| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 465 seats in the House of Representatives 233 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
General elections are scheduled to be held in Japan by 31 October 2025, as required by the constitution. Voting will take place in all Representatives constituencies including proportional blocks, in order to appoint Members of Diet to seats in the House of Representatives, the lower house of the National Diet of Japan. As the cabinet has to resign after a general House of Representatives election in the first post-election Diet session (Constitution, Article 70), the lower house election will also lead to a new election of the Prime Minister in the Diet, and the appointment of a new cabinet (even if the same ministers are re-appointed).
Political parties
| Parties | Leader | Ideology | Seats | Status | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Last election | Before election | |||||
| Liberal Democratic Party | Fumio Kishida | Conservatism | 259 / 465 |
261 / 465 |
Governing coalition | |
| Constitutional Democratic Party of Japan | Kenta Izumi | Social liberalism | 96 / 465 [lower-alpha 1] |
97 / 465 |
Opposition | |
| Nippon Ishin no Kai | Nobuyuki Baba | Right-wing populism | 41 / 465 |
41 / 465 | ||
| Komeito | Natsuo Yamaguchi | Buddhist democracy | 32 / 465 |
32 / 465 |
Governing coalition | |
| Japanese Communist Party | Kazuo Shii | Communism | 10 / 465 |
10 / 465 |
Opposition | |
| Democratic Party for the People | Yuichiro Tamaki | Conservatism | 11 / 465 |
7 / 465 | ||
| Association for Realizing Free Education | Seiji Maehara | Single-issue politics (Free education) | Did not exist | 4 / 465 | ||
| Reiwa Shinsengumi | Tarō Yamamoto | Progressivism | 3 / 465 |
3 / 465 | ||
| Social Democratic Party | Mizuho Fukushima | Social democracy | 1 / 465 |
1 / 465 | ||
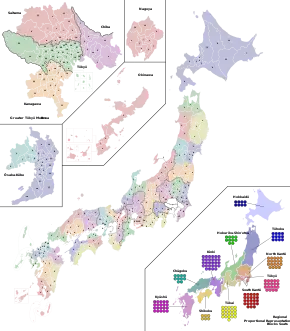
Reapportionment
The electoral districts will be readjusted according to the results of the 2020 Japan census. Originally, it was intended to be readjusted for the last election, but it was held in the existing constituencies not long after the census results came out.[1][2]
Newly created seats
Ten new districts and three new block seats will be created.
- Tokyo-26th
- Tokyo-27th
- Tokyo-28th
- Tokyo-29th
- Tokyo-30th
- Kanagawa-19th
- Kanagawa-20th
- Saitama-16th
- Aichi-16th
- Chiba-14th
- 18th Tokyo block seat
- 19th Tokyo block seat
- 23rd Minami-Kanto block seat
Seats to be eliminated
Ten districts and three block seats will be eliminated.
- Hiroshima-7th
- Miyagi-6th
- Niigata-6th
- Fukushima-5th
- Okayama-5th
- Shiga-4th
- Yamaguchi-4th
- Ehime-4th
- Nagasaki-4th
- Wakayama-3rd
- 13th Tohoku block seat
- 11th Hokurikushinetsu block seat
- 11th Chugoku block seat
Opinion polls
See also
Notes
References
- ↑ "小選挙区「10増10減」へ 国勢調査受け、次々回から" [Single-seat constituencies to increase by 10, decrease by 10]. The Asahi Shimbun (in Japanese). 25 June 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
- ↑ "衆院小選挙区「10増10減」 アダムズ方式で格差是正―政府、来年にも法案提出" [House of Representatives single-seat constituency "10 increase, 10 decrease" Adams method to correct disparities-government to submit bill next year]. Jiji Press (in Japanese). 25 June 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2021.