植物角质层
植物角质层(plant cuticle)是覆盖树叶、嫩枝和其他植物地上器官表皮的保护膜。金鱼藻孢子体,苔藓的两个孢子体和配子体也有植物角质层。它由蜡质、脂质、烃类聚合物组成,只由表皮细胞合成。

羽衣甘蓝叶子上蜡状角质层上的水珠
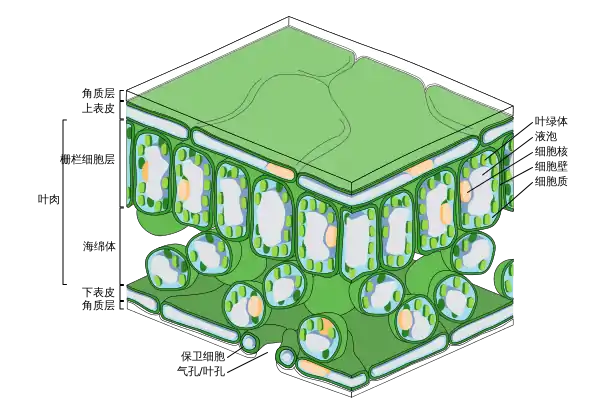
真双子叶植物叶子的解剖学
描述
植物角质层是包覆蜡質的脂质聚合物层,所有维管植物主要器官的外表面都有它。角蒿的孢子体,苔藓的孢子体和配子体都有它[1]。植物角质层形成植物的连贯外层覆盖物,果胶酶和纤维素酶可將植物组织與角質層完整分离。
组成
角质层由可溶蜡包裹不溶角质膜组成。目前比较广泛认可的角质膜成分由酯和环氧键交联构成的羟基酸类聚酯聚合物[2][3]。角质层也可能有非皂化烷烃聚合物。表皮蜡质与角质膜交联包裹并由外表皮角质腊覆盖。这些蜡质主要由疏水脂质化合物的混合物組成,通常是链长16到36粒碳原子的烷烃化合物[4]。
功能
植物表皮主要作为水渗透屏障以防止水分从外表皮快速蒸发,同时也可以防止外部的水或溶质进入细胞组织。角质层外表面的微观蜡质晶体或表皮结构可以防止周围环境污垢和微生物污染。如“荷葉效應”的超疏水和自洁特性。目前,荷叶效应在仿生技术用途甚廣。此外,角质层的蜡质还可作为防御昆虫、病毒、細菌以及真菌侵染的物理屏障。
参考文献
- Budke, J.M., Goffinet, B. and Jones, C.S. (2013). Dehydration protection provided by a maternal cuticle improves offspring fitness in the moss Funaria hygrometrica. Annals of Botany doi:10.1093/aob/mct033
- Holloway, PJ (1982) The chemical constitution of plant cutins. In: Cutler, DF, Alvin, KL and Price, CE The Plant Cuticle. Academic Press, pp. 45-85
- Stark, RE and Tian, S (2006) The cutin biopolymer matrix. In: Riederer, M & Müller, C (2006) Biology of the Plant Cuticle. Blackwell Publishing
- Baker, EA (1982) Chemistry and morphology of plant epicuticular waxes. In: Cutler, DF, Alvin, KL and Price, CE The Plant Cuticle. Academic Press, 139-165
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.