孤束核
孤束核(英文:Nucleus of the solitary tract;拉丁文:Nucleus tractus solitarii,缩写:NTS)是延髓灰质内的一组柱状神經核。於孤束核內的神经纤维稱為孤束,包括从顏面神经、舌咽神经和迷走神经匯入的一般内脏感觉神经纤维和味觉纤维。孤束核发出纤维投射至脑部其他区域,包括网状结构、副交感神经节前神经元、下丘脑和丘脑,参与形成 自主神经调控的回路。孤束核内的细胞根据不同功能分布。例如接受味觉的细胞位于神經核前上部分,而参与调控心血管和呼吸功能的细胞位于孤束核的下后部分[1][2]。
| 孤束核 | |
|---|---|
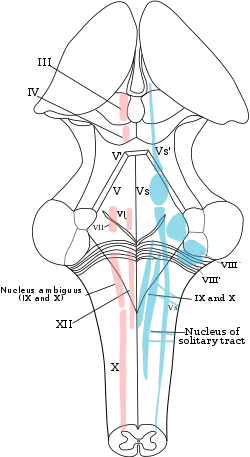 脑神经核背面观,红色为运动神經核;蓝色为感觉神经核。 | |
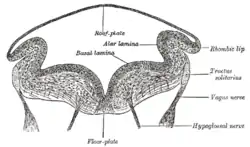 Transverse section of medulla oblongata of human embryo. | |
| 标识字符 | |
| 拉丁文 | Nucleus tractus solitarii medullae oblongatae. |
| MeSH | D017552 |
| NeuroNames | 742 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1429 |
| TA98 | A14.1.04.230 |
| TA2 | 6008 |
| FMA | FMA:72242 |
| 《神经解剖学术语》 | |
訊息輸入
孤束核調控了多項反射,包括嘔吐反射、頸動脈竇反射、主動脈反射、咳嗽反射、機械及化學受器反射、多項呼吸反射以及消化系統的運動及分泌相關反射等等。
訊息輸出
訊息在輸入孤束核後,會被輸出到腦中的不同區域,包含下視丘的腦室壁核、杏仁核,以及腦幹中的不同神經核(例如臂旁核及其他的內臟運動或呼吸網絡)[3]。
由孤束核投射向臂旁核的訊息來自於口腔及消化道。雖然一般相信味覺和消化道臟器感覺最終輸入臂旁核,但仍有部分輸入孤束核[4][5]。孤束核內的神經元可按照其特性不同進行分類,例如分泌正腎上腺素的A2神經元,以及具醛固酮敏感性的HSD2神經元。HSD2神經元會將信息投射至終紋床核[6][7]。
其他圖像
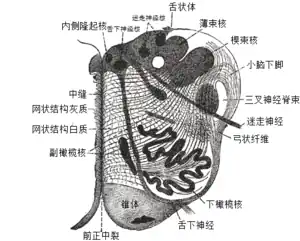 Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive.
Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive.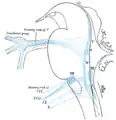 Primary terminal nuclei of the afferent (sensory) cranial nerves schematically represented; lateral view.
Primary terminal nuclei of the afferent (sensory) cranial nerves schematically represented; lateral view.
參見
- 孤束
參考文獻
- Duane E. Haines. . Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2004: 186– [22 January 2013]. ISBN 978-0-7817-4677-9. (原始内容存档于2014-07-04).
- P. Michael Conn. . Springer. 2008: 264 [22 January 2013]. ISBN 978-1-60327-455-5. (原始内容存档于2014-07-04).
- Carlson, Neil R. 10th. Allyn & Bacon. 2010: 253. ISBN 978-0-205-66627-0.
- Karimnamazi, Hamid; Travers, Susan P; Travers, Joseph B. . Brain Research. 2002, 957 (2): 193–206. PMID 12445962. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(02)03438-8.
- Karimnamazi, Hamid; Travers, Joseph B. . Brain Research. 1998, 813 (2): 283–302. PMID 9838165. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(98)00951-2.
- Geerling JC, Loewy AD. Aldosterone-sensitive neurons in the nucleus of the solitary tract: efferent projections. J Comp Neurol. 2006 Jul 10;497(2):223-50. pmid=16705681
- Shin JW, Geerling JC, Loewy AD. Inputs to the ventrolateral bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. J Comp Neurol. 2008 Dec 10;511(5):628-57. doi: 10.1002/cne.21870. pmid=18853414
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.