Carbon emission trading (also called carbon market, emission trading scheme (ETS) or cap and trade) is a type of emission trading scheme designed for carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases (GHG). It is a form of carbon pricing. Its purpose is to limit climate change by creating a market with limited allowances for emissions. This can lower competitiveness of fossil fuels and accelerate investments into low carbon sources of energy such as wind power and photovoltaics. Fossil fuels are the main driver for climate change. They account for 89% of all CO2 emissions and 68% of all GHG emissions.[1]: 12
Emissions trading works by setting a quantitative total limit on the emissions produced by all participating emitters. As a result, the price automatically adjusts to this target. This is the main advantage compared to a fixed carbon tax. Under emission trading, a polluter having more emissions than their quota has to purchase the right to emit more. The entity having fewer emissions sells the right to emit carbon to other entities. As a result, the most cost-effective carbon reduction methods would be exploited first. Carbon emissions trading and carbon taxes are a common method for countries in their attempts to meet their pledges under the Paris Agreement.
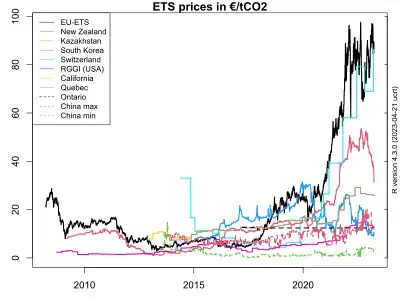
Carbon emissions trading schemes are in operation in China, the European Union, and other countries.[2] However, they are usually not harmonized with any defined carbon budgets, which are required to maintain global warming below the critical thresholds of 1.5 °C or "well below" 2 °C. The existing schemes only cover a limited scope of emissions. The EU-ETS focuses on industry and large power generation, leaving the introduction of additional schemes for transport and private consumption to the member states. Though units are counted in tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent, other potent GHGs such as methane (CH4) or nitrous oxide (N2O) from agriculture are usually not part these schemes yet. Apart from that, an oversupply leads to low prices of allowances with almost no effect on fossil fuel combustion.[3] In September 2021, emission trade allowances (ETAs) covered a wide price range from €7/tCO2 in China's new national carbon market[4] to €63/tCO2 in the EU-ETS.[5] Latest models of the social cost of carbon calculate a damage of more than $3000 per ton CO2 as a result of economy feedbacks and falling global GDP growth rates, while policy recommendations range from about $50 to $200.[6]
Market mechanisms overview
The economic problem with climate change is that the emitters of greenhouse gases (GHGs) do not face the full cost implications of their actions.[8] These other costs are called external costs.[9] External costs may affect the welfare of others. In the case of climate change, GHG emissions affect the welfare of people now and in the future, as well as affecting the natural environment.[10] The social cost of carbon depends on the future development of emissions. This can be addressed with the dynamic price model of emissions trading.
An emissions trading scheme for greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) works by establishing property rights for the atmosphere.[11] The atmosphere is a global public good, and GHG emissions are an international externality. The emissions from all sources of GHGs contribute to the overall stock of GHGs in the atmosphere. In the cap-and-trade variant of emissions trading, a limit on access to a resource (the cap) is defined and then allocated among users in the form of permits. Compliance is established by comparing actual emissions with permits surrendered including any permits traded within the cap.[12] The environmental integrity of emissions trading depends on the setting of the cap, not the decision to allow trading.[13]
For emissions trading where greenhouse gases are regulated, one emissions permit is considered equivalent to one tonne of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. Other emissions permits are carbon credits, Kyoto units, assigned amount units, and Certified Emission Reduction units (CER). These permits can be sold privately or in the international market at the prevailing market price. These trade and settle internationally, and hence allow permits to be transferred between countries. Each international transfer is validated by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Each transfer of ownership within the European Union is additionally validated by the European Commission.
Emissions trading programmes such as the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU-ETS) complement the country-to-country trading stipulated in the Kyoto Protocol by allowing private trading of permits. Under such programmes – which are generally co-ordinated with the national emissions targets provided within the framework of the Kyoto Protocol – a national or international authority allocates permits to individual companies based on established criteria, with a view to meeting national and/or regional Kyoto targets at the lowest overall economic cost.[14]
Other greenhouse gases can also be traded, but are quoted as standard multiples of carbon dioxide with respect to their global warming potential. These features reduce the quota's financial impact on business, while ensuring that the quotas are met at a national and international level.
Exchanges trading in UNFCCC related carbon credits include the European Climate Exchange, NASDAQ OMX Commodities Europe, PowerNext, Commodity Exchange Bratislava and the European Energy Exchange. The Chicago Climate Exchange participated until 2010.[15] NASDAQ OMX Commodities Europe listed a contract to trade offsets generated by a CDM carbon project called Certified Emission Reductions. Many companies now engage in emissions abatement, offsetting, and sequestration programs to generate credits that can be sold on one of the exchanges. At least one private electronic market has been established in 2008: CantorCO2e.[16] Carbon credits at Commodity Exchange Bratislava are traded at special platform called Carbon place.[17] Various proposals for linking international systems across markets are being investigated. This is being coordinated by the International Carbon Action Partnership (ICAP).[18]
Economics
| Part of a series about |
| Environmental economics |
|---|
 |
Efficiency and equity
For the purposes of analysis, it is possible to separate efficiency (achieving a given objective at lowest cost) and equity (fairness).[19] Economists generally agree that to regulate emissions efficiently, all polluters need to face the full costs of their actions (that is, the full marginal social costs of their actions).[20] Regulation of emissions that is applied only to one economic sector or region drastically reduces the efficiency of efforts to reduce global emissions.[21] There is, however, no scientific consensus over how to share the costs and benefits of reducing future climate change (mitigation of climate change), or the costs and benefits of adapting to any future climate change (see also economics of global warming).
Carbon leakage
A domestic carbon emissions trading scheme can only regulate the emissions of the country having the trading scheme. In this case, GHG emissions can "leak" (carbon leakage) to another region or sector with less regulation (p. 21). Leakages may be positive, where they reduce the effectiveness of domestic emission abatement efforts. Leakages may also be negative, and increase the effectiveness of domestic abatement efforts (negative leakages are sometimes called spillover) (IPCC, 2007).[22] For example, a carbon tax applied only to developed countries might lead to a positive leakage to developing countries (Goldemberg et al., 1996, pp. 27–28). However, a negative leakage might also occur due to technological developments driven by domestic regulation of GHGs.[23] This can help to reduce emissions even in less regulated regions.
Competitiveness risks
One way of addressing carbon leakage is to give sectors vulnerable to international competition free emission permits (Carbon Trust, 2009).[24] This acts as a subsidy for the sector in question. Free allocation of permits was opposed by the Garnaut Climate Change Review as it considered there were no circumstances that justify it and that governments could deal with market failure or claims for compensation more transparently with the revenue from full auctioning of permits.[25] The economically efficient option would, however, be border adjustments (Neuhoff, 2009;[26] Newbery, 2009).[27] Border adjustments work by setting a tariff on imported goods from less regulated countries. A problem with border adjustments is that they might be used as a disguise for trade protectionism.[28] Some types of border adjustment may also not prevent emissions leakage.
