| Saurorhynchus Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
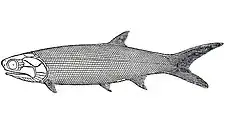
| Fossil of Saurorhynchus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | †Saurorhynchus Reis 1892 |
| Type species | |
| †Saurorhynchus acutus (Agassiz 1844) | |
| Other species | |
|
†Saurorhynchus anningae †Saurorhynchus brevirostris †Saurorhynchus hauffi | |
| Synonyms | |

Saurorhynchus (= Acidorhynchus)[1] is an extinct genus of carnivorous bony fish that lived during the Early and Middle Jurassic epochs.[2] Fossils have been found in Europe (France, Belgium, Luxembourg, United Kingdom, Germany,[3] Italy) and North America (Canada[4]). It is commonly found in pelagic and lagoonal deposits, but mostly marine. Largest specimens can grow up to 1.9 metres (6.2 ft).[5]
Four Jurassic species are recognized.[3] In addition, the Late Triassic species Saurichthys striolatus, Saurichthys calcaratus, and Saurichthys deperditus are sometimes referred to Saurorhynchus, although Saurorhynchus is then treated as a subgenus of Saurichthys.[6]
Saurorhynchus is the youngest representative of the family Saurichthyidae and the order Saurichthyiformes. This family is known for its large, elongate jaws, similar to modern Belonidae. Saurichthyidae also includes the Permian genus Eosaurichthys and the Triassic genus Saurichthys.
See also
References
- 1 2 Kogan, I. (2016). "Acidorhynchus Stensiö, 1925 or Saurorhynchus Reis, 1892: how to call the Jurassic saurichthyid?". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie, Abhandlungen. 279: 123–126. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2016/0545.
- ↑ Maxwell, E.E. (2016). "First Middle Jurassic record of Saurichthyidae (Actinopterygii)". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 90 (2): 287–291. doi:10.1007/s12542-015-0281-5. S2CID 130850983.
- 1 2 Maxwell, E. E.; Stumpf, S. (2017). "Revision of Saurorhynchus (Actinopterygii: Saurichthyidae) from the Early Jurassic of England and Germany". European Journal of Taxonomy (321): 1–29. doi:10.5852/ejt.2017.321.
- ↑ Neuman, A. G.; Wilson, M. V. H. (1985). "A fossil fish of the family Saurichthyidae from the Lower Jurassic of western Alberta, Canada". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 22 (8): 1158–1162. Bibcode:1985CaJES..22.1158N. doi:10.1139/e85-118.
- ↑ Sepkoski, Jack (2002). "A compendium of fossil marine animal genera". Bulletins of American Paleontology. 364: 560. Retrieved 2009-02-27.
- ↑ Maxwell, E.E.; Romano, C. & Wu, F.-X. (2021). "Regional disparity in the axial skeleton of Saurichthyidae and implications for axial regionalization in non‐teleostean actinopterygians". Journal of Zoology. 315: 29–41. doi:10.1111/jzo.12878.