 |
| Part of a series on the |
| Military of ancient Rome |
|---|
|
|
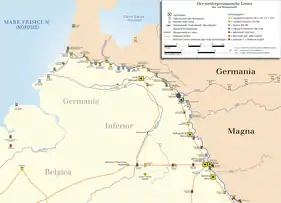
The Limes Germanicus (Latin for Germanic frontier) is the name given in modern times to a line of frontier (limes) fortifications that bounded the ancient Roman provinces of Germania Inferior, Germania Superior and Raetia, dividing the Roman Empire and the unsubdued Germanic tribes from the years 83 to about 260 AD. The Limes used either a natural boundary such as a river or typically an earth bank and ditch with a wooden palisade and watchtowers at intervals. A system of linked forts was built behind the Limes.
The path of the limes changed over time following advances and retreats due to pressure from external threats. At its height, the Limes Germanicus stretched from the North Sea outlet of the Rhine to near Regensburg (Castra Regina) on the Danube. These two major rivers afforded natural protection from mass incursions into imperial territory, with the exception of a gap stretching roughly from Mogontiacum (Mainz) on the Rhine to Castra Regina.
The Limes Germanicus was divided into:
- The Lower Germanic Limes, which extended from the North Sea at Katwijk in the Netherlands along the then main Lower Rhine branches (modern Oude Rijn, Leidse Rijn, Kromme Rijn, Nederrijn)
- The Upper Germanic Limes started from the Rhine at Rheinbrohl (Neuwied (district)) across the Taunus mountains to the river Main (East of Hanau), then along the Main to Miltenberg, and from Osterburken (Neckar-Odenwald-Kreis) south to Lorch (in Ostalbkreis, Württemberg) in a nearly perfect straight line of more than 70 km;
- The Rhaetian Limes extended east from Lorch to Eining (close to Kelheim) on the Danube.
The total length was 568 km (353 mi). It included at least 60 forts and 900 watchtowers. The potentially weakest, hence most heavily guarded, part of the Limes was the aforementioned gap between the westward bend of the Rhine at modern-day Mainz and the main flow of the Danube at Regensburg. This 300-kilometre-wide (190 mi) land corridor between the two great rivers permitted movement of large groups of people without the need for water transport, hence the heavy concentration of forts and towers there, arranged in depth and in multiple layers along waterways, fords, roads, and hilltops.
History



Roman border defences have become much better known through systematic excavations financed by Germany and through other research connected to them. In 2005, the remnants of the Upper Germanic & Rhaetian Limes were inscribed on the List of UNESCO World Heritage Sites as Frontiers of the Roman Empire.[1] In 2021, the Lower Germanic Limes were separately inscribed on the World Heritage List.[2] The Saalburg is a reconstructed fortification and museum of the Limes near Frankfurt.
Augustus
The first emperor who began to build fortifications along the border was Augustus, shortly after the devastating Roman defeat at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in 9 AD. Originally there were numerous Limes walls, which were then connected to form the Upper Germanic Limes along the Rhine and the Rhaetian Limes along the Danube. Later these two walls were linked to form a common borderline.
14 to c. 73
From the death of Augustus (14 AD) until after 70 AD, Rome accepted as her Germanic frontier the water-boundary of the Rhine and upper Danube. Beyond these rivers she held only the fertile plain of Frankfurt, opposite the Roman border fortress of Moguntiacum (Mainz), the southernmost slopes of the Black Forest and a few scattered bridge-heads. The northern section of this frontier, where the Rhine is deep and broad, remained the Roman boundary until the empire fell. The southern part was different. The upper Rhine and upper Danube are easily crossed. The frontier which they form is inconveniently long, enclosing an acute-angled wedge of foreign territory between the modern Baden and Württemberg. The Germanic populations of these lands seem in Roman times to have been scant, and Roman subjects from the modern Alsace-Lorraine had drifted across the river eastwards. The motives alike of geographical convenience and of the advantages to be gained by recognising these movements of Roman subjects combined to urge a forward policy at Rome, and when the vigorous Vespasian had succeeded Nero, a series of advances began which gradually closed up the acute angle, or at least rendered it obtuse.
Flavian dynasty
The first advance came about 74 AD, when what is now Baden was invaded and partly annexed and a road carried from the Roman base on the upper Rhine, Straßburg, to the Danube just above Ulm. The point of the angle was broken off.
The second advance was made by Domitian about 83 AD. He pushed out from Moguntiacum, extended the Roman territory east of it and enclosed the whole within a systematically delimited and defended frontier with numerous blockhouses along it and larger forts in the rear. Among the blockhouses was one which by various enlargements and refoundations grew into the well-known Saalburg fort on the Taunus near Bad Homburg. This advance necessitated a third movement, the construction of a frontier connecting the annexations of 74 and 83 AD. We know the line of this frontier which ran from the Main across the upland Odenwald to the upper waters of the Neckar and was defended by a chain of forts. We do not, however, know its date, save that, if not Domitian's work, it was carried out soon after his death, and the whole frontier thus constituted was reorganised, probably by Hadrian, with a continuous wooden palisade reaching from Rhine to Danube.
Hadrian and the Antonines