Issuing the permits: 'grandfathering' versus auctions
Tradable emissions permits can be issued to firms within an ETS by two main ways: by free allocation of permits to existing emitters or by auction.[29] Allocating permits based on past emissions is called "grandfathering" (Goldemberg et al., 1996, p. 38). Grandfathering permits, just like the other option of selling (auctioning) permits, sets a price on emissions. This gives permit-liable polluters an incentive to reduce their emissions. However, grandfathering permits can lead to perverse incentives, e.g., a firm that aimed to cut emissions drastically would then be given fewer permits in the future. Allocation may also slow down technological development towards less polluting technologies.[30] The Garnaut Climate Change Review noted that 'grandfathered' permits are not 'free'. As the permits are scarce they have value and the benefit of that value is acquired in full by the emitter. The cost is imposed elsewhere in the economy, typically on consumers who cannot pass on the costs.[25] However, profit-maximising firms receiving free permits will raise prices to customers because of the new, non-zero cost of emissions.[31]
A second method of "grandfathering" is to base allocations on current production of economic goods, rather than historical emissions. Under this method of allocation, government will set a benchmark level of emissions for each good deemed to be sufficiently trade exposed and allocate firms units based on their production of this good. However, allocating permits in proportion to output implicitly subsidises production.[32] The Garnaut Report noted that any method for free permit allocation will have the disadvantages of high complexity, high transaction costs, value-based judgements, and the use of arbitrary emissions baselines.[25]
On the other hand, auctioning permits provides the government with revenues. These revenues could be used to fund low-carbon investment, and also fund cuts in distortionary taxes. Auctioning permits can therefore be more efficient and equitable than allocating permits (Hepburn, 2006, pp. 236–237).[33] Ross Garnaut stated that full auctioning will provide greater transparency and accountability and lower implementation and transaction costs as governments retain control over the permit revenue.[25]
Recycling of revenue from permit auctions could offset a significant proportion of the economy-wide social costs of a cap and trade scheme.[34] As well as reducing tax distortions, Kerr and Cramton (1998) note that auctions of units are more flexible in distributing costs, they provide more incentives for innovation, and they lessen the political arguments over the allocation of economic rents.[35]
Lobbying for free allocation
According to Hepburn,[33]: 238–239 "it should be expected that industry will lobby furiously against any auctioning". Hepburn et al. (2006) state that it is an empirical fact that while businesses tend to oppose auctioning of emissions permits, economists almost uniformly recommend auctioning permits.[36] Garnaut notes that the complexity of free allocation, and the large amounts of money involved, encourage non-productive rent-seeking behaviour and lobbying of governments, activities that dissipate economic value.[25]
Distribution of allowances
Emission allowances may be given away for free or auctioned. In the first case, the government receives no carbon revenue and in the second it receives (on average) the full value of the permits. In either case, permits will be equally scarce and just as valuable to market participants. Since the private market (for trading permits) determines the final price of permits (at the time they must be used to cover emissions), the price will be the same in either case (free or auctioned). This is generally understood.
A second point about free permits (usually "grandfathered", i.e. given out in proportion to past emissions) has often been misunderstood. Companies that receive free permits, treat them as if they had paid full price for them. This is because using carbon in production has the same cost under both arrangements. With auctioned permits, the cost is obvious. With free permits, the cost is the cost of not selling the permit at full value—this is termed an "opportunity cost". Since the cost of emissions is generally a marginal cost (increasing with output), the cost is passed on by raising the cost of output (e.g. raising the cost of gasoline or electricity).
Windfall profits
A company that receives permits for free will pass on its opportunity cost in the form of higher product prices. Hence, if it sells the same amount of output as before that cap, with no change in production technology, the full value (at the market price) of permits received for free becomes windfall profits. However, since the cap reduces output and often causes the company to incur costs to increase efficiency, windfall profits will be less than the full value of its free permits.[37]
Generally speaking, if permits are allocated to emitters for free, they will profit from them. But if they must pay full price, or if carbon is taxed, their profits will be reduced. If the carbon price exactly equals the true social cost of carbon, then long-run profit reduction will simply reflect the consequences of paying this new cost. If having to pay this cost is unexpected, then there will likely be a one-time loss that is due to the change in regulations and not simply due to paying the real cost of carbon. However, if there is advanced notice of this change, or if the carbon price is introduced gradually, this one-time regulatory cost will be minimized. There has now been enough advance notice of carbon pricing that this effect should be negligible on average.
Market trends
.png.webp)
Carbon emissions trading increased rapidly in 2021 with the start of the Chinese national carbon trading scheme.[39] The increasing costs of permits on the EU ETS have had the effect of increasing costs of coal power.[40]
A 2019 study by the American Council for an Energy Efficient Economy (ACEEE) finds that efforts to put a price on greenhouse gas emissions are growing in North America. "In addition to carbon taxes in effect in Alberta, British Columbia and Boulder, Colorado, cap and trade programs are in effect in California, Quebec, Nova Scotia and the nine northeastern states that form the Regional Greenhouse gas Initiative (RGGI). Several other states and provinces are currently considering putting a price on emissions."[41]
Business reaction
The International Air Transport Association, whose 230 member airlines comprise 93% of all international traffic, position is that trading should be based on "benchmarking", setting emissions levels based on industry averages, rather than "grandfathering", which would use individual companies' previous emissions levels to set their future permit allowances. They argue grandfathering "would penalise airlines that took early action to modernise their fleets, while a benchmarking approach, if designed properly, would reward more efficient operations".[42]
In 2021 shipowners said they are against being included in the EU ETS.[43]
Criticisms

Emissions trading has been criticized for a variety of reasons. For example, in the popular science magazine New Scientist, Lohmann (2006) argued that trading pollution allowances should be avoided as a climate stabilization policy for several reasons. First, climate change requires more radical changes than previous pollution trading schemes such as the US SO2 market. It requires reorganizing society and technology to "leave most remaining fossil fuels safely underground". Carbon trading schemes have tended to reward the heaviest polluters with 'windfall profits' when they are granted enough carbon credits to match historic production. Expensive long-term structural changes will not be made if there are cheaper sources of carbon credits which are often available from less developed countries, where they may be generated by local polluters at the expense of local communities.[44]
Critics of carbon trading, such as Carbon Trade Watch, argue that it places disproportionate emphasis on individual lifestyles and carbon footprints, distracting attention from the wider, systemic changes and collective political action that needs to be taken to tackle climate change.[45] Groups such as the Corner House have argued that the market will choose the easiest means to save a given quantity of carbon in the short term, which may be different from the pathway required to obtain sustained and sizable reductions over a longer period, and so a market-led approach is likely to reinforce technological lock-in. For instance, small cuts may often be achieved cheaply through investment in making a technology more efficient, where larger cuts would require scrapping the technology and using a different one. They also argue that emissions trading is undermining alternative approaches to pollution control with which it does not combine well, and so the overall effect it is having is to actually stall significant change to less polluting technologies. In September 2010, campaigning group FERN released "Trading Carbon: How it works and why it is controversial"[46]which compiles many of the arguments against carbon trading.
The Financial Times published an article about cap-and-trade systems which argued that "Carbon markets create a muddle" and "...leave much room for unverifiable manipulation".[47] Lohmann (2009) pointed out that emissions trading schemes create new uncertainties and risks, which can be commodified by means of derivatives, thereby creating a new speculative market.[48]
In China some companies started artificial production of greenhouse gases with sole purpose of their recycling and gaining carbon credits. Similar practices happened in India. Earned credit were then sold to companies in US and Europe.[49][50]
Proposals for alternative schemes to avoid the problems of cap-and-trade schemes include Cap and Share, which was considered by the Irish Parliament in 2008, and the Sky Trust schemes.[51] These schemes stated that cap-and-trade schemes inherently impact the poor and those in rural areas, who have less choice in energy consumption options.
Carbon trading has been criticised as a form of colonialism, in which rich countries maintain their levels of consumption while getting credit for carbon savings in inefficient industrial projects.[52] Nations that have fewer financial resources may find that they cannot afford the permits necessary for developing an industrial infrastructure, thus inhibiting these countries economic development.
The Kyoto Protocol's Clean Development Mechanism has been criticised for not promoting enough sustainable development.
