| Boreosomus Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
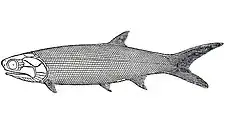
| Boreosomus gillioti: fossil mold and latex cast | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | †Boreosomus Stensiö, 1921 |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Boreosomus (meaning: "boreal body") is an extinct genus of Triassic ray-finned fish. It was first described from the Arctic island of Spitsbergen (Svalbard, Norway), but was later also discovered in other parts of the world. The type species is Boreosomus arcticus (= Acrolepis arctica Woodward, 1912).
Classification


Boreosomus belongs to the family Ptycholepidae (= Boreosomidae/Chungkingichthyidae). Other genera of this family are Acrorhabdus (Spitsbergen), Ardoreosomus (Nevada, United States), Chungkingichthys (China), Ptycholepis (global) and Yuchoulepis (China).[2]
Description
A characteristic feature of Boreosomus and other ptycholepids is the dorsal fin, which inserts at the level of the pelvic fins in the middle portion of the body. Most contemporary ray-fins have their dorsal fin in a more posterior position, often opposite to the anal fin. Also typical for ptycholepids are the somewhat rectangular, horizontally arranged suborbital bones.[3]
Fossil record
Boreosomus had a worldwide distribution during the Early Triassic and is also known from the Middle and Late Triassic. Fossils of Boreosomus were found, apart from Spitsbergen (Svalbard), in Greenland, Madagascar, Kenya, China (Shaanxi), Spain (Catalonia), United States (Alaska, Nevada), and Canada (Alberta, British Columbia, Nunavut).[4][5]
Species
- †Boreosomus arcticus (Woodward, 1912) [Acrolepis arctica Woodward 1912] (type species)
- †Boreosomus gillioti (Priem, 1924) [Diaphorognathus gillioti (Priem 1924); Gyrolepis gillioti Priem 1924]
- †Boreosomus merlei Beltan, 1957
- †Boreosomus piveteaui Nielsen, 1942[3]
- †Boreosomus reuterskioeldi Stensiö, 1921
- †Boreosomus scaber Stensiö, 1921
See also
References
- ↑ "Palaeonisciformes". Paleobiology Database. Retrieved November 17, 2012.
- ↑ Romano, Carlo; López-Arbarello, Adriana; Ware, David; Jenks, James F.; Brinkmann, Winand (2019). "Marine Early Triassic Actinopterygii from the Candelaria Hills (Esmeralda County, Nevada, USA)". Journal of Paleontology. 93 (5): 971–1000. Bibcode:2019JPal...93..971R. doi:10.1017/jpa.2019.18. S2CID 155564297.
- 1 2 Nielsen, Eigil (1942). "Studies on Triassic fishes from East Greenland 1. Glaucolepis and Boreosomus". Palaeozoologica Groenlandica. 1: 1–403.
- ↑ "Fossilworks: Boreosomus".
- ↑ Romano, Carlo; Koot, Martha B.; Kogan, Ilja; Brayard, Arnaud; Minikh, Alla V.; Brinkmann, Winand; Bucher, Hugo; Kriwet, Jürgen (2016). "Permian-Triassic Osteichthyes (bony fishes): diversity dynamics and body size evolution". Biological Reviews. 91 (1): 106–147. doi:10.1111/brv.12161. PMID 25431138. S2CID 5332637.