| Ban'etsu West Line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
| Overview | |||
| Native name | 磐越西線 | ||
| Status | In operation | ||
| Owner | |||
| Locale | Fukushima, Niigata prefectures | ||
| Termini | |||
| Stations | 43 | ||
| Service | |||
| Type | Regional rail | ||
| Operator(s) | |||
| Rolling stock | 719 series EMU, E721 series EMU, KiHa 100 series DMU, GV-E400 series DMU, AT-700 series DMU | ||
| History | |||
| Opened | 1898 | ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 175.6 km (109.1 mi) | ||
| Number of tracks | Entire line single tracked | ||
| Character | Rural | ||
| Track gauge | 1,067 mm (3 ft 6 in) | ||
| Electrification | 20 kV AC, 50 Hz overhead catenary (Kōriyama – Kitakata) None (Kitakata - Niitsu) | ||
| Operating speed | 100 km/h (62 mph) | ||
| |||

The Banetsu West Line (磐越西線, Ban'etsu-sai-sen) is a railway line in Japan operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East). It connects Kōriyama Station in Kōriyama, Fukushima Prefecture, and Niitsu Station in Akiha Ward, Niigata, Niigata Prefecture. The name "Banetsu" is taken from the first characters of the names of the ancient provinces of Iwaki (磐城) and Echigo (越後), which the Banetsu East and Banetsu West lines connect. "Sai" (西) means "west" in Japanese.
The line's nickname is the Mori to Mizu to Roman no Tetsudō (森と水とロマンの鉄道, lit. "the water, forest, and nostalgia railway").
Station list
- Local trains generally stop at all stations, but some trains skip stations marked "▽".
- The column marked "*" refers to the unnamed rapid service between Kōriyama and Aizu-Wakamatsu/Kitakata using 719 series EMUs.
- Trains can pass one another at stations marked "◇", "∨", or "∧"; stations marked "◆" are switchback stations. Trains cannot pass at stations marked "|".
| Station | Japanese | Distance (km) | Rapid | Transfers/Other Notes | Location | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Between stations |
Total | * | Agano | ||||||
| Kōriyama | 郡山 | - | 0.0 | ● | ∨ | Kōriyama | Fukushima | ||
| Kōriyamatomita | 郡山富田 | 3.4 | 3.4 | ● | | | ||||
| Kikuta | 喜久田 | 4.5 | 7.9 | ▲ | ◇ | ||||
| Akogashima | 安子ケ島 | 3.9 | 11.8 | | | ◇ | ||||
| Bandai-Atami | 磐梯熱海 | 3.6 | 15.4 | ● | ◇ | ||||
| Nakayamajuku | 中山宿 | 5.4 | 20.8 | | | | | ||||
| Jōko | 上戸 | 6.5 | 27.3 | | | | | Inawashiro, Yama District | |||
| Inawashirokohan (closed) | 猪苗代湖畔 | 2.0 | 29.3 | Closed in 2007 | | | ||||
| Sekito | 関都 | 1.7 | 31.0 | | | ◇ | ||||
| Kawageta | 川桁 | 2.4 | 33.4 | ▲ | ◇ | ||||
| Inawashiro | 猪苗代 | 3.3 | 36.7 | ● | ◇ | ||||
| Okinashima | 翁島 | 4.4 | 41.1 | ▲ | ◇ | ||||
| Bandaimachi | 磐梯町 | 10.1 | 51.2 | ● | ◇ | Bandai, Yama District | |||
| Higashi-Nagahara | 東長原 | 6.0 | 57.2 | ▲ | ◇ | Aizuwakamatsu | |||
| Hirota | 広田 | 2.8 | 60.0 | ▲ | ◇ | ||||
| Aizu-Wakamatsu | 会津若松 | 4.6 | 64.6 | ● | ● | ■Tadami Line ■Aizu Line[* 2] |
◆ | ||
| Dōjima▽ | 堂島 | 5.5 | 70.1 | | | | | | | |||
| Oikawa▽ | 笈川 | 3.1 | 73.2 | | | | | | | Yugawa, Kawanuma District | ||
| Shiokawa | 塩川 | 1.9 | 75.1 | ● | ● | ◇ | Kitakata | ||
| Ubadō▽ | 姥堂 | 2.4 | 77.5 | | | | | | | |||
| Aizu-Toyokawa▽ | 会津豊川 | 2.0 | 79.5 | | | | | | | |||
| Kitakata | 喜多方 | 1.7 | 81.2 | ● | ● | Terminus of electrification | ◇ | ||
| Yamato | 山都 | 9.9 | 91.1 | ● | ◇ | ||||
| Ogino | 荻野 | 6.1 | 97.2 | ● | | | ||||
| Onobori | 尾登 | 3.8 | 101.0 | | | | | Nishiaizu, Yama District | |||
| Nozawa | 野沢 | 5.2 | 106.2 | ● | ◇ | ||||
| Kami-Nojiri | 上野尻 | 5.1 | 111.3 | | | | | ||||
| Tokusawa | 徳沢 | 6.7 | 118.0 | | | ◇ | ||||
| Toyomi | 豊実 | 3.3 | 121.3 | | | | | Aga, Higashikanbara District | Niigata | ||
| Hideya | 日出谷 | 7.1 | 128.4 | | | | | ||||
| Kanose | 鹿瀬 | 5.2 | 133.6 | ● | | | ||||
| Tsugawa | 津川 | 3.4 | 137.0 | ● | ◇ | ||||
| Mikawa | 三川 | 7.4 | 144.4 | ● | | | ||||
| Igashima | 五十島 | 4.2 | 148.6 | | | ◇ | ||||
| Higashi-Gejō | 東下条 | 3.9 | 152.5 | | | | | ||||
| Sakihana | 咲花 | 3.1 | 155.6 | ● | | | Gosen | |||
| Maoroshi | 馬下 | 2.8 | 158.4 | ▲ | ◇ | ||||
| Saruwada | 猿和田 | 3.5 | 161.9 | | | | | ||||
| Gosen | 五泉 | 3.8 | 165.7 | ● | ◇ | ||||
| Kita-Gosen | 北五泉 | 1.8 | 167.5 | | | | | ||||
| Shinseki | 新関 | 2.5 | 170.0 | | | ◇ | Akiha-ku, Niigata | |||
| Higashi-Niitsu | 東新津 | 2.8 | 172.8 | | | | | ||||
| Niitsu | 新津 | 2.8 | 175.6 | ● | ∧ | ||||
- ↑ Although the official start of the Suigun Line is Asakanagamori, all trains run through to/from Kōriyama.
