| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 379 seats in the House of Representatives 190 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This article is part of a series on |
| Politics of Japan |
|---|
 |
|
|
General elections were held in Japan on 1 March 1904.[1][2] The Rikken Seiyūkai party remained the largest in the House of Representatives, winning 133 of the 379 seats.
Electoral system
The 379 members of the House of Representatives were elected in 51 multi-member constituencies based on prefectures and cities. Voting was restricted to men aged over 25 who paid at least 10 yen a year in direct taxation.[3]
Results
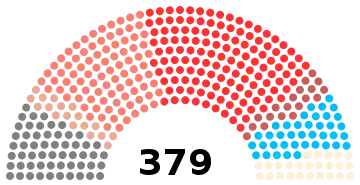 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
| Rikken Seiyūkai | 217,691 | 33.47 | 133 | –42 | |
| Kensei Hontō | 170,319 | 26.19 | 90 | +5 | |
| Kōshin Club | 55,709 | 8.57 | 39 | +8 | |
| Jiyu Club | 31,772 | 4.89 | 18 | New | |
| Mumei Club | 31,197 | 4.80 | 25 | New | |
| Teikokutō | 27,244 | 4.19 | 19 | +2 | |
| Others | 116,419 | 17.90 | 55 | 0 | |
| Total | 650,351 | 100.00 | 379 | +3 | |
| Valid votes | 650,351 | 99.12 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 5,777 | 0.88 | |||
| Total votes | 656,128 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 762,445 | 86.06 | |||
| Source: Mackie & Rose, Voice Japan | |||||
Notes
- ↑ As Chūsei Club
References
- ↑ Thomas T Mackie & Richard Rose (1991) The International Almanac of Electoral History, Macmillan, p281
- ↑ Garner, James Wilford (1904). "Record of Political Events". Political Science Quarterly. 19 (2): 367–368. doi:10.2307/2140296. ISSN 0032-3195. JSTOR 2140296.
- ↑ Mackie & Rose, p276
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.