Another criticism is the claimed possibility of non-existent emission reductions being recorded under the Kyoto Protocol due to the surplus of allowances that some countries possess. For example, Russia had a surplus of allowances due to its economic collapse following the end of the Soviet Union.[52] Other countries could have bought these allowances from Russia, but this would not have reduced emissions. Rather, it would have been simply be a redistribution of emissions allowances. In practice, Kyoto Parties have as yet chosen not to buy these surplus allowances.[53]
Flexibility, and thus complexity, inherent in cap and trade schemes has resulted in a great deal of policy uncertainty surrounding these schemes. Such uncertainty has beset such schemes in Australia, Canada, China, the EU, India, Japan, New Zealand, and the US. As a result of this uncertainty, organizations have little incentive to innovate and comply, resulting in an ongoing battle of stakeholder contestation for the past two decades.[54]
Lohmann (2006b) supported conventional regulation, green taxes, and energy policies that are "justice-based" and "community-driven".[55] According to Carbon Trade Watch (2009), carbon trading has had a "disastrous track record". The effectiveness of the EU ETS was criticized, and it was argued that the CDM had routinely favoured "environmentally ineffective and socially unjust projects".[56]
Annie Leonard's 2009 documentary The Story of Cap and Trade criticized carbon emissions trading for the free permits to major polluters giving them unjust advantages, cheating in connection with carbon offsets, and as a distraction from the search for other solutions.[57]
Offsets
Forest campaigner Jutta Kill (2006) of European environmental group FERN argued that offsets for emission reductions were not substitute for actual cuts in emissions. Kill stated that "[carbon] in trees is temporary: Trees can easily release carbon into the atmosphere through fire, disease, climatic changes, natural decay and timber harvesting."[58]
Permit supply level
Regulatory agencies run the risk of issuing too many emission credits, which can result in a very low price on emission permits.[59] This reduces the incentive that permit-liable firms have to cut back their emissions. On the other hand, issuing too few permits can result in an excessively high permit price.[60] This is an argument for a hybrid instrument having a price-floor, i.e., a minimum permit price, and a price-ceiling, i.e., a limit on the permit price. However, a price-ceiling (safety value) removes the certainty of a particular quantity limit of emissions.[61]
Permit allocation versus auctioning
If polluters receive emission permits for free ("grandfathering"), this may be a reason for them not to cut their emissions because if they do they will receive fewer permits in the future.[62]
This perverse incentive can be alleviated if permits are auctioned, i.e., sold to polluters, rather than giving them the permits for free.[60] Auctioning is a method for distributing emission allowances in a cap-and-trade system whereby allowances are sold to the highest bidder. Revenues from auctioning go to the government and can be used for development of sustainable technology[63] or to cut distortionary taxes, thus improving the efficiency of the overall cap policy.[64]
On the other hand, allocating permits can be used as a measure to protect domestic firms who are internationally exposed to competition.[60] This happens when domestic firms compete against other firms that are not subject to the same regulation. This argument in favor of allocation of permits has been used in the EU ETS, where industries that have been judged to be internationally exposed, e.g., cement and steel production, have been given permits for free).[65]
Structuring issues
Corporate and governmental carbon emission trading schemes have been modified in ways that have been attributed to permitting money laundering to take place.[66][67] The principal point here is that financial system innovations (outside banking) open up the possibility for unregulated (non-banking) transactions to take place in relativity unsupervised markets.
Carbon leakage
The current state of carbon emissions trading shows that roughly 22% of global greenhouse emissions are covered by 64 carbon taxes and emission trading systems as of 2021.[68] This means that there are still several member states that have not ratified the Kyoto Protocol. This is a cause of concern for energy intensive industries that are covered by such instruments that claim that there is a loss of competitiveness. Such corporations are thereby forced to take strategic production decisions that contribute to the issue of carbon leakage. To mitigate carbon leakage and its effects on the environment, policymakers need to harmonize international climate policies and provide incentives to prevent companies from relocating production to regions with more lenient environmental regulations.[69] A level playing field for businesses across the globe is essential for maintaining competitiveness while effectively combating climate change.
History
"Economy-wide pricing of carbon is the centre piece of any policy designed to reduce emissions at the lowest possible costs".
Ross Garnaut, lead author of the Garnaut Climate Change Review in 2011[70]
The process began in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, when 160 countries agreed the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). The necessary detail was left to be settled by the UN Conference of Parties (COP).
In 1997, the Kyoto Protocol was the first major agreement to reduce greenhouse gases. 38 developed countries (Annex 1 countries) committed themselves to targets and timetables.[71] The resulting inflexible limitations on GHG growth could entail substantial costs if countries have to solely rely on their own domestic measures.[72]
The following is the estimated size of the worldwide carbon market according to the World Bank:[73][74]
Volume (millions metric tonnes, MtCO2)
- 2005: 718 (330 in Main Allowances Markets & 388 in Project based transactions)
- 2006: 1,745 (1,134 in Main Allowances Markets & 611 in Project based transactions)
- 2007: 2,983 (2,109 in Main Allowances Markets & 874 in Project based transactions)
Examples by country
Australia
In 2003 the New South Wales (NSW) state government unilaterally established the New South Wales Greenhouse Gas Abatement Scheme[75] to reduce emissions by requiring electricity generators and large consumers to purchase NSW Greenhouse Abatement Certificates (NGACs). This has prompted the rollout of free energy-efficient compact fluorescent lightbulbs and other energy-efficiency measures, funded by the credits. This scheme has been criticised by the Centre for Energy and Environmental Markets (CEEM) of the UNSW because of its lack of effectiveness in reducing emissions, its lack of transparency and its lack of verification of the additionality of emission reductions.[76]
Both the incumbent Howard Coalition government and the Rudd Labor opposition promised to implement an emissions trading scheme (ETS) before the 2007 federal election. Labor won the election, with the new government proceeding to implement an ETS. The government introduced the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme, which the Liberals supported with Malcolm Turnbull as leader. Tony Abbott questioned an ETS, saying the best way to reduce emissions is with a "simple tax".[77] Shortly before the carbon vote, Abbott defeated Turnbull in a leadership challenge, and from there on the Liberals opposed the ETS. This left the government unable to secure passage of the bill and it was subsequently withdrawn.
Julia Gillard defeated Rudd in a leadership challenge and promised not to introduce a carbon tax, but would look to legislate a price on carbon[78] when taking the government to the 2010 election. In the first hung parliament result in 70 years, the government required the support of crossbenchers including the Greens. One requirement for Greens support was a carbon price, which Gillard proceeded with in forming a minority government. A fixed carbon price would proceed to a floating-price ETS within a few years under the plan. The fixed price lent itself to characterisation as a carbon tax and when the government proposed the Clean Energy Bill in February 2011,[79] the opposition claimed it to be a broken election promise.[80]
The bill was passed by the Lower House in October 2011[81] and the Upper House in November 2011.[82] The Liberal Party vowed to overturn the bill if elected.[83] The bill thus resulted in passage of the Clean Energy Act, which possessed a great deal of flexibility in its design and uncertainty over its future.
The Liberal/National coalition government elected in September 2013 has promised to reverse the climate legislation of the previous government.[84] In July 2014, the carbon tax was repealed as well as the Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) that was to start in 2015.[85]
Canada
The Canadian provinces of Quebec and Nova Scotia operate an emissions trading scheme. Quebec links its program with the US state of California through the Western Climate Initiative.
China
The Chinese national carbon trading scheme is the largest in the world. It is an intensity-based trading system for carbon dioxide emissions by China, which started operating in 2021.[86] The initial design of the system targets a scope of 3.5 billion tons of carbon dioxide emissions that come from 1700 installations.[87] It has made a voluntary pledge under the UNFCCC to lower CO2 per unit of GDP by 40–45% in 2020 when comparing to the 2005 levels.[88]
In November 2011, China approved pilot tests of carbon trading in seven provinces and cities—Beijing, Chongqing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Tianjin, as well as Guangdong Province and Hubei Province, with different prices in each region.[89] The pilot is intended to test the waters and provide valuable lessons for the design of a national system in the near future. Their successes or failures will, therefore, have far-reaching implications for carbon market development in China in terms of trust in a national carbon trading market. Some of the pilot regions can start trading as early as 2013/2014.[90] National trading is expected to start in 2017, latest in 2020.