The angle between the rivers was now almost full. But there remained further advance and further fortification. Either Hadrian or, more probably, his successor Antoninus Pius pushed out from the Odenwald and the Danube, and marked out a new frontier roughly parallel to, but in advance of these two lines, though sometimes, as on the Taunus, coinciding with the older line. This is the frontier which is now visible and visited by the curious. It consists, as we see it today, of two distinct frontier works, one, known as the Pfahlgraben, is a palisade of stakes with a ditch and earthen mound behind it, best seen in the neighbourhood of the Saalburg but once extending from the Rhine southwards into southern Germany. The other, which begins where the earthwork stops, is a wall, though not a very formidable wall, of stone, the Teufelsmauer; it runs roughly east and west parallel to the Danube, which it finally joins at Heinheim near Regensburg. The southern part of the Pfahlgraben is remarkably straight; for over 50 km (31 mi) it points almost absolutely true for Polaris.
This frontier remained for about 100 years, and no doubt in that long period much was done to it to which precise dates are difficult to fix. It cannot even be absolutely certain when the frontier laid out by Pius was equipped with the manpitts and other special fortifications. But we know that the pressure of the barbarians began to be felt seriously in the later part of the second century, and after long struggles the whole or almost the whole district east of the Rhine and north of the Danube was lost, seemingly all within one short period, about 250.
Late Roman Empire
Germanic invasions in the late third century led to the abandonment of the so-called "Upper Raetian Limes" in favour of a Roman defence line along the rivers Rhine, Iller and Danube (Donau-Iller-Rhine-Limes). Support was provided to some degree by fast river boats, the navis lusoria being the standard type, that could reach outposts or points of crisis quickly. Watch towers were in sight contact and heavily fortified castra placed at important passes (e.g. Castrum Rauracense instead of the previously unwalled Augusta Raurica near to Basel) and in the hinterland of the frontier (e.g. Vindonissa in today's Switzerland).
Description and functionality of the limes

The limes itself is a relatively simple construction. It is similar to the fortification that a travelling troop of Roman soldiers would construct every evening to protect their camp from attacks. On the outside, the soldiers dug a ditch. The earth from the ditch was used to build a mound. On top of the mound, stakes were attached. The limes had a deeper ditch and a higher mound than a camp fortification. The stakes were higher, too, and placed in front of the ditch; on several parts of the limes, instead of stakes, there was a simple stone wall.
Behind the wall or mound a system of control towers, built of wood or stone, was installed, each within sight of the next one, and usually able also to signal to the forts several kilometers to the rear.
.jpg.webp)
The limes was never able to prevent whole Germanic tribes from entering the territory of the Roman Empire. This was not the intention of the builders. Near the watch towers, the limes was open to passage, especially by traders or persons coming to live or work within the Empire. The purpose of the limes was control of this traffic. To cross the limes it was necessary to pass the towers and so come to the notice of the garrison, or try to climb or destroy the wall and the stakes. Only individuals or small groups could climb the obstacles without being noticed, and they could not drive much stolen livestock with them. Large groups would be noticed; they could destroy one or several towers, but this also would draw the attention of the Romans.
This knowledge of all traffic crossing the border was crucial to the Roman military. For a territory as large as the Roman Empire, there were few soldiers, and almost all of the legions were based close to the frontiers. Any hostile band that managed to pass this outer area of defense could travel within the Empire without much resistance. The limes provided an early warning system, deterrence of casual small-scale raiding, and the ability to counteract attacks while the enemy was still near the border fortresses and garrisons. The limes may also have been a bulwark to control the movement of groups of people, like the fence system along the American-Mexican border.[3]
Roman forts along the limes
Lower Germanic LimesThe Netherlands:[4]
Germany:
|
 Castellum Nigrum Pullum (Zwammerdam), artist impression Stevie Xinas Upper Germanic Limes
Rhaetian Limes
|
See also
References
- ↑ "Frontiers of the Roman Empire". UNESCO.
- ↑ "Frontiers of the Roman Empire -- Lower German Limes". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization.
- ↑ such as Klee, M., quoted in Schmid, A., Schmid, R., Möhn, A., Die Römer an Rhein und Main (Frankfurt: Societäts-Verlag, revised edition 2006). ISBN 3-7973-0985-6
- ↑ As with the Upper Germanic Limes, sorted in geographical order: from northwest to southeast. For the location of these castella, see: the Tabula Peutingeriana; Ravennatis Anonymus Cosmographia IV.24.
- ↑ Tacitus Histories 5.20 gives Arenacium, while the Tabula Peutingeriana gives Arenatio. The older Itinerarium Antonini gives its name as Harenatium.
- ↑ In the Itinerarium Antonini nine leagues (ca. 20 km) south of Vetera and nine leagues north of Gelduba.
- ↑ Based on the Roman name for the town of Lorch (Austria). See the article on Lauriacum.
Sources
Primary sources
Secondary sources
- This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Limes Germanicus". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 16 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 695–696.
- A good English account can be found in H. F. Pelham's essay in Trans. of the Royal Hist. Soc. vol. 20, reprinted in his Collected Papers, pp. 178–211 (Oxford, 1910), where the German authorities are fully cited.
- D.J. Woolliscroft, Roman Military Signalling. Stroud and Charleston: Tempus Publishing, 2001. p. 191. ISBN 0-7524-1938-2. A study mainly of intervisibility along the Rhine and British limites.
External links
- Vici.org Interactive map of the full Limes Germanicus
- Interactive map of the Deutsche Limeskommission
- The Upper German-Raetian border wall

.svg.png.webp)