| Canobius Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | †Palaeonisciformes |
| Genus: | †Canobius Traquair, 1881 |
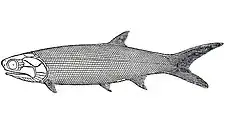
Canobius (named for Canobie, the district where it was discovered)[1] is an extinct genus of early ray-finned fish that lived in the Carboniferous period of Europe.
Canobius was a small fish, 7 centimetres (3 in) in length. Compared with its earlier relatives, it had specialized jawbones and hyomandibulars which attached the upper jaw to the braincase, meaning that the jaws were hung vertically under the braincase. This allowed Canobius to open its jaws wider and expand its gill slits further at the same time. In turn, this meant that the fish could take in more oxygen, making it a more active creature. Canobius is presumed to have fed on plankton which is filtered from the water using its small teeth and gills.[2]
References
- ↑ Traquair, Ramsay H. (1881). "III.— Report on Fossil Fishes collected by the Geological Survey of Scotland in Eskdale and Liddesdale . Part I.— Ganoidei". Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 30 (1): 47. doi:10.1017/S0080456800028970. S2CID 129109130.
- ↑ Palmer, D., ed. (1999). The Marshall Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs and Prehistoric Animals. London: Marshall Editions. p. 35. ISBN 1-84028-152-9.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.