The effort to start a national trading system has faced some problems that took longer than expected to solve, mainly in the complicated process of initial data collection to determine the base level of pollution emission.[91] According to the initial design, there will be eight sectors that are first included in the trading system: chemicals, petrochemicals, iron and steel, non-ferrous metals, building materials, paper, power and aviation, but many of the companies involved lacked consistent data.[87] Therefore, by the end of 2017, the allocation of emission quotas have started but it has been limited to only the power sector and will gradually expand, although the operation of the market is yet to begin.[92] In this system, Companies that are involved will be asked to meet target level of reduction and the level will contract gradually.[87]
European Union
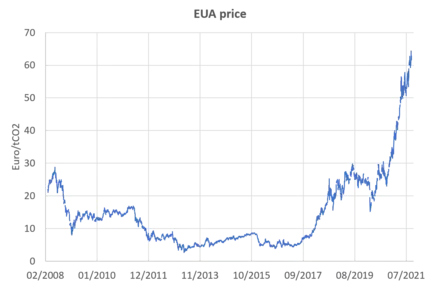
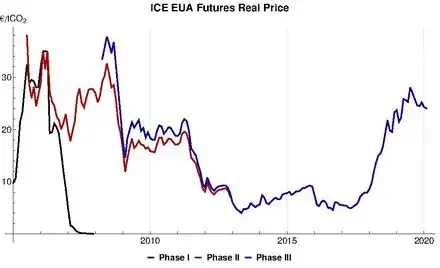
The European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) is a carbon emission trading scheme (or cap and trade scheme) which began in 2005 and is intended to lower greenhouse gas emissions by the European Union countries. Cap and trade schemes limit emissions of specified pollutants over an area and allow companies to trade emissions rights within that area. The EU ETS covers around 45% of the EUs greenhouse gas emissions.[93]
The scheme has been divided into four "trading periods". The first ETS trading period lasted three years, from January 2005 to December 2007. The second trading period ran from January 2008 until December 2012, coinciding with the first commitment period of the Kyoto Protocol. The third trading period lasted from January 2013 to December 2020. Compared to 2005, when the EU ETS was first implemented, the proposed caps for 2020 represents a 21% reduction of greenhouse gases. This target has been reached six years early as emissions in the ETS fell to 1.812 billion (109) tonnes in 2014.[94]
The fourth phase started in January 2021 and will continue until December 2030. The emission reductions to be achieved over this period are unclear as of November 2021, as the European Green Deal necessitates tightening of the current EU ETS reduction target for 2030 of −43% with respect to 2005. The EU commission proposes in its "Fit for 55" package to increase the EU ETS reduction target for 2030 to −61% compared to 2005.[95][96]
EU countries view the emissions trading scheme as necessary to meeting climate goals. A strong carbon market guides investors and industry in their transition from fossil fuels.[97] A 2020 study found that the EU ETS successfully reduced CO2 emissions even though the prices for carbon were set at low prices.[98] A 2023 study on the effects of the EU ETS identified a reduction in carbon emissions in the order of -10% between 2005 and 2012 with no impacts on profits or employment for regulated firms.[99] The price of EU allowances exceeded 100€/tCO2 ($118) in February 2023.[97]India
Trading is set to begin in 2014 after a three-year rollout period. It is a mandatory energy efficiency trading scheme covering eight sectors responsible for 54 per cent of India's industrial energy consumption. India has pledged a 20 to 25 per cent reduction in emission intensity from 2005 levels by 2020. Under the scheme, annual efficiency targets will be allocated to firms. Tradable energy-saving permits will be issued depending on the amount of energy saved during a target year.[90]
Japan
Japan as a country does not have a compulsory emissions trading scheme. The government in 2010 (the Hatoyama cabinet) had planned to introduce one, but the plan lost momentum after Hatoyama resigned as prime minister, due partly from industrial opposition,[100] and was eventually shelved. Japan has a voluntary scheme. Furthermore, the Kyoto Prefecture has a voluntary emissions trading scheme.[101]
Two regional mandatory schemes exist however, in Tokyo and Saitama Prefecture. The city of Tokyo consumes as much energy as "entire countries in Northern Europe, and its production matches the GNP of the world's 16th largest country". A cap-and-trade carbon trading scheme launched in April 2010 covers the top 1,400 emitters in Tokyo, and is enforced and overseen by the Tokyo Metropolitan Government.[102][103] Phase 1, which was similar to Japan's voluntary scheme, ran until 2015.[104] Emitters had to cut their emissions by 6% or 8% depending on the type of organization; from 2011, those who exceed their limits were required to buy matching allowances, or invest in renewable-energy certificates, or offset credits issued by smaller businesses or branch offices.[105] Polluters that failed to comply were liable up to 500,000 yen in fines plus credits for 1.3 times excess emissions.[106] In its fourth year, emissions were reduced by 23% compared to base-year emissions.[107] In phase 2 (FY2015–FY2019), the target was expected to increase to 15–17%. The aim was to cut Tokyo's carbon emissions by 25% from 2000 levels by 2020.[105]
One year after Tokyo launched its cap-and-trade scheme, the neighbouring Saitama Prefecture launched a highly similar scheme. The two schemes are connected.[101]
New Zealand
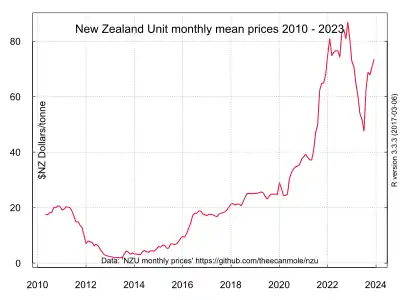
The New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme (NZ ETS) is an all-gases partial-coverage uncapped domestic emissions trading scheme that features price floors, forestry offsetting, free allocation and auctioning of emissions units.
The NZ ETS was first legislated in the Climate Change Response (Emissions Trading) Amendment Act 2008 in September 2008 under the Fifth Labour Government of New Zealand[108][109] and then amended in November 2009[110] and in November 2012[111] by the Fifth National Government of New Zealand.
The NZ ETS was until 2015 highly linked to international carbon markets as it allowed unlimited importing of most of the Kyoto Protocol emission units. There is a domestic emission unit; the 'New Zealand Unit' (NZU), which was initially issued by free allocation to emitters until auctions of units commenced in 2020.[112] The NZU is equivalent to 1 tonne of carbon dioxide. Free allocation of units varies between sectors. The commercial fishery sector (who are not participants) received a one-off free allocation of units on a historic basis.[113] Owners of pre-1990 forests received a fixed free allocation of units.[114] Free allocation to emissions-intensive industry,[115][116] is provided on an output-intensity basis. For this sector, there is no set limit on the number of units that may be allocated.[117][118] The number of units allocated to eligible emitters is based on the average emissions per unit of output within a defined 'activity'.[119] Bertram and Terry (2010, p 16) state that as the NZ ETS does not 'cap' emissions, the NZ ETS is not a cap and trade scheme as understood in the economics literature.[120]
Some stakeholders have criticised the New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme for its generous free allocations of emission units and the lack of a carbon price signal (the Parliamentary Commissioner for the Environment),[121] and for being ineffective in reducing emissions (Greenpeace Aotearoa New Zealand).[122]South Korea
South Korea's national emissions trading scheme officially launched on January 1, 2015, covering 525 entities from 23 sectors. With a three-year cap of 1.8687 billion tCO2e, it now forms the second largest carbon market in the world following the EU ETS. This amounts to roughly two-thirds of the country's emissions. The Korean emissions trading scheme is part of the Republic of Korea's efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 30% compared to the business-as-usual scenario by 2020.[107]
United Kingdom
United States
As of 2017, there is no national emissions trading scheme in the United States. Failing to get Congressional approval for such a scheme, President Barack Obama instead acted through the United States Environmental Protection Agency to attempt to adopt through rulemaking the Clean Power Plan, which does not feature emissions trading. The plan was subsequently challenged by the administration of President Donald Trump.