- ↑ Although the official start of the Aizu Line is Nishi-Wakamatsu, all trains run through to/from Aizu-Wakamatsu.
- ↑ Most Banetsu West Line trains travel through to/from Niigata.
Rolling stock
As of April 2020, the following rolling stock is used on the Banetsu West Line.
Kōriyama—Kitakata
- 719 series EMUs (since June 2007)
- E721-0 series EMUs (since 4 March 2017)[1]
From 25 April 2015, a two-car 719 series set entered service on FruiTea (フルーティア) services on the line between Koriyama and Aizu-Wakamatsu. The train accommodates 36 passengers.[2]
 A Banetsu West Line 719 series EMU in January 2008
A Banetsu West Line 719 series EMU in January 2008 The 719-700 series FruiTea trainset in April 2015
The 719-700 series FruiTea trainset in April 2015
Aizu-Wakamatsu—Niitsu
- KiHa 110 series DMUs
- GV-E400 series DEMUs (since August 2019[3])
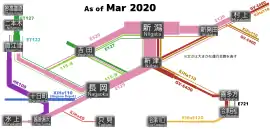 Operations in Niigata area
Operations in Niigata area SL "Banetsu Monogatari"
SL "Banetsu Monogatari"
Past
- 455 series EMUs (from 1967 until March 2008)
- 485 series EMUs (Aizu Liner rapid services)
- KiHa 40/47/48 DMUs (until March 2020)
- KiHa 52 DMUs (until 2009)
- KiHa 58 DMUs (until 2009)
- KiHa E120 DMUs (until March 2020)
_Banetsu_West_Line_Akabe_at_Koriyama_2006_1224size.jpg.webp) A Banetsu West Line 455 series EMU in December 2006
A Banetsu West Line 455 series EMU in December 2006 485 series Aizu Liner rapid service at Koriyama Station in March 2012
485 series Aizu Liner rapid service at Koriyama Station in March 2012 KiHa 40/47/48 series at Tokusawa Station in June 2013
KiHa 40/47/48 series at Tokusawa Station in June 2013 KiHa E120 and 110 at Gosen Station in December 2009
KiHa E120 and 110 at Gosen Station in December 2009
History

The private Ganetsu Railway opened the initial section from Kōriyama to Nakayamajuku on July 26, 1898, and extended the line to Aizu-Wakamatsu the following year.
Japanese National Railways (JNR) started to modernize the line in the 1960s, introducing the line's first limited express service (as a part of the Yamagata-bound Yamabata) in 1965 between Ueno Station in Tokyo and Aizu-Wakamatsu via the Tōhoku Main Line. In 1968 the train was renamed Aizu Yamabata, but from 1993 onward it was renamed Viva Aizu and ran only between Koriyama and Aizu-Wakamatsu. The train was finally discontinued as a limited express service in 2003.
In 1967, JNR electrified the section between Kōriyama and Kitakata at 20 kV AC.
In 2011 the line was closed for 15 days in March following the Tohoku earthquake, two days in April as a result of aftershocks, and for 10 weeks following torrential rain at the end of July.
A new station, called Kōriyamatomita, opened on 1 April 2017 between and Kōriyama and Kikuta stations.[4]
The railway bridge connecting Kitakata and Yamato collapsed due to heavy rain on 4 August 2022. All services are suspended between Kitakata and Nozawa.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ 磐越西線でE721系の運転開始 [E721 series enter service on the Banetsu West Line]. Japan Railfan Magazine Online (in Japanese). Japan: Koyusha Co., Ltd. 9 March 2017. Archived from the original on 9 March 2017. Retrieved 9 March 2017.
- ↑ Genbi Shinkansen jreast.co.jp
- ↑ "「SLばんえつ物語」号運行開始!祝・20 周年! 7月27日(土) 新津駅でお祝いのイベントを開催します!" (PDF) (Press release) (in Japanese). JR East Niigata Branch. 2019-06-27. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-06-27. Retrieved 2020-07-19.
- ↑ JR郡山富田駅開業 県内の新駅30年ぶり [JR Koriyamatomita Station opens - First new station in prefecture for 30 years]. Fukushima Minpo (in Japanese). Japan. 2 April 2017. Archived from the original on 3 April 2017. Retrieved 3 April 2017.
- ↑ "福島・喜多方 橋りょう崩落、線路宙づり 通勤・通学に打撃". 河北新報オンラインニュース (in Japanese). 2022-08-05. Retrieved 2022-08-06.