 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Capitrol |
| Other names | cloroxinum, kloroxin, chlorquinol, dichlorchinolinolum, halquinol(s) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.144 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
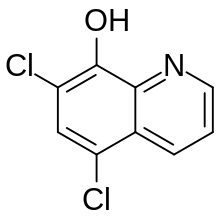
| Formula | C9H5Cl2NO |
| Molar mass | 214.05 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Chloroxine (trade name Capitrol; Kloroxin, Dichlorchinolinol, chlorquinol, halquinol(s)); Latin cloroxinum, dichlorchinolinolum) is an antibacterial drug.[1] Oral formulations (under trade name such as Endiaron[2]) are used in infectious diarrhea, disorders of the intestinal microflora (e.g. after antibiotic treatment), giardiasis, inflammatory bowel disease. It is also useful for dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis.,[3] as used in shampoos (Capitrol) and dermal creams like (Valpeda, Triaderm).
Mechanism of action
Chloroxine has bacteriostatic, fungistatic, and antiprotozoal properties. It is effective against Streptococci, Staphylococci, Candida, Candida albicans, Shigella, and Trichomonads.
Adverse effects
Rarely occurs, but may cause nausea and vomiting associated with oral administration. It may also cause skin irritation.
Pregnancy and lactation
The FDA lists chloroxine in Pregnancy Category C (risk cannot be ruled out) because no pregnancy studies on the medication have been performed with animals or humans. For this reason, use of chloroxine oral or topical during pregnancy or when breast-feeding is not recommended.[4]
History
Chloroxine was first prepared in 1888 by A. Hebebrand.
References
- ↑ Pharmaceutical Manufacturing, Books.Google.com
- ↑ Endiaron.cz
- ↑ Chloroxine, drugs.com
- ↑ Capitrol - FDA prescribing information Archived 2018-11-24 at the Wayback Machine, drugs.com