Concerned at the lack of federal action, several states on the east and west coasts have created sub-national cap-and-trade programs.
President Barack Obama in his proposed 2010 United States federal budget wanted to support clean energy development with a 10-year investment of US$15 billion per year, generated from the sale of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions credits. Under the proposed cap-and-trade program, all GHG emissions credits would have been auctioned off, generating an estimated $78.7 billion in additional revenue in FY 2012, steadily increasing to $83 billion by FY 2019.[126] The proposal was never made law.
The American Clean Energy and Security Act (H.R. 2454), a greenhouse gas cap-and-trade bill, was passed on 26 June 2009, in the House of Representatives by a vote of 219–212. The bill originated in the House Energy and Commerce Committee and was introduced by Representatives Henry A. Waxman and Edward J. Markey.[127] The political advocacy organizations FreedomWorks and Americans for Prosperity, funded by brothers David and Charles Koch of Koch Industries, encouraged the Tea Party movement to focus on defeating the legislation.[128][129] Although cap and trade also gained a significant foothold in the Senate via the efforts of Republican Lindsey Graham, Independent and former Democrat Joe Lieberman, and Democrat John Kerry,[130] the legislation died in the Senate.[131]
Society and culture
Public opinion
In the United States, most polling shows large support for emissions trading (often referred to as cap-and-trade). This majority support can be seen in polls conducted by The Washington Post/ABC News,[132] Zogby International[133] and Yale University.[134] According to PolitiFact, it is a misconception that emissions trading is unpopular in the United States because of earlier polls from Zogby International and Rasmussen which misleadingly include "new taxes" in the questions (taxes are not part of emissions trading) or high energy cost estimates.[135]
See also
References
- ↑ Olivier, J.G.J.; Peters, J.A.H.W. (2020). "Trends in global CO2 and total greenhouse gas emissions (2020)" (PDF). The Hague: PBL Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency.
- ↑ "Emissions Trading Worldwide: Status Report 2021". Berlin: International Carbon Action Partnership (ICAP). Retrieved August 8, 2021.
- ↑ "Policy Brief: EU emissions trading". Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change. Archived from the original on March 2, 2022. Retrieved August 8, 2021.
- ↑ Yuan, Lin (July 22, 2021). "China's national carbon market exceeds expectations". Archived from the original on November 4, 2022. Retrieved August 8, 2021.
- ↑ "Carbon Price Viewer". EMBER. Archived from the original on March 2, 2023. Retrieved August 8, 2021.
- ↑ Kikstra, Jarmo S; Waidelich, Paul; Rising, James; Yumashev, Dmitry; Hope, Chris; Brierley, Chris M (September 6, 2021). "The social cost of carbon dioxide under climate-economy feedbacks and temperature variability". Environmental Research Letters. 16 (9): 094037. Bibcode:2021ERL....16i4037K. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/ac1d0b. S2CID 237427400.
- ↑ "Carbon Pricing Dashboard | Up-to-date overview of carbon pricing initiatives". carbonpricingdashboard.worldbank.org. Archived from the original on May 30, 2022. Retrieved May 31, 2022.
- ↑ IMF (March 2008). "Fiscal Implications of Climate Change" (PDF). International Monetary Fund, Fiscal Affairs Department. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 6, 2010. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- ↑ Halsnæs, K.; et al. (2007). "2.4 Cost and benefit concepts, including private and social cost perspectives and relationships to other decision-making frameworks". In B. Metz; et al. (eds.). Framing issues. Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. p. 6. Archived from the original on May 2, 2010. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- ↑ Toth, F.L.; et al. (2005). "10.1.2.2 The Problem Is Long Term.". In B. Metz; et al. (eds.). Decision-making Frameworks. Climate Change 2005: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Print version: Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, N.Y., U.S.A.. This version: GRID-Arendal website. Archived from the original on December 7, 2013. Retrieved January 10, 2010.
- ↑ Goldemberg, J.; et al. (1996). "Introduction: scope of the assessment.". In J.P. Bruce; et al. (eds.). Climate Change 1995: Economic and Social Dimensions of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Second Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. p. 29. ISBN 978-0-521-56854-8.
- ↑ Tietenberg, Tom (2003). "The Tradable-Permits Approach to Protecting the Commons: Lessons for Climate Change". Oxford Review of Economic Policy. 19 (3): 400–419. doi:10.1093/oxrep/19.3.400.
- ↑ David M. Driesen. "Capping Carbon". Environmental Law. 40 (1): 1–55.
Setting the cap properly matters more to environmental protection than the decision to allow, or not allow, trades
- ↑ "Tax Treaty Issues Related to Emissions Permits/Credits" (PDF). OECD. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved November 22, 2014.
- ↑ Lavelle, Marianne (November 3, 2010). "A U.S. Cap-And-Trade Experiment to End". National Geographic. Archived from the original on November 6, 2010. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ↑ "CantorCO2e Launches First Internet CER Auction" (Press release). CantorCO2e. September 9, 2008. Archived from the original on May 1, 2011. Retrieved January 27, 2010.
- ↑ "Carbon Place . EU – Market with carbon credits – EUA, CER, ERU, VER, AAU-S, AAU-G". Archived from the original on August 17, 2019. Retrieved September 25, 2015.
- ↑ International Carbon Action Partnership Archived July 22, 2010, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Goldemberg et al., 1996, p. 29
- ↑ Goldemburg et al., 1996, pp. 29, 37
- ↑ Goldemburg et al., 1996, p. 30
- ↑ IPCC (2007). "Glossary A-D". In B. Metz; et al. (eds.). Annex I: Glossary. Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Print version: Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., and New York, N.Y., U.S.A.. This version: IPCC website. Archived from the original on May 3, 2010. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- ↑ Barker, T.; et al. (2007). "Executive Summary". In B. Metz; et al. (eds.). Mitigation from a cross-sectoral perspective. Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Print version: Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., and New York, N.Y., U.S.A.. This version: IPCC website. Archived from the original on March 31, 2010. Retrieved May 6, 2010.
- ↑ Carbon Trust (March 2009). "Memorandum submitted by The Carbon Trust (ET19)". The role of carbon markets in preventing dangerous climate change. Minutes of Evidence, Tuesday 21 April 2009. UK Parliament House of Commons Environmental Audit Select Committee. The fourth report of the 2009-10 session. Retrieved April 30, 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Garnaut, Ross (2008). "Releasing permits into the market". The Garnaut Climate Change Review. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-74444-7. Retrieved April 28, 2010.
- ↑ Neuhoff, K. (February 22, 2009). "Memorandum submitted by Karsten Neuhoff, Assistant Director, Electric Policy Research Group, University of Cambridge". The role of carbon markets in preventing dangerous climate change. Written evidence. UK Parliament House of Commons Environmental Audit Select Committee. The fourth report of the 2009-10 session. Retrieved May 1, 2010.
- ↑ Newbery, D. (February 26, 2009). "Memorandum submitted by David Newbery, Research Director, Electric Policy Research Group, University of Cambridge". The role of carbon markets in preventing dangerous climate change. Written evidence. UK Parliament House of Commons Environmental Audit Select Committee. The fourth report of the 2009-10 session. Retrieved April 30, 2010.
