreck and of other disasters at sea: designed to be interesting and useful to mariners, with an appendix, containing Dr. Payson's address to seamen and a few prayers for their use.
- This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. The entry can be found here.
