异柠檬酸裂合酶
有关缩写为ICL的其他条目,请参见此
| Isocitrate Lyase | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||
| Homotetrameric structure of Isocitrate lyase from E. coli. Based on PDB 1IGW.[1] | |||||||
| |||||||
| 识别码 | |||||||
| EC編號 | 4.1.3.1 | ||||||
| CAS号 | 9045-78-7 | ||||||
| 数据库 | |||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz浏览 | ||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA入口 | ||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme浏览 | ||||||
| KEGG | KEGG入口 | ||||||
| MetaCyc | 代谢路径 | ||||||
| PRIAM | 概述 | ||||||
| PDB | RCSB PDB PDBj PDBe PDBsum | ||||||
| 基因本体 | AmiGO / EGO | ||||||
| |||||||
| Isocitrate lyase family | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 鑑定 | |||||||||
| 標誌 | ICL | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00463(旧版) | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000918 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00145 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1f8m / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
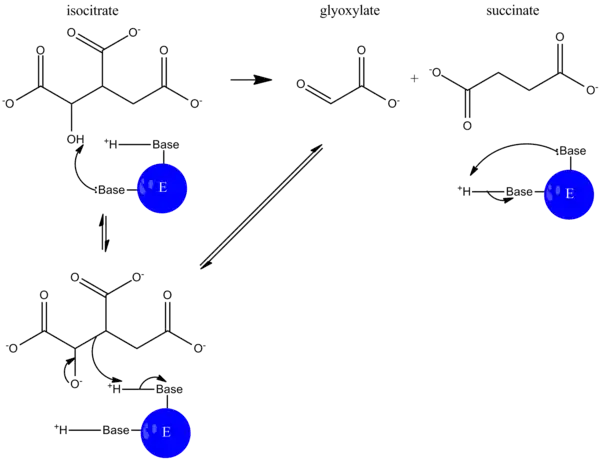
异柠檬酸裂合酶(英語:,缩写ICL,EC 4.1.3.1)是以一种在乙醛酸循环中将异柠檬酸切割为乙醛酸和琥珀酸的酶[2][3]。其产物再通过苹果酸合酶合成苹果酸,跳过了三羧酸循环(TCA循环)中脱去CO2的两步。这一途径广泛存在于细菌、真菌与植物中。[4]
机制
异柠檬酸裂合酶属于异柠檬酸裂合酶家族,该家族的其它成员有羧乙烯基-羧基膦酸酯磷酰基变位酶(EC 2.7.8.23),以及磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸变位酶(EC 5.4.2.9,参与草丁膦类三肽抗生素的合成)。
另见
- 乙醛酸循环
- 异柠檬酸裂合酶家族
参考文献
- Britton, KL; Abeysinghe IS, Baker PJ, Barynin V, Diehl P, Langridge SJ, McFadden BA, Sedelnikova SE, Stillman TJ, Weeradechapon K, Rice DW. . Acta Crystallogr D. Sep 2001, 57 (9): 1209–1218. PMID 11526312. doi:10.1107/S0907444901008642.
- Beeching JR. . Protein Seq. Data Anal. 1989, 2 (6): 463–466. PMID 2696959.
- Tanaka A, Atomi H, Ueda M, Hikida M, Hishida T, Teranishi Y. . J. Biochem. 1990, 107 (2): 262–266. PMID 2361956.
- Dunn, MF; Ramirez-Trujill JA; Hernandez-Lucas I. . Microbiology. Oct 2009, 155 (10): 3166–3175. PMID 19684068. doi:10.1099/mic.0.030858-0.
延伸阅读
- McFadden BA and Howes WV. . J. Biol. Chem. 1963, 238: 1737–1742.
- Shiio I, Shiio T and McFadden BA. . Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1965, 96: 114–22. PMID 14285253. doi:10.1016/0005-2787(65)90615-5.
- VICKERY HB. . J. Biol. Chem. 1962, 237: 1739–41. PMID 13925783.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.