- ↑ Grubb, M.; et al. (August 3, 2009). "Climate Policy and Industrial Competitiveness: Ten Insights from Europe on the EU Emissions Trading System". Climate Strategies: 5. Archived from the original on February 6, 2010. Retrieved April 14, 2010.
- ↑ Gupta, S.; et al. (2007), "Section 13.2.1.3 Tradable permits", in B. Metz; et al. (eds.), Chapter 13: Policies, instruments, and co-operative arrangements, Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., and New York, N.Y., U.S.A., retrieved July 10, 2010
- ↑ Fisher, B.S.; et al. (1996). "An Economic Assessment of Policy Instruments for Combating Climate Change.". In J.P. Bruce; et al. (eds.). Climate Change 1995: Economic and Social Dimensions of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Second Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., and New York, N.Y., U.S.A. p. 417. ISBN 978-0-521-56854-8.
- ↑ Goulder, Lawrence H.; Pizer, William A. (2006). The Economics of Climate Change (PDF). DP 06-06. Resources for the Future. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 26, 2006.
- ↑ Fischer, C; Fox, A (2007). "Output-based allocation of emissions permits for mitigating tax and trade interactions" (PDF). Land Economics. 83 (4): 575–599. doi:10.3368/le.83.4.575. S2CID 55649597. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 17, 2004. Retrieved August 10, 2010.
However, there often are important trade-offs in terms of efficiency because OBA implicitly subsidizes production, unlike conventional lump-sum allocation mechanisms like grandfathering.
- 1 2 Hepburn, C. (2006). "Regulating by prices, quantities or both: an update and an overview" (PDF). Oxford Review of Economic Policy. 22 (2): 226–247. doi:10.1093/oxrep/grj014. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 23, 2008. Retrieved August 30, 2009.
- ↑ Stavins, Robert N. (2008). "Addressing climate change with a comprehensive US cap-and-trade system" (PDF). Oxford Review of Economic Policy. 24 (2 24): 298–321. doi:10.1093/oxrep/grn017. hdl:10419/53231. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 10, 2020.
- ↑ Kerr, Suzi; Cramton, Peter (1998). "Tradable Carbon Permit Auctions: How and Why to Auction Not Grandfather" (PDF). Discussion Paper Dp-98-34. Resources For the Future. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 26, 2003.
An auction is preferred to grandfathering (giving companies permits based on historical output or emissions), because it allows reduced tax distortions, provides more flexibility in distribution of costs, provides greater incentives for innovation, and reduces the need for politically contentious arguments over the allocation of rents.
- ↑ Hepburn, Cameron J; Neuhoff, Karsten; Grubb, Michael; Matthes, Felix; Tse, Max (2006). "Auctioning of EU ETS Phase II allowances: why and how?" (PDF). Climate Policy. 6 (1): 137–160. doi:10.3763/cpol.2006.0608. Retrieved May 19, 2010.
- ↑ Don Fullerton & Gilbert E. Metcalf (1997). "Environmental Taxes and the Double-Dividend Hypothesis" (PDF). NBER. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 9, 2021. Retrieved July 29, 2014.
- ↑ State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2021, World Bank, May 25, 2021, archived from the original on July 16, 2021, retrieved July 7, 2021
- ↑ "China's carbon market scheme too limited, say analysts". Financial Times. July 16, 2021. Archived from the original on July 16, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ↑ "Study: EU emission trading system makes coal more expensive". CompressorTECH2. June 24, 2021. Archived from the original on July 16, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ↑ eschwass (January 2, 2019). "State and Provincial Efforts to Put a Price on Greenhouse Gas Emissions, with Implications for Energy Efficiency". ACEEE. Archived from the original on January 9, 2019. Retrieved January 8, 2019.
- ↑ "What You Need to Know About Emissions Trading" (PDF). International Air Transport Association. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 3, 2007. Retrieved September 26, 2009.
- ↑ Meredith, Sam (July 12, 2021). "The world's largest carbon market is set for a historic revamp. Europe's shipowners are concerned". CNBC. Archived from the original on July 16, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ↑ Lohmann, Larry (December 5, 2006). "A licence to carry on polluting?". New Scientist. 2580. Archived from the original on January 30, 2009. Retrieved July 17, 2010. Alt URL Archived 2011-05-01 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Carbon Trade Watch". Archived from the original on May 1, 2010. Retrieved April 28, 2010.
- ↑ "Trading Carbon". Archived from the original on April 27, 2011. Retrieved December 17, 2010.
- ↑ "Carbon markets create a muddle". Financial Times. April 26, 2007. Archived from the original on May 7, 2015. Retrieved April 3, 2009.
- ↑ Larry Lohmann: Uncertainty Markets and Carbon Markets. Variations on Polanyian Themes, New Political Economy, first published August 2009, abstract Archived February 16, 2010, at the Wayback Machine and full text Archived December 21, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Carbon-Credits System Tarnished by WikiLeaks Revelation". Archived from the original on September 30, 2011. Retrieved September 28, 2011.
- ↑ "Imminent EU proposals to clamp down on fridge gas scam". Archived from the original on July 29, 2023. Retrieved September 28, 2011.
- ↑ Ray Barrell, Alan Barrett, Noel Casserly, Frank Convery, Jean Goggin, Ide Kearney, Simon Kirby, Pete Lunn, Martin O'Brien and Lisa Ryan. 2009. Budget Perspectives, Tim Callan (ed.)
- 1 2 Liverman, D.M. (2008). "Conventions of climate change: constructions of danger and the dispossession of the atmosphere" (PDF). Journal of Historical Geography. 35 (2): 279–296. doi:10.1016/j.jhg.2008.08.008. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 4, 2009. Retrieved August 8, 2009.
- ↑ PBL (October 16, 2009). "Industrialised countries will collectively meet 2010 Kyoto target". Netherlands Environmental Assessment Agency (PBL) website. Archived from the original on April 9, 2010. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- ↑ Teeter, Preston; Sandberg, Jorgen (2016). "Constraining or Enabling Green Capability Development? How Policy Uncertainty Affects Organizational Responses to Flexible Environmental Regulations" (PDF). British Journal of Management. 28 (4): 649–665. doi:10.1111/1467-8551.12188. S2CID 157986703. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 6, 2020. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ↑ Lohmann, Larry (2006b). "Ways forward (The Corner House)". The Corner House. Archived from the original on August 25, 2009. Retrieved April 3, 2009.
- ↑ Carbon Trade Watch (November 2009). "Carbon Trading – How it works and why it fails". Dag Hammarskjöld Foundation. Archived from the original on August 25, 2017. Retrieved August 4, 2010.
- ↑ Annie Leonard (2009). "The Story of Cap and Trade". The Story of Stuff Project. Archived from the original on November 3, 2010. Retrieved October 31, 2010.
- ↑ Kill, J. (July 2006). "10 things you should know about tree 'offsets'". New Internationalist. Archived from the original on July 26, 2010. Retrieved April 28, 2010.
- ↑ "Chapter 4: Carbon markets and carbon price". Building a low-carbon economy – The UK's contribution to tackling climate change. Committee on Climate Change. December 2008. pp. 140–149. Archived from the original on May 25, 2010. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- 1 2 3 Hepburn, C. (2006). "Regulating by prices, quantities or both: an update and an overview" (PDF). Oxford Review of Economic Policy. 22 (2): 236–239. doi:10.1093/oxrep/grj014. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 14, 2009. Retrieved August 30, 2009.
- ↑ Bashmakov, I.; et al. (2001). "6. Policies, Measures, and Instruments". In B. Metz; et al. (eds.). Climate Change 2001: Mitigation. Contribution of Working Group III to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC. Archived from the original on August 5, 2009. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- ↑ "Fiscal Implications of Climate Change" (PDF). International Monetary Fund. March 2008. pp. 25–26. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 6, 2010. Retrieved April 26, 2010.
