| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
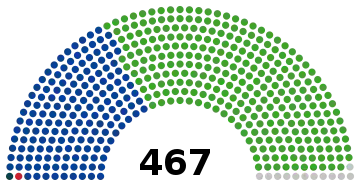
All 467 seats in the House of Representatives of Japan 234 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 76.98% ( | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| This article is part of a series on |
| Politics of Japan |
|---|
 |
|
|
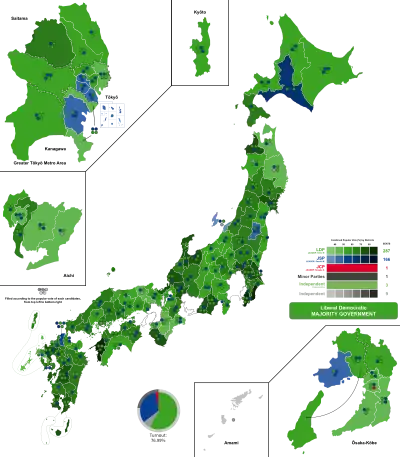
General elections were held in Japan on 22 May 1958. The result was a victory for the Liberal Democratic Party, which won 298 of the 467 seats.[1] Voter turnout was 77.0%.
Results
 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Votes | % | Seats | +/– | |
| Liberal Democratic Party | 22,976,846 | 57.80 | 287 | –10 | |
| Japan Socialist Party | 13,093,993 | 32.94 | 166 | +6 | |
| Japanese Communist Party | 1,012,036 | 2.55 | 1 | –1 | |
| Other parties | 287,991 | 0.72 | 1 | – | |
| Independents | 2,380,795 | 5.99 | 12 | +6 | |
| Total | 39,751,661 | 100.00 | 467 | 0 | |
| Valid votes | 39,751,661 | 99.27 | |||
| Invalid/blank votes | 290,828 | 0.73 | |||
| Total votes | 40,042,489 | 100.00 | |||
| Registered voters/turnout | 52,013,529 | 76.98 | |||
| Source: Mackie, Masumi | |||||
By prefecture
| Prefecture | Total seats |
Seats won | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDP | JSP | JCP | Others | Ind. | ||
| Aichi | 19 | 10 | 8 | 1 | ||
| Akita | 8 | 5 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Aomori | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Chiba | 13 | 10 | 3 | |||
| Ehime | 9 | 8 | 1 | |||
| Fukui | 4 | 3 | 1 | |||
| Fukuoka | 19 | 12 | 7 | |||
| Fukushima | 12 | 7 | 4 | 1 | ||
| Gifu | 9 | 5 | 4 | |||
| Gunma | 10 | 7 | 3 | |||
| Hiroshima | 12 | 9 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Hokkaido | 22 | 11 | 11 | |||
| Hyōgo | 18 | 10 | 7 | 1 | ||
| Ibaraki | 12 | 8 | 4 | |||
| Ishikawa | 6 | 5 | 1 | |||
| Iwate | 8 | 5 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Kagawa | 6 | 4 | 2 | |||
| Kagoshima | 11 | 8 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Kanagawa | 13 | 6 | 7 | |||
| Kōchi | 5 | 4 | 1 | |||
| Kumamoto | 10 | 7 | 3 | |||
| Kyoto | 10 | 6 | 4 | |||
| Mie | 9 | 5 | 4 | |||
| Miyagi | 9 | 5 | 4 | |||
| Miyazaki | 6 | 4 | 2 | |||
| Nagano | 13 | 7 | 5 | 1 | ||
| Nagasaki | 9 | 5 | 3 | 1 | ||
| Nara | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 | ||
| Niigata | 15 | 8 | 6 | 1 | ||
| Ōita | 7 | 5 | 2 | |||
| Okayama | 10 | 6 | 4 | |||
| Osaka | 19 | 11 | 7 | 1 | ||
| Saga | 5 | 3 | 2 | |||
| Saitama | 13 | 9 | 4 | |||
| Shiga | 5 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shimane | 5 | 3 | 2 | |||
| Shizuoka | 14 | 10 | 4 | |||
| Tochigi | 10 | 6 | 4 | |||
| Tokushima | 5 | 3 | 2 | |||
| Tokyo | 27 | 12 | 15 | |||
| Tottori | 4 | 3 | 1 | |||
| Toyama | 6 | 4 | 2 | |||
| Wakayama | 6 | 4 | 2 | |||
| Yamagata | 8 | 6 | 2 | |||
| Yamaguchi | 9 | 6 | 3 | |||
| Yamanashi | 5 | 4 | 1 | |||
| Total | 467 | 287 | 166 | 1 | 1 | 12 |
Notes
- ↑ as Democratic Party and Liberal Party
References
- ↑ Dieter Nohlen, Florian Grotz & Christof Hartmann (2001) Elections in Asia: A data handbook, Volume II, p381 ISBN 0-19-924959-8
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.