- ↑ "Climate change; The greening of America". The Economist. January 25, 2007. Archived from the original on February 12, 2009. Retrieved April 3, 2009.
- ↑ Fisher, B.S.; et al. (1996). "An Economic Assessment of Policy Instruments for Combating Climate Change" (PDF). In J.P. Bruce; et al. (eds.). Climate Change 1995: Economic and Social Dimensions of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Second Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC. p. 417. ISBN 978-0-521-56854-8.
- ↑ Cambridge Centre for Climate Change Mitigation Research (June 19, 2008). "The Revision of the EU's Emissions Trading System". UK Parliament. Archived from the original on February 25, 2021. Retrieved April 28, 2010.
- ↑ "Carbon trading used as money-laundering front: experts" www.saigon-gpdaily.com.vn Archived August 28, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ I. Lippert. Enacting Environments: An Ethnography of the Digitalisation and Naturalisation of Emissions Archived January 17, 2023, at the Wayback Machine. University of Augsburg, 2013.
- ↑ World Bank. (2021, May 25). State and trends of carbon pricing 2021. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/35620
- ↑ Carbon Market Watch. (2017). Carbon Leakage: A short history of an industry lobbying buzzword. Retrieved from https://carbonmarketwatch.org/2017/02/28/carbon-leakage-a-short-history-of-an-industry-lobbying-buzzword/
- ↑ "Key points: Update Paper 6: Carbon pricing and reducing Australia's emissions". Garnaut Climate Change Review. March 17, 2011. Archived from the original on April 21, 2013. Retrieved July 16, 2013.
- ↑ Grimeaud, D, 'An overview of the policy and legal aspects of the international climate change regime' (2001) 9(2) Environmental Liability 39.
- ↑ Stewart, R, "Economic incentives for environmental protection: opportunities and obstacles", in Revesz, R; Sands, P; Stewart, R (eds.), Environment Law, the Economy and Sustainable Development, 2000, Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ "State and Trends of the Carbon Market 2007" (PDF). World Bank. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 18, 2007. Retrieved June 10, 2008.
- ↑ "State and Trends of the Carbon Market 2008" (PDF). World Bank. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 29, 2008. Retrieved June 10, 2008.
- ↑ "The Greenhouse Gas Reduction Scheme". NSW: Greenhouse Gas Reduction Scheme Administrator. January 4, 2010. Archived from the original on January 7, 2010. Retrieved January 16, 2010.
- ↑ Passey, Rob; MacGill, Iain; Outhred, Hugh (2007). "The NSW Greenhouse Gas Reduction Scheme: An analysis of the NGAC Registry for the 2003, 2004 and 2005 Compliance Periods" (PDF). CEEM discussion paper DP_070822. Sydney: The UNSW Centre for Energy and Environmental Markets (CEEM). Archived from the original (PDF) on September 29, 2009. Retrieved November 3, 2009.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ Thompson, Jeremy (June 7, 2011). "Abbott defends carbon tax interview". ABC News. Archived from the original on August 14, 2021. Retrieved September 25, 2015.
- ↑ "Julia Gillard's carbon price promise" Archived March 18, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, The Australian, 20 August 2010.
- ↑ Leslie, Tim (February 24, 2011). "Gillard unveils Carbon Price Details". ABC News. Archived from the original on July 1, 2011. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ↑ Hudson, Phillip (February 26, 2011). "Tony Abbott calls for election on carbon tax". Herald Sun. Archived from the original on May 1, 2011. Retrieved May 5, 2011.
- ↑ Johnston, Matt (October 12, 2011). "Carbon tax bills pass lower house of federal Parliament". Herald Sun. Retrieved October 12, 2011.
- ↑ AAP with Reuters (November 8, 2011). "Carbon tax gets green light in Senate". Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on June 21, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ↑ "Opposition vows to repeal carbon tax". Sydney Morning Herald. October 2, 2011. Archived from the original on February 6, 2015. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ↑ "Abbott Government's first actions: trash climate change education, carbon pricing" Archived September 23, 2021, at the Wayback Machine, Indymedia Australia, 20 September 2013. Accessed 8 November 2013.
- ↑ "Carbon tax scrapped: PM Tony Abbott sees key election promise fulfilled after Senate votes for repeal". ABC News. July 17, 2014. Archived from the original on July 15, 2022. Retrieved September 25, 2015.
- ↑ "China National ETS". Archived from the original on June 3, 2019.
- 1 2 3 "China Looks Towards Next Steps For Implementing National Carbon Market". ICTSD. January 18, 2018. Archived from the original on September 8, 2018.
- ↑ "China could launch national carbon market in 2016". CLIMATE HOME. September 2014. Archived from the original on February 25, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ↑ Andrews-Speed, Philip (November 2014). "China's Energy Policymaking Processes and Their Consequences". The National Bureau of Asian Research Energy Security Report. Archived from the original on July 22, 2018. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- 1 2 "Factbox: Carbon trading schemes around the world". Reuters. July 11, 2011. Archived from the original on September 24, 2015. Retrieved September 25, 2015.
- ↑ Feng, Emily (December 19, 2017). "China moves towards launch of carbon trading scheme". Financial Times. Archived from the original on August 26, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ↑ "China to Launch World's Largest Emissions Trading System". UNFCCC. December 19, 2017. Archived from the original on March 8, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ↑ "EU Emissions Trading System".
- ↑ "Transform -". www.environmentalistonline.com. Retrieved April 19, 2018.
- ↑ European Commission (July 14, 2021). "Delivering the European Green Deal". Archived from the original on November 1, 2021. Retrieved November 1, 2021.
- ↑ "EU Emissions Trading System reaches provisional agreement - SAFETY4SEA". March 7, 2023. Retrieved March 15, 2023.
- 1 2 Twidale, Susanna; Abnett, Kate; Chestney, Nina; Chestney, Nina (February 21, 2023). "EU carbon hits 100 euros taking cost of polluting to record high". Reuters. Retrieved March 19, 2023.
- ↑ Bayer, Patrick; Aklin, Michaël (April 2, 2020). "The European Union Emissions Trading System reduced CO2 emissions despite low prices". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 117 (16): 8804–8812. doi:10.1073/pnas.1918128117. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 7183178. PMID 32253304.
- ↑ Dechezleprêtre, Antoine; Nachtigall, Daniel; Venmans, Frank (March 1, 2023). "The joint impact of the European Union emissions trading system on carbon emissions and economic performance". Journal of Environmental Economics and Management. 118: 102758. doi:10.1016/j.jeem.2022.102758. ISSN 0095-0696.
- ↑ Watanabe, Rie (January 1, 2012). "14. Northeast Asia: A. Japan". Yearbook of International Environmental Law. 23 (1): 454. doi:10.1093/yiel/yvt038. ISSN 0965-1721. Archived from the original on July 29, 2023. Retrieved May 31, 2022.
- 1 2 "Japan: Greenhouse gas emissions trading schemes | White & Case LLP". www.whitecase.com. Archived from the original on May 17, 2022. Retrieved May 31, 2022.
- ↑ "Tokyo Metropolitan Government Leads Japan, Launches Own GHG Emissions Cap-and-Trade Program". Artcraft Japan. July 16, 2010. Archived from the original on May 1, 2011. Retrieved August 5, 2010.
- ↑ China's Carbon Emission Trading Archived October 30, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, 2012.
- ↑ "Tokyo CO2 credit trading plan may become a model". Reuters. February 11, 2010. Archived from the original on March 8, 2021. Retrieved April 25, 2017.
- 1 2 Business Green (April 8, 2010). "Tokyo kicks off carbon trading scheme". The Guardian. Archived from the original on July 27, 2021. Retrieved December 29, 2010.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ↑ "Urban Environment and Climate Change – Publications". Archived from the original on January 24, 2019. Retrieved September 25, 2015.
- 1 2 "Emissions Trading Worldwide ICAP Status Report 2015" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 8, 2021. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ↑ Parker, David (September 10, 2008). "Historic climate change legislation passes" (Press release). New Zealand Government. Retrieved September 10, 2008.
- ↑ "Climate Change Response (Emissions Trading) Amendment Act 2008 No 85". legislation.govt.nz. Parliamentary Counsel Office. September 25, 2008. Retrieved January 25, 2010.
- ↑ Hon Nick Smith (November 25, 2009). "Balanced new law important step on climate change" (Press release). New Zealand Government. Retrieved June 14, 2010.
- ↑ "ETS Amendment Bill passes third reading" (Press release). New Zealand Government. November 9, 2012. Retrieved November 12, 2012.
- ↑ "New Zealand Units (NZUs)". Climate change information New Zealand. Ministry for the Environment, NZ Government (www.climatechange.govt.nz). June 18, 2010. Retrieved August 13, 2010.
In the short term, the Government is unlikely to sell emission units because the Kyoto units allocated to New Zealand will be needed to support New Zealand's international obligations, as well as allocation to eligible sectors under the emissions trading scheme.
- ↑ MfE (September 2009). "Summary of the proposed changes to the NZ ETS". Emissions trading bulletin No 11. Ministry for the Environment, NZ Government. Retrieved May 15, 2010.
- ↑ MfE (January 14, 2010). "How will the changes impact on forestry?". Questions and answers about amendments to the New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS). Ministry for the Environment, NZ Government (www.climatechange.govt.nz). Retrieved May 16, 2010.
- ↑ "Who will get a free allocation of emission units?". Questions and answers about the emissions trading scheme. Ministry for the Environment, NZ Government. January 14, 2010. Retrieved May 15, 2010.
- ↑ MfE (September 2009). "Agriculture". Summary of the proposed changes to the NZ ETS - Emissions Trading Bulletin 11. Ministry for the Environment, NZ Government. Retrieved May 16, 2010.
- ↑ MfE (September 1, 2009). "Emissions trading bulletin No 11: Summary of the proposed changes to the NZ ETS". Ministry for the Environment, NZ Government. Retrieved September 17, 2022.
- ↑ MfE (September 2009). "Industrial allocation update". Emissions trading bulletin No 12, INFO 441. Ministry for the Environment, NZ Government. Retrieved August 8, 2010.
The Bill changes the allocation provisions of the existing CCRA from allocating a fixed pool of emissions to an uncapped approach to allocation. There is no longer an explicit limit on the number of New Zealand units (NZUs) that can be allocated to the industrial sector.
- ↑ MfE (January 14, 2010). "How will free allocation of emission units to the industrial sector work now?". Questions and answers about amendments to the New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS). Ministry for the Environment, NZ Government. Retrieved May 16, 2010.
- ↑ Bertram, Geoff; Terry, Simon (2010). The Carbon Challenge: New Zealand's Emissions Trading Scheme. Bridget Williams Books, Wellington. ISBN 978-1-877242-46-5.
The New Zealand ETS does not fit this model because there is no cap and therefore no certainty as to the volume of emissions with which the national economy must operate
- ↑ "New bill 'weakens ETS' says Environment Commissioner" (Press release). Parliamentary Commissioner for the Environment. October 15, 2009. Retrieved October 15, 2009.
The allocation of free carbon credits to industrial processes is extremely generous and removes the carbon price signal where New Zealand needs one the most
- ↑ "Revised ETS an insult to New Zealanders" (Press release). Greenpeace New Zealand. September 14, 2009. Retrieved October 12, 2009.
We now have on the table a pathetic ETS which won't actually do anything to reduce emissions
- ↑ "Policy briefing: Get ready for the UK's emissions trading scheme". www.endsreport.com. Retrieved February 2, 2021.
- ↑ Department of Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy, Participating in the UK Emissions Trading Scheme (UK ETS), published 17 December 2021, accessed 15 January 2021
- ↑ Ng, Gabriel (January 23, 2021). "Introducing the UK Emissions Trading System". Cherwell. Retrieved February 2, 2021.
- ↑ "President's Budget Draws Clean Energy Funds from Climate Measure". Renewable Energy World. Archived from the original on January 14, 2015. Retrieved April 3, 2009.
- ↑ "The American Clean Energy and Security Act (H.R. 2454)". Energycommerce.house.gov. June 1, 2009. Archived from the original on February 5, 2016. Retrieved June 14, 2010.
- ↑ Dryzek, John S.; Norgaard, Richard B.; Schlosberg, David (2011). The Oxford Handbook of Climate Change and Society. Oxford University Press. p. 154. ISBN 9780199683420.
- ↑ Mayer, Jane (August 30, 2010). "Covert Operations: The billionaire brothers who are waging a war against Obama". The New Yorker. Archived from the original on March 21, 2022. Retrieved March 20, 2015.
- ↑ Lizza, Ryan (October 11, 2010). "As the World Burns: How the Senate and the White House missed their best chance to deal with climate change". The New Yorker. Archived from the original on June 30, 2014. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ↑ Turin, Dustin R. (2012). "The Challenges of Climate Change Policy: Explaining the Failure of Cap and Trade in the United States With a Multiple-Streams Framework". Student Pulse. 4 (6). Archived from the original on May 25, 2016. Retrieved August 6, 2021.
- ↑ "Majority of Poll Respondents Say U.S. Should Limit Greenhouse Gases Archived January 31, 2021, at the Wayback Machine", The Washington Post. 25 June 2009.
- ↑ "Poll Position: New Zogby Poll Shows 71% Support for Waxman-Markey Archived July 31, 2020, at the Wayback Machine", The Wall Street Journal. 11 Aug. 2009
- ↑ "Poll: Americans Support Strong Climate, Energy Policies", Yale Climate & Energy Institute Archived 2012-01-28 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "IBD editorial board claims that cap-and-trade is unpopular in America Archived May 3, 2019, at the Wayback Machine", PolitiFact
Further reading
- Constanze Haug; Michel Frerk; Marissa Santikarn (2015). "Towards a global price on carbon: Pathways for linking carbon pricing instruments". adelphi. Retrieved June 11, 2015.
- Camille Serre; et al. (2015). "Emissions Trading Worldwide: International Carbon Action Partnership (ICAP) Status Report 2015". International Carbon Action Partnership, ICAP. Retrieved March 14, 2015.
- Yujie Lu; Qingbin Cui; Xinyuan Zhu (2012). "Effectiveness and equity implications of carbon policies in the United States construction industry". Building and Environment. Elsevier Ltd. 49: 259–269. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2011.10.002.
- DuPont, Kyle (2010). "Cities and Climate Change Mitigation: Case Study on Tokyo's Emissions Trading System" (PDF). World Bank. Retrieved November 22, 2012.
External links
- C. Haug, M. Frerk and M. Santikarn: Towards a global price on carbon: Pathways for linking carbon pricing instruments. Berlin: adelphi 2015
- Emissions Trading Worldwide: International Carbon Action Partnership (ICAP) Status Report 2015
- "The Making of a Market-Minded Environmentalist", article by Fred Krupp in Strategy+Business (registration reqd) that articulates some of the reasoning and history behind emissions trading in California
- The Stern Review on the economics of climate change – Chapters 14 and 15 have extensive discussions on emission trading schemes and carbon taxes
- Carbon Trading – How it works and why it fails, published November 2009 by Dag Hammarskjöld Foundation: A booklet on various Emissions Trading Schemes (CDM, REDD, ETS) with case studies from Indonesia, Brazil, Thailand and India.
- Chandler: More Flexibility Needed for Effective Emissions Cap-and-Trade Policy Council on Foreign Relations
- Green Structured Products are likely to Proliferate piece by Edmund Parker and Nicole Purin, Mayer Brown, published in Financial News, 3 December 2007
- Emissions Trading and CDM – International Energy Agency